Starch is considered a natural polymer, as it is a polysaccharide, that is, it is a carbohydrate formed by the successive union of several α-glucose molecules. In fact, it is made up of two polysaccharides, amylose and amylopectin, which are made up of α-glucose molecules, but are slightly different.
THE amylose it corresponds to a normal chain polymer with more than 1000 α-glucose molecules joined by means of an α-1,4glic-glycosidic bond and is present in the proportion of 20 to 30%. already the amylopectin it is made up of long, highly branched chains of α-glucose units joined between the α-1,4’-glycosidic bond. Branching is the result of cross-links between carbon number 1 of one glucose unit and carbon number 6 of another unit (α-1,6’-glycosidic bond). Amylopectin accounts for the remaining 70 to 80% of starch.
The structure of starch can be represented by:
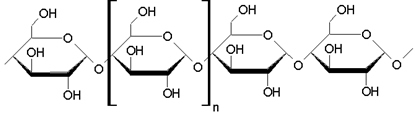
Stretch of starch macromolecule formed by glycosidic bonds between α-glucose molecules
The highlighted part in the figure is an α-glucose unit, and “n” can range from 60,000 to 1,000,000 units. In addition, starch is considered a
condensation polymer, as in its formation the condensation of α-glucose molecules occurs with the elimination of water.Starch is the main source of energy storage in plants and, therefore, it is present in roots, fruits, tubers and seeds. Among the main sources of starch in food are potatoes, peas, beans, rice, corn and flour.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)

Starch sources in food
Starch undergoes hydrolysis in saliva and the stomach through an enzyme called amylase. Starch hydrolysis in the presence of acid gives glucose:
(Ç6H10O5)n + n H2O → n C6H10O5
starch glucose
This glucose is transformed into glycogen, also called "animal starch", as starch is the energy reserve of vegetables, glycogen is the energy reserve of animals and humans, being stored mainly in the liver and muscles. In this way, when the body needs energy, glycogen is again broken down into glucose, which is transported by the blood to the tissues, where it is oxidized, releasing energy.
In addition to being used in food, in the manufacture of glucose, ethyl alcohol, powder for the skin, among others, starch is also used to make cassava gum, from which a glue called stick.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Starch"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/amido.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
Chemistry

Main sources of carbohydrates, natural sources of carbohydrates, role of carbohydrates in the body, carbohydrates, energy action, group of macronutrients that constitute the main source of energy, disease prevention, horm changes



