The organic group of alcohols is well known in Organic Chemistry, being characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl (OH) bonded to a saturated carbon. There are alcohols that are unsaturated, like the but-3-en-1-ol below:
H2C ═ CH ─ CH2 CH2 ─ oh
However, some compounds have the hydroxyl directly bonded to a carbon with a double bond. This type of compound is not an alcohol, it belongs to the organic function called: enol.
Enols, therefore, are characterized by the following functional group:
│
─ C ═ CH ─ oh
The nomenclature of enols is made according to the following scheme:
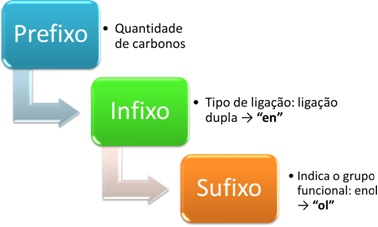
For example, consider the following simpler enol:
H2C CH ─ oh
Prefix: has 2 carbons: et
Infix: double bond: en → ethylene
Suffix: enol: hello
In the case of ethenol, it was not necessary to number the location of the functional group or unsaturation because there was no other possibility. But, in the cases below, it is necessary:
H3C─ CH═CH ─ OH: prop-1-en-1-ol
H3C─C═CH2: prop-1-en-2-ol
│
oh
H3C─ CH═C CH2 CH3: pent-2-en-3-ol
│
oh
H3C─C═CH CH3: but-2-en-2-ol
│
oh
Enols are very unstable compounds, as they can go through a type of dynamic isomerism called tautomery, in which the isomers coexist in dynamic equilibrium in the same liquid phase.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
The oxygen in an enol is very electronegative, which attracts the electrons from the double bond of carbon, which is a weak bond that is easy to displace, forming an aldehyde or a ketone.
For example, in an acetic aldehyde solution (ethanal), a small part is transformed into ethenol, which in turn regenerates back into aldehyde. Thus, there is a chemical balance between these compounds that have the same molecular formula C2H4O:
Ethanal Ethanol
oh
║ │
H3Ç - Ç - H ↔ H2Ç ═ C — H
enol aldehyde
Another enol, prop-1-en-2-ol, can enter into dynamic equilibrium with a ketone, propanone:
Propanone Prop-1-en-2-ol
OH OH
║ │ │
H3C — C — C — H ↔ H2Ç ═ C — CH2
enol ketone
For more details, read the text: Dynamic Constitutional Isomery or Tautomery.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Enols and its nomenclature"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/enois-sua-nomenclatura.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
Chemistry

Access this link and learn about the organic function of phenols, a group of oxygenated substances, from great reactivity, whose acidity is greater than that of alcohols (compounds that also have a group hydroxyl). Its structure stands out for presenting a hydroxide group (OH) directly linked to an aromatic compound.
Main phenols, aspirin, picric acid, bakelites, phenolphthalein repellent property of cresol, creoline, lysol, cresols, oil taken from coal tar, manufacture of preservatives for wood.
Chemistry
Know what the various types of plane and spatial isomers are all about, such as function, position, chain, tautomerism, metamerism, cis-trans geometric and optical isomerism.
Chemistry

Hydroxyl functional group, Primary alcohols, Secondary alcohols, Tertiary alcohols, Methanol, Glycerol, Ethanol, preparation of nitroglycerin, manufacture of paints, production of alcoholic beverages, acetic acid, fuel automobiles.