A molecule is a group of atoms of the same or different elements. See some examples:
H2O – molecule formed by two different elements (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom);
Cl2– molecule formed by only a single chemical element (two Chlorine atoms).
At molecules can be classified into polar or apolar:
non-polar: molecules that do not have poles (positive and negative);
polar: molecules that have poles (positive and negative).
In this text, we will emphasize the polar molecules. To identify a polar molecule, we can use one of the proposed strategies below:
The) ionic compound (formed by ionic bond)
If the substance is originated by ionic bond (between a metal and a non-metal), it means that it is formed by ions (cation and anion). Therefore, this substance automatically presents polar molecules, since ions have positive and negative charges.
Examples:
NaCl (Na is a metal, and Cl is a non-metal);
CaO (Ca is a metal, and O is a non-metal);
MgS (Mg is a metal, and S is a non-metal).
B) Molecular compounds (formed by covalent bond)
When the compound is molecular, we must analyze each case, as we have the possibility of several different molecules. The following are some examples and rules that can help in the determination of polar molecular compounds:
- Diatomic molecule with different elements
If the molecular compound is made up of just two atoms and these two atoms are from different elements, automatically the molecule will be polar because the two atoms have different electronegativities. Examples: HBr and NO.
- Molecules with two or more atoms (same or different)
In molecules that have a number of atoms greater than two, we must take into account the amount of clouds binders and non-binders present in the central atom of the molecule and compare it with the number of equal atoms attached to the atom central. The binding clouds are single bonds (one electron from the valence shell of each atom involved), double bonds (two electrons from the valence shell of each atom involved) or triples (three electrons from the valence shell of each atom involved). The non-binding clouds are the pairs of electrons in the valence shell that are not participating in the bonds.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Observation: To know the number of electrons in the valence shell of a given atom, just know its periodic family:

To determine if the molecule is polar, it is enough to check if the number of clouds existing in the central atom is different from the number of equal atoms attached to it. See some examples:
HCN
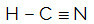
The central atom of the molecule is carbon and has two different binders,two binding clouds (single and triple) and no pair of non-bonding electrons (it is from the VIA Family, it has four electrons in the valence shell and is using all four, one in the single bond and three in the triple). For this reason, it forms a polar molecule.
in short:
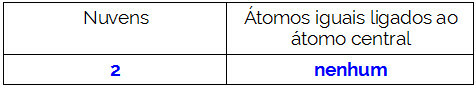
NH3
The central atom of the molecule is nitrogen and has three equal ligands and a total of four clouds, being three binding clouds (three single bonds) and one non-bonding (it is from the VA Family, it has five electrons) in the valence layer and is using only three, one in each single connection, leaving two not binders).
Because of this, the central atom of NH3 forms a polar molecule.
In short:

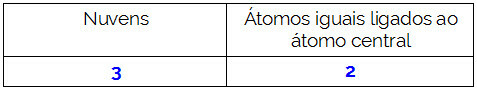
CH2O
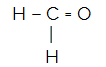
The central atom of the molecule is carbon and has two identical and one different ligands, as well asthree binding clouds (two single and one double bonds), no pair of non-bonding electrons (Family VIA, has four electrons in the valence shell and is using the 4, two in the singles and two in the pair). Because of this, it forms a polar molecule.
in short:
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "Polar molecules"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/moleculas-polares.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Ionic compounds, main characteristics of ionic compounds, bonding between ions, definitive transfer of electrons, electrostatic attraction forces between ions, negative and positive ions, anions, cations, ionic bonding, molecular structure he
Chemistry
Molecular substances, boiling temperature, contact surface, boiling point, intermolecular forces of attraction, chemical bond, molecular compounds, covalent chemical bonds, ionic bonds, metallic bonds, physical states of bad