Vladimir Vasilyevich Markovnikov (1838-1904) was a Moscow chemist who in 1869 began to study some reactions of adding hydrogen halides to alkenes and alkynes.
In these reactions, an alkene reacts with a hydrogen halide or hydrohalic acid, such as hydrogen chloride (HCl), hydrogen bromide (HBr), and hydrogen iodide (HI). The product formed from the alkene is an alkyl halide, as hydrogen bonds to one of the carbons of the pair and halogen bonds to the other. See the example below:
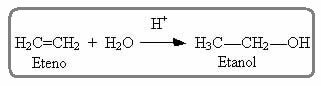
Something similar also occurs in the hydration reaction of alkenes in an acidic medium; in which the product formed is an alcohol:
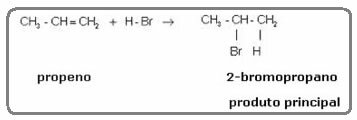
The ethylene molecule mentioned above is symmetrical; so it does not matter which carbon the hydrogen and the halogen will be added to, respectively. However, in asymmetric molecules, such as propene, one would expect the formation of two possible products. However, Markovnikov saw that this did not happen in practice. To understand, look at the reaction below:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
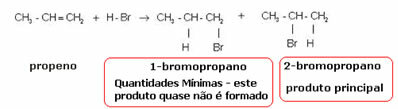
The product formed practically alone is 2-bromopropane. And Markovnikov saw that this was true for other substances as well. So he formulated the following rule:

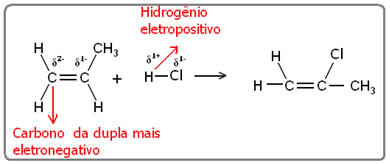
The same goes for adding water. Because both the water molecule and the hydrogen halides are polar, thus, the hydrogen of these molecules acquires an electropositive character.
Hδ+_ X δ- and Hδ+_ oh δ-
Being electropositive, hydrogen will bond to the most electronegative carbon, which will be the one bonded to the greatest amount of hydrogen. So we have:
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Brazil School Team
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Markovnikov's Rule"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/regra-markovnikov.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.