The reaction called pyrolysis is a type of chemical reaction of decomposition or analysis, in which the heat of fire decomposes a substance, originating two or more products.
Its name is very convenient, as it derives from the Greek terms piro, which means "fire" and lysis, which means “break”. Thus, pyrolysis can be defined as "break by fire”.
Heat is represented in chemical equations by the symbol ∆. This symbol can be seen in the example below, where copper nitrate goes through the pyrolysis process and produces a black solid, which is cupric oxide (CuO); it also produces a red gas, which is nitrogen dioxide (NO2); and the other product is colorless oxygen gas (O2):

Another example is the decomposition of calcium carbonate, which when heated produces calcium oxide and carbon dioxide:
CaCO3(s) Dog(s) + CO2(g)
Dog(s) + CO2(g)
This type of reaction is widely used in industry, and is often called a calcination. And there is also the separation between fast pyrolysis and carbonization, which is considered a
slow pyrolysis. The difference between the two methods is that rapid pyrolysis occurs at moderate temperatures (450°C - 550ºC) and the biomass has a low particle size; carbonization occurs at low temperatures (400-450°C) and the biomass particles are large.In this era in which the fear that oil reserves will be depleted and the search for new renewable fuels intensify more and more, this type of reaction has become an ally; as it is a very efficient method for the decomposition of organic material (biomass) when it is in a medium of almost or complete absence of oxygen.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
For example, through this thermal decomposition of biomass, a product obtained is the bio-oil or pyrolytic tar, which can be used in place of oil and coal. Bio-oil has a brown color and its constitution is close to that of the biomass that originated it. It is a complex mixture of organic compounds that, although chemical in nature different from petroleum, can be considered as petroleum of vegetable origin. Furthermore, bio-oil produces less ash, does not contain heavy metals such as lead, mercury and does not release sulfur.
Another important by-product of wood pyrolysis is the charcoal, which is an energy resource, cheap and renewable, used in various industries. In addition, urban waste can also be subjected to pyrolysis and, thus, various by-products such as tar, oil and oil are obtained. ammonium sulfate (which can also be used as raw materials and energy sources), in addition to reducing waste in landfills Sanitary.

From the pyrolysis of some residues from the oil refinement, it is possible to take advantage of the oil almost entirely and providing great savings. This process consists of the also called cracking (or cracking) in which long-chain molecules are broken down into smaller molecules.
O chemical reactor, called pyrolytic reactor, in this case, is the main element in the applied chemical processes and it has three specific zones, which are: drying zone, pyrolysis zone and cooling zone. Below is a photo of a pyrolysis reactor:
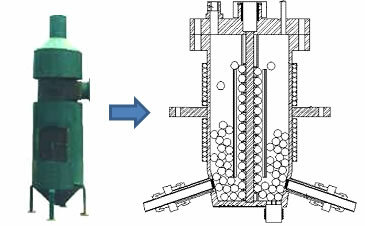
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Renewable Fuels through Pyrolysis"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/combustiveis-renovaveis-por-meio-pirolise.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Chemistry

Get to know some clean energy sources, such as: wind, solar, tidal, geothermal, hydraulic, nuclear and biofuels.


