O tectonism – also called diastrophism - it is one of the endogenous agents of land relief transformation, arising from the movement, integration, collision and removal of tectonic plates. Thanks to these movements, a series of relief forms, such as mountains, are manifested on the earth's surface, in addition to phenomena such as volcanism and earthquakes.
At tectonic plates are some parts that make up the earth's crust and exist thanks to the thin thickness of this layer and the great pressure exerted by the movement of magma located in the region of the mantle.
What causes the movement of tectonic plates?
Tectonic plates move thanks to the action of calls cells or convection currents, which are the circular movements exerted by the magma and which work as a kind of “mat” that, when rotating, causes the displacement of these plates.
How do these boards move?
The tectonic plates move and interact based on two main movements: a orogeny and the epirogenesis.
Orogeny refers to horizontal movements performed by tectonic plates, which are responsible for the approximation or distance between them. They usually occur in unstable and geologically recent regions, causing the occurrence of earthquakes and volcanism, in addition to the formation of mountain ranges.
Epyrogenesis refers to the vertical movements performed by tectonic plates, usually associated with the emigration or immigration of magma from the subsoil, causing the uplift or declination of the relief. It usually occurs in continental areas, far from plate tectonics, stable regions with recent geological formation.
In meeting zones - also called endogenous stress zones – among the tectonic plates, there is a classification that segments the different types and their consequences. On the one hand, we have the convergence zones and, on the other hand, the divergence zones.
Convergence zones, as the name suggests, occur when tectonic plates converge, as a function of moving towards each other. They occur in two ways, when the movements of the plates are opposite (subduction) and when they are tangent (obduction). Note the diagrams below:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)

The convergence movements of obduction and subduction
The divergence zones, in turn, occur with the separation of tectonic plates, a phenomenon that usually occurs in oceanic regions, causing the formation of pits, also known as dorsal oceanic.
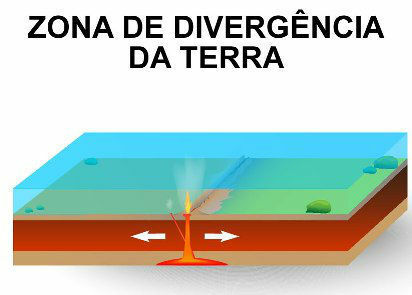
The divergence movement of tectonic plates
How many tectonic plates are there?
There are 12 tectonic plates, namely: African, Antarctic, Arabic, Caribbean, Coco, Eurasian, Filipino, Indo-Australian, Nazca, North American, Pacific and South American. It is in the latter where the Brazilian territory is located.
What are the main consequences of tectonism?
In addition to earthquakes and volcanism, usually present in the border regions between two tectonic plates, the movement of tectonic plates causes the modeling of our relief, such as mountains, faults, depressions and folds in the surface. Furthermore, it is thanks to these movements that the continents find themselves in their current form, as their distribution over the Earth's surface was previously quite different.
At first, according to the theory of Continental Drift, there was only one continent, called the pangea, which was divided over and over again, forming the Gondwana and the Laurasia, which again split, giving rise to the current continents. As the tectonic plates continue to move, it is possible that in a few thousand years the configurations of the planet's emerged lands will be different from today's.
By Me. Rodolfo Alves Pena