THE ecological succession is a sequence of gradual and progressive changes in the community of a ecosystem, which can occur after a disturbance or after the appearance of a new habitat.
In an ecological succession, we progressively observe the change in the composition and structure of communities, until the establishment of the climax community, that is, of a stable community.
Read too:Difference between population and community
→ Primary ecological succession
The primary ecological succession takes place in previously unoccupied environments by other organisms, that is, in practically lifeless areas. This situation occurs, for example, in rocky outcrops, recently exposed sand surfaces and recently solidified volcanic lava.
Imagine, for example, ecological succession on a rocky outcrop. Initially what we observe is the presence of organisms such as bacteria and protozoa, and, later, the development of other beings. In general, the first organisms photosynthesizers fixing themselves in the environment are the lichen and the mosses, these species being called pioneers.

As these organisms fix themselves and the action of the wind and the sun occurs on the environment, we see the formation of the ground.
The soil then develops and the organic matter accumulates on site. After this moment, the colonization by other species, such as herbaceous plants, shrubs and trees. This replacement of species occurs until a stable community (climax community) is observed, a process that it may take decades.
In 1883 the volcano Cracatoa erupted and was responsible for the destruction of the island of the same name. Life on the site was wiped out, and island fragments became important for the study of primary ecological succession.
Initially, on this island, the emergence of grasses and ferns, and, with time, a true forest was formed. In 1920, several pioneer species had already disappeared and a dense forest had developed over much of the island.
Read too:Yellowstone Super Volcano
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
→ Secondary ecological succession
Secondary ecological succession takes place in areas that have already had a community. In this case, what is observed is that that area suffered some kind of disturbance, which caused the destruction of its original community.

Secondary ecological succession can be observed, for example, in areas deforested, regions hit by hurricanes and clearings.
In these places can be found traces of some organisms, as seeds and roots, and, due to this factor, this succession occurs faster than the primary. In addition, because there was already a community in that area, we have a more conducive to the development of species.
Read too:invasive species
Mind Map: Ecological Succession

* To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
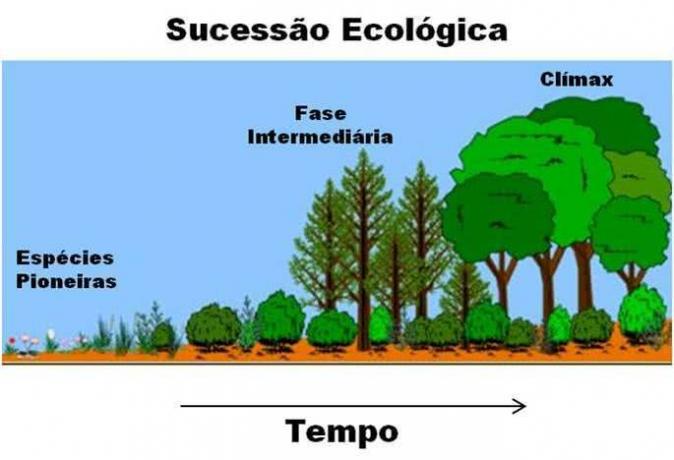
→ Stages of ecological succession
Ecological succession can be divided into three stages: pioneer community, intermediate community and climax community. See more about each of these stages below.
pioneer community
It is formed by the first organisms to settle in a region, such as lichens and mosses on rocks. In general, pioneer species present the following characteristics: fast growth and ripening, easy dispersion and shoots that are intolerant to shade. These characteristics make the species pioneer organisms with great colonization capacity.
The development of the pioneer community is directly related to that of the intermediate communities. Sometimes we observe that the pioneer community is responsible for facilitating the development of other species, as it is responsible for increasing, among other factors, the biomass Of region.
However, this is not always observed. Some species can inhibit the development of others, and other species, however, can develop without influencing others.

intermediate community
It is the one that presents itself as a transition community, in which an increase in diversity is observed, but the ecosystem has not yet reached its peak.
climax community
It's the one where you observe the peak of diversity in an ecosystem. In this community, what is generally perceived is a greater biomass and also a food web more complex than in other communities.
→ Events that occur along a succession
As ecological succession occurs, we can observe a series of modifications in the ecosystem. See some of these changes:
Increased biodiversity and ecosystem community complexity.
Increase in biomass.
Tendency to increase the size of individuals.
Emergence of organisms with a longer and more complex life cycle.
Rapid increase in species that make up the community (initially) and slower change in composition (later).
Formation of complex food webs.
Increased rate of photosynthesis in relation to respiration rate (initially), followed by equalization between both rates (over the years).
→ solved exercises
|
EXERCISE 1- (IFSul) Ecological succession represents the process of successive changes in the communities that make up an ecosystem. During this process, several events occur, along the succession, until the establishment of a stable community. About these events, the following statements are made: I. Gross primary productivity increases early in the process, then stabilizes. II. Species diversity increases, as does biomass, peaking at the climax. III. Nutrient recycling increases early in the process, making it faster. IV. Food chains become simpler as the number of ecological niches increases. Only the statements are correct: a) I, III and IV. b) I, II and III. c) II, III and IV. d) I, II and IV. |
Resolution of exercise 1: Letter B. Only statement IV is incorrect, as as ecological succession occurs, the more complex food chains become.
|
EXERCISE 2- (PUC-RIO) “Krakatau, an island the size of Manhattan, located between Java and Sumatra, was destroyed in 1883 after a series of powerful volcanic eruptions. Only a small piece of the original island remained above sea level. This small island, called Rakata, had no life at all, it was a barren island. But life soon began to emerge again…” WILSON, E. O. Diversity of life. Company of Letters, 1992. Adapted. When biologist E. O. Wilson says that "life soon began to emerge again", he was referring to what ecological phenomenon? a) Secondary succession. b) Biomagnification. c) Primary succession. d) Insularization. e) Geographic isolation. |
Resolution of exercise 2: Letter C. Primary ecological succession occurs in environments that were not previously occupied, therefore, the succession reported by biologist E. O. Wilson can be classified as such.
By Ma Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos