the phrasal verbs(phrasal verbs) are formed by a verb and a particle (adverbs or prepositions). Furthermore, they have a sense that takes into account their unity as a whole, that is, the verb + preposition or the verb + adverb. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the usage and classification of phrasal verbs. We will discuss these two aspects in more detail below.
Read too: Modal verbs: How to use them? What are worth for?
List of top examples of phrasal verbs
In this list, you will find some of the main ones. phrasal verbs. How about, based on it, you create your own list and expand your vocabulary in English? Come on!
Phrasal Verbs |
Examples |
Fall for |
Clarice fell for her best friend. (Clarice fell in love with her best friend). |
Find out |
They found out she is missing classes. (They found out she is missing classes). |
get away |
The thief didn’t get away from the police. (The thief failed to escape the police). |
give back |
He gave me back my wallet. (He gave me back my wallet). |
give up |
Don’t give up on your dreams! (Do not give up on your dreams)! |
Keep on |
Keep on doing your homework. (Keep doing your homework). |
Look up |
Try to look up this word in the dictionary. (Try looking up this word in the dictionary). |
Make up for (offset) |
I promise I’ll make up for you next month. (I promise I will make it up to you next month). |
Put off |
Stop putting off your New Year’s resolutions! (Stop putting off your New Year's resolutions)! |
Rule out |
They decided to rule me out of the team. (They decided to exclude me from the team). |
Stand up |
Stand up and read it! (Get up and read it)! |
Take back |
Take back what you said to my brother! (Remove what you said to my brother)! |
Take over (take over/control) |
It’s time to take over the chief’s place. (It's time to take the boss's place). |
|
turn off (to switch off) |
Please turn off the lights. (Please turn off the lights). |
|
turn on (to connect) |
Please turn on the TV. (Please turn on the tv). |
|
wake up (wake up) |
He isn't able to wake up early. (He is not able to wake up early). |

How to use phrasal verbs?
To learn how to correctly use the phrasal verbs, it is important to keep in mind that they work as a unit. For example, the verb get it's a word polysemic (it has several meanings) in the English language, which can mean: receive, obtain, bring, buy etc. However, when we look at the image below, the verb get may be accompanied by the following particles: across, along, by, away, at, among others.
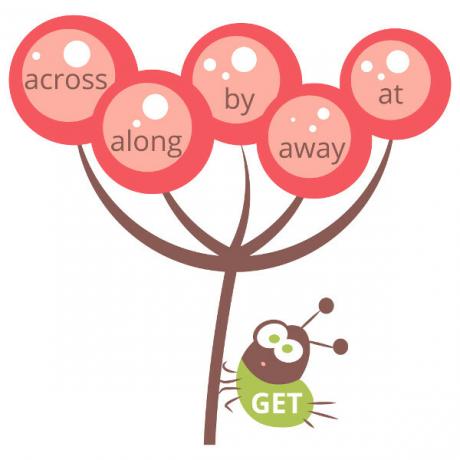
Thus, the first questions arise: “How should we use each particle?”, “What is the meaning of get in each of them?”. To answer these questions, let's take an example: get something across. This phrasal verb can be translated as communicate, make understood or transmit. if we try translate the verb apart from its particle, it is very likely that we have a erroneous translation.
Note the following sentence:
⇒ The message isn't getting across. |1|
- Translation of the verb and the particle separately:
The message is not getting through.
- Translation of the unit as a whole:
The message is not being transmitted (or understood).
Therefore, we must not translate the phrasal verbs according to each part that makes them up, as they usually have a senseidiomatic at English language. Consequently, it is necessary to use some strategies to learn when and how to use phrasal verbs efficiently.
See too: Adverbial sentences in English - structure and function
Helpful hints for learning phrasal verbs

In this case, to learn the phrasal verbs, we can:
- use the dictionary to confirm whether a verb followed by a preposition or an adverb is really a phrasal verb;
- in case that happens, it is interesting to create your personalized list of phrasal verbs, putting their translation in front;
- another strategy, in addition to translating, is to write sentences and create your own examples, making learning more dynamic.
Classification of phrasal verbs
As for your classification, we can separate the phrasal verbs in verbs transitive and intransitives, taking into account if they are separable or inseparable.
You verbsintransitives are not followed by an object, but can have a complement. For example:
The plane took off.
(The plane took off).
The plane took off early.
(The plane took off early).
Jane and her family eat out her every weekend.
(Jane and her family eat out every weekend).
Also, they are inseparable because we cannot put anything between the verb and the adverb or the preposition. Thus, if the verb phrasal has a complement (examples 2 and 3), it comes right after the phrasal verb.
already the transitive verbs are accompanied by an object to have its full meaning. They are separable if it is possible to place the object between the verb and the preposition or the adverb. When it is not possible to place the object directly between the verb and the preposition or the adverb, are called inseparable transitive phrasal verbs, as we can see in the following examples:
She gave her books away.
(She gave her books).
She gave away her books.
(She gave her books).
She she gave them away.
(She gave them).
Carlos ran into me last Friday.
(Carlos ran into me last Friday).
She took off her shoes.
(She took off her shoes).
In the third example, we have how objectapronoun, in this case, the pronoun must always come between the verb and the preposition or the adverb. The fifth example brings the phrasal verb “take off”, which works both as intransitive (meaning to take off) and transitive (meaning to take off), changing only its meaning.
There are no grammatical rules to explain when a phrasal verb is transitive or intransitive. Therefore, the tip we gave to create a personalized list becomes indispensable for a good learning of this subject.
Also know: Position of adverbs - see what the rules are
Solved exercises on phrasal verbs
question 1
(Nucepe) The alternative that best replaces the underlined phrasal verb in the sentence:
“Doctors diagnosis Alzheimer's on the basis of medical examination, patient history and cognitive tests, and can use imaging to rule out other forms of dementia" is:
The. Eliminate
B. include
ç. allow
d. add
and. accept
Resolution: The correct answer is the letter The, because rule out means “delete”.
question 2
English phrasal verbs can be classified as transitive or intransitive. According to the rules, which sentence below is incorrect:
The. He woke up late for work.
B. The noise woke up everyone.
ç. The noise woke everyone up.
d. Clara woke them up.
and. Clear woke them up.
Resolution: The incorrect answer is the letter d. According to the rules, some transitive verbs can be separable, but when we have a pronoun as a direct object, it must always come between the verb and the preposition/adverb.
Grades:
|1| Example taken from dictionary longman, online version. Available in: https://www.ldoceonline.com/dictionary/get-across.
By Patricia Veronica Moreira
English teacher
