O infra-red is a kind of electromagnetic radiation which has a lower frequency than the light red and therefore it is not within the electromagnetic spectrum visible. For this reason, this radiation cannot be perceived by the human eye. O infra-red has a wavelength between 1 μm (1 x 10 – 6m) and 1 mm (1 x 10-3m) and it is not ionizing radiation, that is, it does not pose a risk to human health.

Infrared is not visible to the human eye because it is a longer wavelength than red light.
THE infrared radiation originates from molecular vibration, which generates oscillations in the electrical charges constituents of atoms and causes the emission of radiation, so this type of radiation is associated with heat. An example of this is that, when placing your hand near a hot iron plate, you can feel the heat. This occurs because of the body's reception of infrared waves produced by the heated body.
Discovery
Infrared radiation was discovered thanks to studies carried out by astronomer Willian Herschel (1738-1822). After repeating the experiment done by
Isaac Newton to the scatter sunlight with the help of a prism, Herschel was looking for the color that has the highest temperature by focusing the beams on the bulb of a thermometer. That's when he realized that the frequency region slightly lower than that of red light was the hottest region.Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)

By passing sunlight through a prism, Isaac Newton was able to observe the phenomenon of light scattering
The name infrared originates precisely from the fact that the frequency of radiation is lower than the frequency of red light, which, in turn, is the lowest frequency captured by the human eye.
Infrared Applications
It can be used to detect the temperature of distant objects and for that reason it is very useful for astronomy;
Guided missiles are programmed to follow infrared radiation from enemy aircraft turbines;
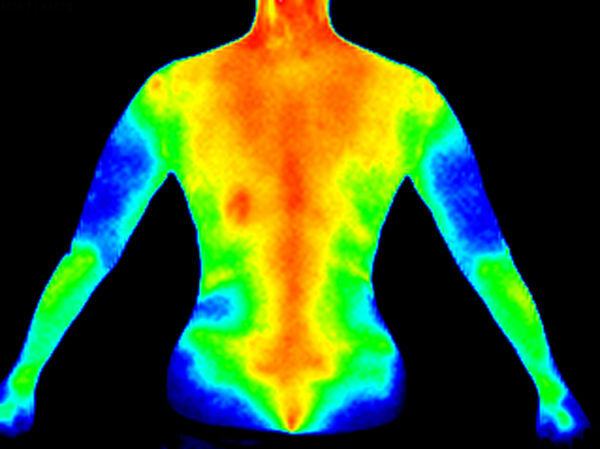
Thermal photographs are used in medicine to diagnose, for example, atherosclerosis, blocking blood vessels. This is possible because the poorly irrigated region has a lower temperature, therefore emitting less infrared radiation than normally irrigated regions, as the following image demonstrates:
Remote controls send information to their receivers via infrared radiation;
Whatever the temperature of a body, it emits waves in the infrared region. Animals like the snakes they have the ability to see this type of radiation and thus can hunt their prey even in the dark.
By Joab Silas
Graduated in Physics
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
JUNIOR, Joab Silas da Silva. "What is infrared?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/fisica/o-que-e-infravermelho.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.