Ether it is an oxygenated organic function, that is, it has the chemical element oxygen, in addition to carbon and hydrogen. This function has as its main structural characteristic the presence of two organic radicals attached to an oxygen atom.
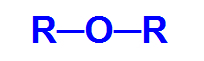
General structural formula of an ether
Thus, the carbon chain of an ether is heterogeneous and can have two identical or different radicals, either alkyl, types of radicals that do not have an aromatic structure, or aryl, radicals that do not have a structure aromatic.
Physical characteristics of ether
As for the physical state at room temperature: when the ether it has four or more carbon atoms in its composition, it is liquid;
As for melting point and boiling point: when compared to other mass organic compounds approximate molar, have a melting point similar to that of alkanes and lower than the rest of the compounds organic;
As for density: they are compounds that have a small density when compared to water;
As for the interaction forces: the ethers are composed with low polarity, interacting with each other through a weak permanent dipole interaction. With water and alcohols, ethers have the ability to interact through hydrogen bonds.
As for the polarity: are compounds that have angular geometry, thus, they are polar.
As for the organoleptic characteristic: they are substances that give off a very pleasant odor, but their inhalation can cause dependence.
Official nomenclature of the ether
Minor stem prefix + oxy + major stem prefix + infix + o
To carry out the official nomenclature of a ether, It is critical to determine which is your major ligand and which is your minor ligand. To do so, follow two examples of application for this naming rule below:
1st Example:
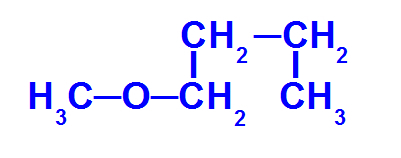
Structural formula of an ether with fewer carbons
The ether above has the following radicals:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Methyl (CH3-);
Butyl (CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-).
To name this compound, we have:
minor radical prefix: Met
+
oxy
+
major stem prefix: but
+
an (because it only has single links)
+
O
So, the name of this ether it will be methoxybutane.
2nd Example:
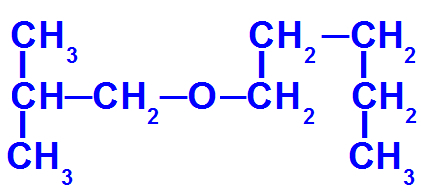
Structural formula of an ether with more carbons
This ether has the following radicals:
Isobutyl [(CH3)2-CH-CH2-);
pentyl (CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2).
To name it, therefore, we have:
minor radical prefix: isobut
+
oxy
+
major stem prefix: pent
+
an (because it only has single links)
+
O
Thus, the name of the ether in question will be isobutoxypentane.
Usual nomenclature of ether
Ether + name of radicals (simplest and then most complex) + ico
or
Radical names + ether
Follow below two examples of application for this naming rule:
1st Example:

Structural formula of an ether that has four carbons
That ether presents the following radicals:
Methyl (CH3);
Isopropyl (CH3-CH-CH3).
So, for this compound, we have:
Ether
+
minor radical: Methyl
+
major radical prefix: isopropyl
+
ich
Thus, the name of the ether in question will be methyl isopropyl ether, or else methyl isopropyl ether.
2nd Example:

Structural formula of an ether that has five carbons
The ether above has the following radicals:
Ethyl (CH3-CH2-);
Propyl (CH3-CH2-CH2-).
To name this compound, we have:
Ether
+
minor radical: ethyl
+
major radical prefix: propyl
+
ich
Thus, the name of the ether in question will be ethyl propyl ether, which can also be ethyl propyl ether.
Uses of ethers
In general, ethers are used:
As inert organic solvents, that is, not participating in any reaction;
Used in the extraction of essences, such as flowers, wood, etc.;
Used in the extraction of various oils and fats.
By Me. Diogo Lopes
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "What is ether?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-eter.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Chemistry

Esters, Food Flavoring, Flavoring, Esterification Reaction, Methyl Anthranilate, Pentyl Acetate, Butyl Ethanoate, Ethyl Butanoate, Propanetriol, Glycerin, Stearin.