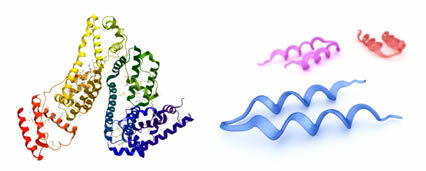
In the text Protein Structures it has been shown that proteins can have primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures. Many of the functions of these proteins are directly linked to their structures. However, they can lose their secondary, tertiary and even quaternary structures, and, consequently, cease to be active.
When these spatial conformations are altered or destroyed, we say that the protein has been denatured or denaturation has occurred. protein, keeping only the primary structure, which is the peptide chain itself, formed by the sequence of amino acids linked between themselves.
The factors that change the structure of a protein can be diversified, including changes in the temperature and pH of the medium, action of organic solvents, oxidizing and reducing agents and even agitation intense.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
A common example is what happens to an egg when it is boiled or fried. When heated, there is agglutination and precipitation of albumin, which is the egg white protein, which is why it turns white.
Another example occurs when we boil milk, cream is denatured protein.

When we use alcohol as a disinfectant, it penetrates and permanently dissolves the protein structure of a bacteria.

By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Protein denaturation"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/desnaturacao-das-proteinas.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.