The first scientist to come up with the idea of building a space telescope was German missile engineer Herman Oberth. His idea assumed that a telescope located outside the Earth's atmosphere would be more advantageous, since water vapor, the air currents and dust distort the fragile light rays emanating from stars, that is, the atmosphere prevents a clear observation of the Universe.
The Hubble telescope (named after the American astronomer Edwin Hubble) was built in the 1970s and 1980s, and began operating in 1990. Initially, the telescope had some defects, first in one of the mechanical arms and then it had a defect in the transferred images. Due to a defect known in optics as spherical aberration, images sent to Earth were blurry.

The first Hubble telescope repair mission took place in 1993, which by the way was very successful. The focusing error was then corrected, sending perfect images.
Currently, NASA is working on a project whose objective is to launch a telescope that aims to capture radiation into space. infrared, having also the mission of making observations about the first galaxies and stars in the Universe.
O James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is intended to replace Hubble because it uses new technologies in its construction and has a primary pickup mirror 2.5 times larger than the Hubble mirror. The JWST will operate in an orbit beyond the Moon's orbit, at a point called the Lagrangian point L2.
Its launch, according to NASA, is expected to take place in 2014 and the telescope is expected to take about three months to reach its final orbit. The JWST, scientists say, was designed to be the most powerful telescope ever built.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
By Domitiano Marques
Graduated in Physics
Brazil School Team
mechanics - Physics - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SILVA, Domitiano Correa Marques da. "James Webb, Hubble's successor"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/james-webb-sucessor-hubble.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
Physics
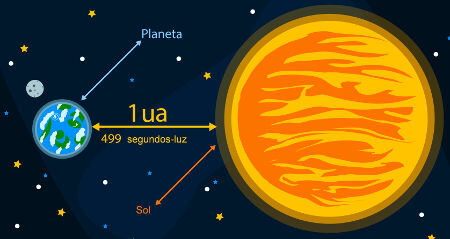
Do you know what an astronomical unit is? It is a measure of length that uses as a reference the average distance from the Earth to the Sun. An astronomical unit is equivalent to approximately 499 light seconds, that is, the distance traveled by light in a vacuum in 499 seconds, or even about 150 million kilometers.