Linear momentum, also known as amount of movement, is a vector physical quantity, as it has module, direction and sense. It is defined by the product of pasta of the body, in kg, for your velocity, in m/s. In this way, your unit of International System it's the kg.m/s.
Linear momentum is an essential quantity for the study of motion transfer in systems with two or more bodies where they occur collisions or any forms of interaction between bodies.
Thus, the amount of movement is calculated using the following expression:
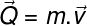
The amount of movement always has the samedirection it's the samesense gives velocity of the body. Also, if a particle acquires momentum in directions or sensesmany different, it is necessary to make the vector sum of the quantitiesof movement. Note in the following figure some rules for vector sum applied to momentum:

To find the direction and direction of the resulting momentum, we link the vectors, connecting the arrow of one to the beginning of the other. Finally, we turn on the
start of firstvector à tipoflast. The latter gives us the vector of the amountinmovementresultant.To calculate the module of the resulting vector of momentum, we take the following operations according to the situation. Represented in the following figure, we have three different situations, in which the vectors the amountinmovement find themselves in situations parallel, opposite and perpendicular.

Example:
A car of mass equal to 980 kg it moves at a speed of 72 km/h. Calculate your movement amount in International System units:
Resolution:
The amount of movement is calculated by the equation:
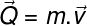
Mass (m) of the car is from 980 kgwhile yours velocity it's from 72 km/h. To calculate its velocity in SI units, we must transform it into meters per second (m/s). To do so, we divide its value by 3,6. To learn more about this type of conversion, click on here. Thus, we are left with:

By Rafael Hellerbrock
Graduated in Physics
