Evangelista Torricelli was born in the year 1608, in an Italian town called Faenza. He studied math in Rome, he was a pupil of Benedito Castelli and a pupil of Galileo Galilei. In the year 1641 Torricelli moved to Florence to become an assistant to Galileo, whom he replaced as official mathematician to Grand Duke Ferdinand II of Tuscany.
At various times in our studies in Physics, we usually solve some types of exercises from Straight and Uniformly Varied Movement(MRUV) making use of the time function of spaces and speed. However, it is very interesting to use an equation that makes a direct relationship between the velocity (V) and the space (S) traversed by a rover, regardless of time. This equation was obtained by Torricelli around 1644.
In order to arrive at the same equation obtained by Torricelli, just eliminate the variable t between the time function of spaces and the time function of velocity. To do this, just isolate the variable t in the hourly speed function and replace this value in the time function of spaces.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
From the hourly velocity equation, given by:
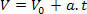
Isolating the time variable t, we can get:

Then just replace this variable in the hourly space equation. Look:

Thus, we have:
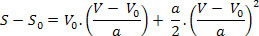
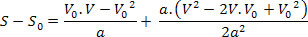
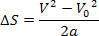
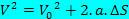
The above equation is known as the Torricelli equation, which can be very helpful in solving problems.
By Joab Silas
Graduated in Physics
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
JUNIOR, Joab Silas da Silva. "Determining the Torricelli Equation"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/determinando-equacao-torricelli.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.