Before introducing the concept of molar mass and mole number, let's look at some important definitions in this context:
→ Molar term
Molar comes from the word molecule, but what exactly is a molecule? It is the set of atoms that are linked through chemical bonds.
→ Molecular mass (MM)
It is possible to calculate the mass of a molecule by the sum of the atomic masses of each atom that makes up the respective molecule. The result is called Molecular Mass (MM).
What would be the molecular mass of hydrogen sulphide (H2S) for example?
First you need to know what the atomic mass of each atom, which is given by the Periodic Table of elements.
Atomic mass of hydrogen (H) = 1 a.m.u. (unit per atomic mass)
Atomic mass of sulfur (S) = 32.1 a.u.u.
Molecular mass is the sum of the atomic masses of atoms.
Note: the hydrogen of the H molecule2S has a coefficient of 2, so you need to multiply its mass by 2. Calculating:
Molecular mass of H2S = 1 • 2 + 32.1 = 34.1 u
(H) + (S) = (H)2S)
Molar mass and the number of moles
The molar mass, as well as the number of moles, is related to the Avogadro's Constant (6.02 x 1023) through the following concept:
''The number of elementary entities contained in 1 mole corresponds to Avogadro's constant, whose value is 6.02 x 1023 mol-1.''
Therefore, the molar mass is the mass of 6.02 x 1023 chemical entities and is expressed in g/mol.
Mind Map - Mol
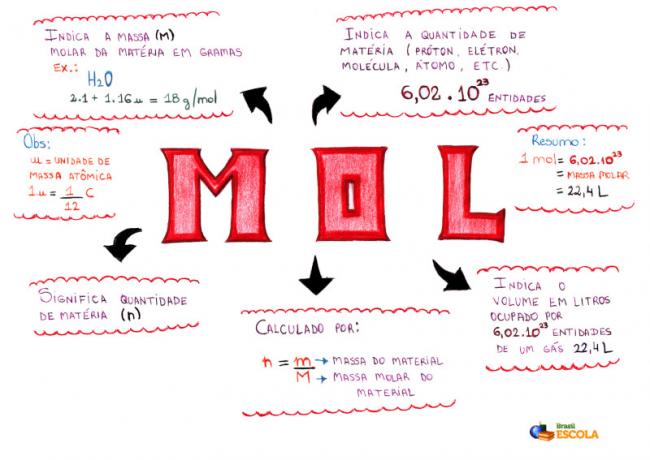
* To download the mind map, Click here!
Example: H2s
Molecular Mass = 34.1 u
Molar mass (M) = 34.1 g/mol
This means that, at 34.1 g/mol of hydrogen sulfide, we have 6.02 x 1023 molecules or 1 mole of hydrogen sulfide molecules.
Conclusion
Molecular mass and molar mass have the same values, what differs is the unit of measurement. The molar mass is related to the number of moles which is given by Avogadro's constant.
* Mind Map by Me. Diogo Lopes
By Líria Alves
Graduated in Chemistry
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/massa-molar-numero-mol.htm

