Hydrochloric acid is a hydracid with high ionization potential, it is a yellowish liquid, highly corrosive and toxic. It is used in various industrial processes, such as the manufacture of cleaning products and pharmaceutical hydrochlorides, in foods and in steelmaking processes.
It is also present in the human organism; O gastric juice which acts in the digestion of proteins is an acid solution; of hydrochloric and other substances, such as enzymes and salts. Exposure, inhalation or ingestion of Concentrated hydrochloric acid is highly harmful to health, which can even cause death.
Read too: Sulfuric acid - substance that has high corrosive power
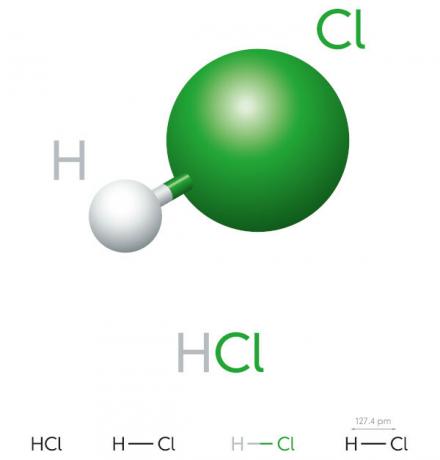
Hydrochloric acid properties
- inorganic compound
- strong acid
- High ionization potential
- Liquid
- yellowish appearance
- Toxic
- Corrosive
- Volatile
- Hygroscopic (tends to absorb áwater of the environment)
- Soluble in water
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Hydrochloric acid production
The hydrochloric acid was discovered by a muslim alchemist called Jabir Ibne Haiane, also known as Gaber and considered the father of Arab chemistry. He synthesized the substance based on a reaction between sea salt (NaCl) and the sulfuric acid (At2ONLY4).
2NaCl + H2ONLY4 → In2ONLY4 + 2HCl
Currently hydrochloric acid is produced on a large scale through the electronicólysis of sodium chloride in aqueous solution. From this process, gas is obtained chlorine (Cl2), gas hydrogen (H2) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH). Chlorine and hydrogen gases react to form hydrochloric acid:
Cl2 + H2 → 2HCl
However, this reaction is extremely exothermic and highly dangerous. Currently, most of the hydrochloric acid produced industrially is associated with the production of organic compounds, being a more economical and safer process.
R-H + Cl2 → R-Cl + HCl
(Consider R to be an organic radical.)
See too: Tips to determine-if the strength of acids

Hydrochloric acid application
- Metal pickling: Hydrochloric acid is used to “clean” metals before they are processed, removing rust, scale and other impurities from their surface.
- Production of organic compounds: hydrochloric acid is used as a reagent to obtain vinyl chloride, which is used in the manufacture of plastics. Hydrochloric acid also comes from chloroprene, which is used in synthetic rubbers.
- Production of inorganic compounds: hydrochloric acid is present in several industrial processes for manufacturing reagents and compounds Inorganic products, among them are products for water treatment, such as iron(III) chloride and iron (III) chloride aluminum.
- Used as a cleaning product: Also marketed as muriatic acid, hydrochloric acid is used for post-construction, domestic, and chemical cleaning of tools and machinery.
- Food processing: Hydrochloric acid is applied in various reactions for the production of food and additives, such as hydrolysis of starch and proteins, or in the final product for pH balance.
- Drug production: Hydrochloric acid is used in the production of soluble hydrochlorides present in several drugs, such as doxycycline hydrochloride, used in the treatment of typhoid fever and smallpox.
Hydrochloric acid in the body
Hydrochloric acid is present in our digestive system, the gastric juice produced by our stomach is a solution of water, enzymes, hydrochloric acid, inorganic salts and a small percentage of lactic acid.
O food cake is transformed into chyme, an acidic mass (thanks to the action of gastric juice and its acidic composition), this is when the digestion of proteins, transformed into polypeptides and amino acids that will be absorbed by the body.
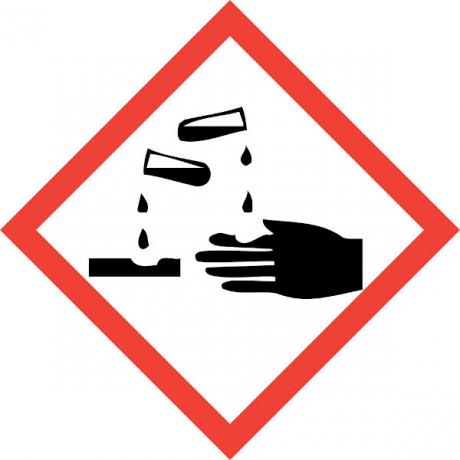
Hydrochloric Acid Hazards
Hydrochloric acid is a very strong and corrosive acid, so contact with the substance causes several damages:
- Skin: Causes burns and irritation.
- Eyes: Causes severe irritation and may cause blindness.
- Inhalation: Causes irritation and injury to the upper airways.
- ingestion: causes corrosion throughout the oral system, and in the gastrointestinal tract, it can cause vomiting, bleeding, diarrhea, circulation problems, which can lead to death.
- Exposureto be continued: attacks mucosal areas first, causing dermatitis and conjunctivitis, bleeding gums, photosensitization; frequent inhalation, even in low concentration of the compound, can cause gastritis and nosebleeds.
Also access: Characteristics and properties of acetic acid

solved exercises
Question 1 - (Udesc) Regarding hydrochloric acid, it can be said that:
A) when in aqueous solution, it allows the passage of electric current.
B) is a diacid.
C) is a weak acid.
D) has a low degree of ionization.
E) is an ionic substance.
Resolution
Alternative A. Hydrochloric acid is not a diacid as it has only one ionizable H, but one strong acid, molecular substance with high ionization potential. THE ionization in an aqueous medium promotes the conduction of electric current due to the existence of free ions.
Question 2 - In a solution of hydrochloric acid and water, we can say that the occurrence of molecular hydrogen chloride (HCl) is minimal, this is because
A) hydrochloric acid in contact with water is diluted.
B) hydrogen chloride is a substance that does not solubilize in water.
C) hydrogen chloride has a high ionization potential, therefore, when in an aqueous medium, the HCl molecule forms H ions+ Cl-.
D) the hydrochloric acid, being very volatile, separates from the solution, leaving only water molecules.
E) hydrochloric acid is an ionic substance, therefore, in aqueous solution, it dissociates, forming ions.
Resolution
Alternative C.
A) The answer does not agree with the question, diluting hydrochloric acid in water does not justify the absence of molecular HCl.
B) Incorrect, hydrogen chloride is soluble and has an affinity for water.
C) Correct
D) Although hydrochloric acid is volatile, this segregation of the two species in the solution does not occur significantly.
E) Hydrochloric acid is a solution of hydrogen chloride and water, where hydrogen chloride is a non-ionic molecular substance.
By Laysa Bernardes Marques de Araujo
Chemistry teacher
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
ARAúJO, Laysa Bernardes Marques de. "Hydrochloric acid"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/Acido-cloridrico.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.