Dark matter is the name given to a large number of matter of unknown nature whose effect gravitationally affects the dynamics of galaxies and the Universe itself. It is believed that dark matter can be formed by compact and super massive objects, like black holes primordial or hypothetical and virtually undetectable particles known as inert neutrinos.
See too: What are exoplanets?
What is dark matter?
About 95% of all the matter that makes up our Universe, apparently, is made of something we don't know and can't directly observe. Furthermore, a third of all this unknown matter, dubbed dark matter, does not interact electromagneticandethically, that is, it is not capable of emitting or absorbing any type of radiation.
However, astronomical observations indicate that dark matter may interact gravitationally with ordinary matter, which is known to us and is formed by protons, neutrons, electrons and all other particles present in the standard model.

The existence of dark matter was deduced from the observation ofeffectsgravitational that could not exist if we considered exclusively the existence of the ordinary matter that forms planets, stars and galaxies. According to these gravitational effects, it is estimated that
- only 5% of the mass of the entire Universe is constituted from baryons (ordinary matter);
- 25% is formed by dark matter;
- 70% is made in an exotic and little understood form of energy, called dark energy.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
How does dark matter affect the Universe?
According to the law of universal gravitation, a gravitational force what one body is capable of exerting over another is proportional to the product of its masses. Such force, which is always attractive, points towards the center of mass of each of these bodies, for this reason, the gravitational force works as a centripetal force, capable of making planets, asteroids and other celestial bodies describe orbits around more massive objects such as stars, black holes etc.
Take, for example, the orbits of all celestial bodies that move around the center of our galaxy. It is known that, up to a certain distance from this position (about 15 kpc - kiloparsecs), the orbital velocity of the bodies obeys the Kepler's laws, derived from universal gravitation, that is, these speeds decrease with the square root of the distance that separates the celestial bodies to the center of our galaxy.
From a distance of 15 kpc, the phenomena start to get strange, and the orbital speed of the celestial bodies remains constant for a great distance and, from a certain point, starts to increase as if something were accelerating the expansion of its orbits.|1|
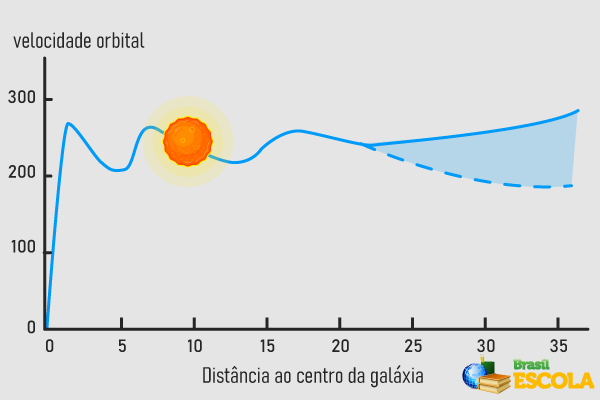
See too: Iincredible trivia about the ssystem shello
What is dark matter made of?
There is currently no completely satisfactory answer as to what dark matter is made of, however, physicists have some candidates for the post:
- Brown dwarf stars and primordial black holes: they are objects of planetary dimensions, endowed with enormous masses and almost impossible to detect. Some cosmologists believe these celestial bodies may hold the key to explaining dark matter.
- Inert neutrinos: There are theories that indicate that dark matter may be formed by a hypothetical type of particle – the inert neutrinos, much more massive than the known neutrinos. Theoretically, inert neutrinos do not interact with any of the forces present in the standard model, but only through gravity.
Note
|1| To access image reference data, click on here.
By Rafael Hellerbrock
Physics teacher
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
HELERBROCK, Rafael. "What is dark matter?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/fisica/o-que-e-materia-escura.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Physics
Do you know what an astronomical unit is? It is a measure of length that uses as a reference the average distance from the Earth to the Sun. An astronomical unit is equivalent to approximately 499 light seconds, that is, the distance traveled by light in a vacuum in 499 seconds, or even about 150 million kilometers.


