Radiation is the reverse math operation potentiation. While the potentiation is multiplication in which all factors are equal, radiciation seeks to discover which factors these are, giving the result of this multiplication.
Examples:
given to potency:
42 = 4·4 = 16
We say that the square root (root with index 2) of 16 is equal to 4.
given to potency:
26 = 64
We say that the sixth root of 64 is equal to 2. Note that by saying sixth root, we are making it clear that we are looking for a number that has been multiplied by itself 6 times and whose result of that multiplication is equal to 64.
The notation used for the roots is as follows:

In the previous example, 64 is the rooting, 6 is the index and 2 is the sixth root of 64 and result of the root.
Observation: If a is a negative real number and n is an even natural number, then there is no solution for this source in the set of real numbers.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Radiation properties
1 – THE sourceumpteenth from a number raised to n is equal to that same number:
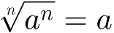
2 – Index and exponent of rooting can be multiplied or divided by the same number. Thus, given the real numbers a, m, n and p, we will have:
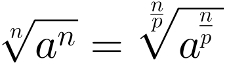
3 – To simplify the source from a root, enough multiply its indexes. Mathematically, this can be represented as follows:
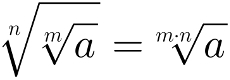
4 – THE sourceumpteenth of the product is equal to the product of the nth roots:
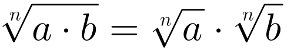
5 – the nth root of the reason is equal to the nth-root ratio, that is:
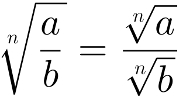
By Luiz Paulo Moreira
Graduated in Mathematics
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SILVA, Luiz Paulo Moreira. "What is Radiciation?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/matematica/o-que-e-radiciacao.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.

