Exportation and importation they are activities related to the entry and exit of products, goods or services in a country. Both can involve buying, selling and donating.
Export
Export refers to the sale, shipment or donation of products, goods and services from one country to another. It is, therefore, the departure of a national good or service to another country. Exports mainly happen when companies decide to expand their business in order to expand the market, supplying not only the internal but also the external. Exporting, therefore, represents an attempt at economic growth through market diversification.
Read too: Made in China: How did China become a power?
The export can be, according to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs:
direct: the invoicing belongs to the producer, that is, the exported product is invoiced by the producer in relation to the importer. The entire export process is fully known by the exporting company. This process involves: market research, documentation, packaging, banking transactions, among others.
indirect: the sale of the products does not occur by the company that produced them, that is, the company producer does not take care of the external trade of the product and also does not take care of the transport of the product to the country of destiny. Usually this type of export is carried out by companies without experience in foreign trade.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Import
THE import refers to the purchase or receipt of products, goods or services by countries. It is, therefore, the entry of foreign goods or services into national territory.
It is very difficult for a country to be self-sufficient in all sectors. Normally, importing countries do not produce the goods that are imported and it is therefore inevitably necessary to import them. Imported goods, goods and services generally supply the industrial sectors with raw materials, enable research and also supply the population with food.
Read too: Europe: a major consumer of raw materials
According to the Import Manual prepared by Unesp, there are three basic phases in the import process:
→ Administrative: represents the authorization phase of the import process, which is done according to the operation or type of goods that will be imported. At this stage, the import license is generated.
→ Exchange: represents the payment stage to the exporter.
→ Supervisor: represents the customs clearance phase (clearance of goods by customs). In this phase, taxes are collected and the goods are removed at customs.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages and disadvantages of exporting and importing are variable and not always applied to all commercial relationships. These are possibilities that vary according to the commercial nature and the countries/traders involved. See below the possible advantages and disadvantages, according to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, of each of these commercial activities:
Export |
→ Benefits
Increased productivity in the exporting country.
Companies start to improve their services to meet market trends.
Strengthening of exporting companies, which end up becoming a reference for other companies wishing to venture into the foreign market.
→ Disadvantages
There may be a longer financial payback time, as the first exports may not be as satisfactory as expected by companies.
Because there are cultural and climatic differences between some countries, it is necessary to be more careful with the items to be exported so that there is no damage during the journey.
If the company does not have a group of qualified employees for the market, foreign trade, which can be more demanding, can become a problem and bring several losses to the company.
Some obstacles, such as fiscal strikes, can hinder or delay exports, resulting in discontent for both the importer and the exporter.
Import |
→ Benefits
There is exchange advantage, that is, there is an advantage of one currency over another. When the exporter's currency is devalued against the importer's currency, there are financial advantages for the importer.
The Federal Government, in the case of Brazil, can offer incentives to companies.
Usually the import time is reduced in relation to the time that would be spent producing the imported product.
Production and labor costs are reduced.
→ Disadvantages
It is possible that there are delays in the delivery periods of imported products, thus bringing losses to the importer.
If there is no planning, it is possible that there are failures with regard to the quantity of products purchased.
If there is no trust between the importing company and the exporting company, possible conflicts can arise and generate problems during the execution of commercial activities.

Brazil is one of the largest exporting economies in the world.
Export and Import in Brazil
Currently, the Brazil is the world's largest exporter of beef. In 2018, around 1.64 million tons of the protein were exported, according to data from the Brazilian Meat Exporting Industry Association (Abiec). According to the Economic Complexity Observatory, the country is the 24th largest exporting economy in the world. In 2016, the country imported 140 billion dollars and exported around 191 billion dollars, presenting, therefore, a positive trade balance of 50.7 billion dollars.
Read more: Soy expansion in Brazil
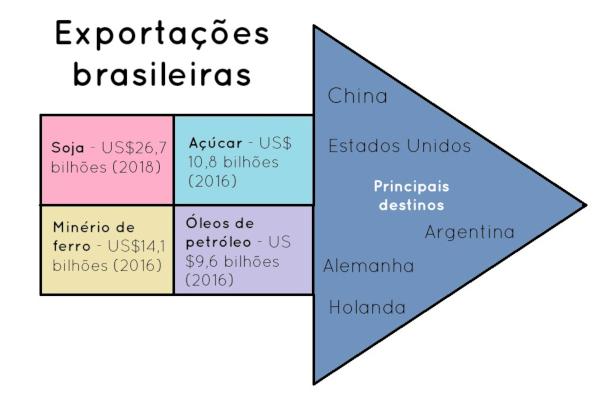
→ Products and export destinations from Brazil
Know more: Sugarcane in São Paulo
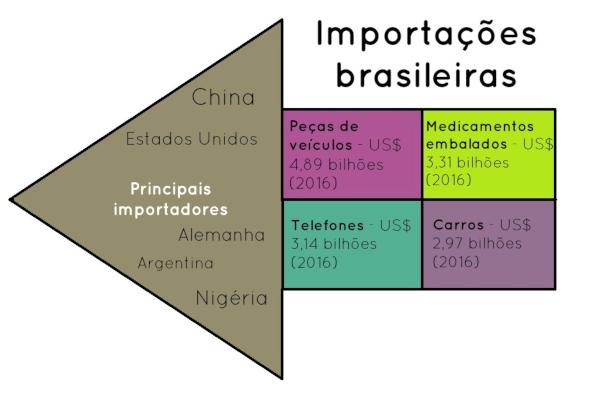
→ Main products imported by Brazil and the main destinations
Regarding imports, between January 2017 and January 2018, Brazilian imports totaled US$ 152.753 billion. The most recent imports turn to refined petroleum products.
What is better for a country: exporting or importing?
It's hard to say what's best for a country, whether exporting or importing. When we refer to the trade balance, which represents the difference between the value of what was exported in relation to the value of what was imported, the country is expected to have this balance positive/favorable. For this to be possible, the country must export more than it imports, that is, sell more than it buys. However, this does not mean that a country should stop importing. Importing means meeting the deficiencies and needs of a certain place, which, for various reasons, cannot provide a certain service or produce a certain product.
by Rafaela Sousa
Graduated in Geography
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SOUSA, Rafaela. "Difference between export and import"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/geografia/diferenca-entre-exportacao-importacao.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.