You esters are oxygenated organic compounds that are formed by the chemical reaction between a carboxylic acid it is a alcohol. Present the functional group (composed of two oxygen atoms and two radicals R) represented below:
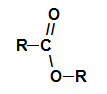
General functional group of an ester
Structurally, what characterizes the ester it is the presence of some alkyl radical attached directly to the oxygen atom. In this case, the radical (R) attached to carbon – which, in turn, is doubly attached to oxygen – can be either an alkyl radical or a hydrogen atom.
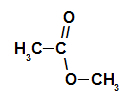
Carbonic chain of an ester
esterification reaction
it is about the chemical reaction that originates an ester and a water molecule from the interaction between a carboxylic acid and any alcohol, as in the equation below:
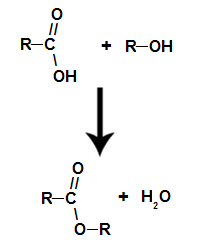
Chemical equation representing the formation of an ester
During esterification, the hydroxyl group (OH) of the alcohol interacts with the hydrogen (H) ionizable from the hydroxyl of the acid and forms the water molecule.
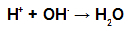
Water molecule forming groups in esterification
already the ester it is formed by linking the radical (R) of the alcohol with oxygen, which is left over from the hydroxyl of the acid after the formation of water.
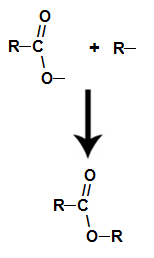
Formation of the ester molecule
Characteristics of esters
Main physical properties presented by esters:
They have fruit and flower aromas;
low esters molar mass they are liquid at room temperature and those with a high molar mass are solid;
When compared to alcohols and carboxylic acids, esters have lower melting and boiling points;
Compared to water, lower molar mass esters are less dense;
The lower molar mass esters are polar and the higher molar mass ones are non-polar;
In polar esters, forces predominate permanent dipole; in the non-polar, forces predominate induced dipole;
Esters with lower molar mass are poorly soluble in water and those with greater mass are insoluble in water.
An Ester Naming Rule
Before using the naming rule of a ester, it is essential to remember that this compound is formed by the union of two parts, one coming from of carboxylic acid (in red) and the other of alcohol (in blue), as represented by image a follow:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
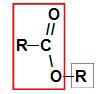
Identification of the parts that originate the ester
According to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), the official rule for naming an ester is:
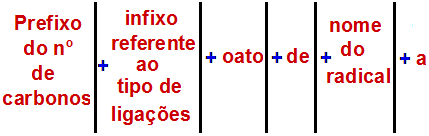
An Ester Naming Rule
Note: The prefix and infix always correspond to the carboxylic acid part, and the radical corresponds to the alcohol part.
See below some examples of application of the naming rule for esters:
1st Example: raspberry essence
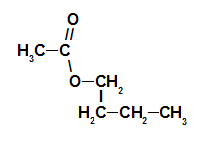
Structural formula of the raspberry essence ester
To name this ester, we use:
No. PrefixO of carbons: et, since the forming acid has two carbons;
Infix on the type of links: an, as the forming acid has only single bonds between carbons;
the act;
in;
Radical: butyl, by having four carbons in sequence;
The.
Thus, the name of the ester corresponding to the raspberry essence is butyl ethanoate.
2nd Example: pine cone essence
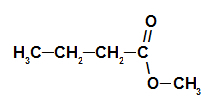
Structural formula of the pine cone ester
To form the name of this ester, we use:
No. PrefixO of carbons: but, since forming acid has four carbons;
Infix on the type of links: an, as the forming acid has only single bonds between carbons;
the act;
in;
Radical: methyl, as the forming alcohol has only one carbon;
The.
Thus, the name of the ester corresponding to the pine cone essence is methyl butanoate.
3rd Example: strawberry essence
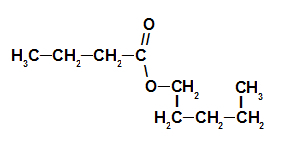
Strawberry Essence Ester Structural Formula
To name this ester, we use:
No. PrefixO of carbons: but, since the forming acid has four carbons;
Infix on the type of links: an, as the forming acid has only single bonds between carbons;
the act;
in;
Radical: pentyl, as the forming alcohol has five carbons in sequence;
The.
Thus, the name of the ester corresponding to the strawberry essence is pentyl butanoate.
Uses of esters
Esters are well known for their use as flavoring in processed foods, that is, substances that simulate the characteristic flavor and aroma of natural foods, such as fruits. Furthermore, the esters are still used in the manufacture of medicines, cosmetics, perfumes and waxes.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "What is ester?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-ester.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Chemistry

Esters, Food Flavoring, Flavoring, Esterification Reaction, Methyl Anthranilate, Pentyl Acetate, Butyl Ethanoate, Ethyl Butanoate, Propanetriol, Glycerin, Stearin.