As stated in the text "Fuel Octane Number”, the octane of a gasoline measures its quality, based on its resistance to compression within the internal combustion engine.
In addition, the octane rating is a scale on which the strength of gasoline is compared with the strength of heptane (zero) and isoctane (100). So, if we have an octane rating of 70, it means that the compressive strength of gasoline is the same as a mixture of 70% isoctane and 30% heptane.
However, there are some specialty gasolines that have an octane rating greater than 100. This is possible thanks to the addition of antiknocks to these gasolines.

Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
The name itself says, they prevent the detonation or combustion of gasoline before the right time, which is when the spark plug of the four-stroke internal combustion engine releases the spark. Before that, it is being compressed and the antiknock “helps” the gasoline not to explode during this compression; which would result in less power for the engine.
The National Petroleum Council (CNP) authorized Petrobrás to add gasoline using the compoundmethyl-t-butyl-ether (MTBE) up to 7% by volume to increase the octane rating.
See some information related to this antiknock in the table below:
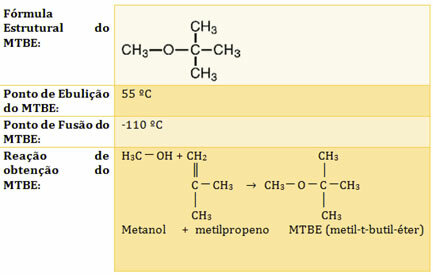
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Anti-knocks"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/antidetonantes.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
Chemistry

Fuel consisting of hydrocarbons, atmospheric pollutant, gasoline molecular structure, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, incomplete combustion, catalysts, smog.
Volumetric percentage of cetane and alpha-methylnaphthalene, fuel oil, diesel fuels, ignition speed, fuel injection, combustion, cetane index values, piston erosion, pollutant emission, carbon monoxide carbon.


