THE mitosisis a kind of divisioncell which one cell (mother cell) divides and gives rise to two daughter cells, each with a chromosome set identical to the mother's. Cell division is a process divided into five main phases, these phases being just a didactic classification, since mitosis is a process that occurs continuously. Next, we will talk about mitosis, its stages and the importance of this cell division process for living beings.
Mitosis and the cell cycle
O cell cycle involves the interphase and mitotic phase, which includes mitosis and cytokinesis. Interphase is a phase that precedes and follows mitosis and can be divided into three subphases: G1, Mon2. During the three steps, it is possible to observe intense metabolic activity in order to prepare the cell for the division that will begin.
phase G1 it occurs just after mitosis and before the S phase, being characterized by a period of cell growth and synthesis of enzymes and cell structures. In those tissues that renew quickly, it is noticed that the G step
1 is short. It is noteworthy that some cells do not continue the cell cycle and assume a quiescent state called G0.At phase called S, there is an important point of the interface, since it is the stage of duplication of DNA. After phase S, the phase G2, a step in which the DNA is verified to be correctly duplicated. At this stage, the cell also accumulates energy to carry out cell division.
Read too:What is a chromosome?

Note the steps in the cell cycle and some of the events that take place in those steps.
phases of mitosis
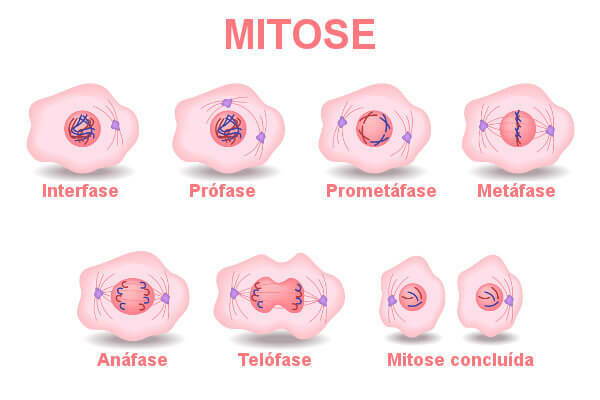
Mitosis is divided into five phases that are just a didactic division, since mitosis is an ongoing process. The phases of mitosis are shown in the table below:
phases of mitosis |
prophase |
Prometaphase |
metaphase |
Anaphase |
telophase |
Read too: cell theory
→ prophase
The first stage of mitosis. In this phase, some important modifications are observed. Among the prophase alterations, the condensation of chromosomes, the disappearance of nucleoli and the beginning of the formation of the mitotic spindle stand out.
Mitotic spindles are formed by spindle fibers, which are bundles of microtubules. The assembly of the microtubules that form the spindles takes place in the centrosome, also called the microtubule organizing center.
In this step, we verify that each duplicated chromosome is present as two sister chromatids, which are joined through their centromeres (a constriction located on the chromosome) and along their arms.
Mind Map: Mitosis

To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
→ Prometaphase
At promise, the nuclear envelope fragments, and the chromosomes continue their condensation. In the centromere of the chromosomes, the presence of the kinetochore (complexes formed by specialized proteins) is noted, which serves as a site for the connection of microtubules.
Each sister chromatid features its own kinetochore. The microtubules that attach to the kinetochores are called the kinetochore microtubules. It is worth emphasizing that some microtubules do not interact with kinetochores, extending from one pole to another.
Prometaphase is not a phase described by all authors. Many consider only prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase to be phases of mitosis. |
→ metaphase
At metaphase, we observe that the centrosomes are positioned at opposite poles of the cell, and the chromosomes are joined together in the so-called metaphase plate (equatorial plane). In this phase, neither the nuclear envelope nor the nucleolus is observed anymore.
→ Anaphase
THE anaphase it is the shortest phase of mitosis, starting abruptly with the simultaneous separation of the sister chromatids and completing within a few minutes. In this step, each chromatid starts moving towards the opposite side of the cell.
This movement occurs as a result of the shortening of the kinetocotus microtubules due to the loss of tubulin subunits. At this stage, we see the elongation of the cell and at the end of the anaphase stage it is observed that there is, at each end, a complete collection of chromosomes.
→ telophase
At telophase, it is possible to notice the formation of nuclei because of the resurgence of nuclear envelopes around each chromosome lot. Envelopes arise from fragments of the mother cell's nucleus and also from other portions of the cell's endomembrane system. In addition to the nucleus, the nucleolus also reappears.
In this phase, it is also verified that the chromosomes decondense, the microtubules that are still present disappear. In this phase, mitosis is terminated and the daughter cell nuclei enter into interphase.
→ Cytokinesis
THE cytokinesis it is the division of the cytoplasm, which gives rise to the two daughter cells. Cytokinesis usually occurs at the end of telophase. Cytokinesis is a process that occurs differently in plant cells and animal cells.
While in animal cells, the formation of a groove that leads to division is observed in the cell; plant, what is verified is the formation of the cell plaque that forms in the middle region of the cell and grows outwards.
→ Importance of Mitosis
Mitosis is a cell division process that is of great importance to organisms. In multicellular beings, mitosis is important to ensure the growth of these individuals and also for tissue regeneration. In unicellular ones, mitosis plays an important role in ensuring asexual reproduction.
Read too: Understand the relationship of cancer to cell division
→ Differences between mitosis and meiosis
Like mitosis, meiosis is a process of cell division. However, although they lead to cell division, these two processes are distinct. Below are the main differences between them.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS | |
Mitosis |
Meiosis |
At the end of the process, the formation of two genetically identical daughter cells is observed. |
At the end of the process, the formation of four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes of the mother cell is observed. |
Occurs in somatic cells. |
Occurs in germ cells. |
Cell division occurs. |
There are two cell divisions. |
To learn more, read this text: What is Meiosis?
By Ma. Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
