Automotive vehicles are powered by converting forms of energy into mechanical energy, which is generated in combustion engines and transferred in the form of movement to the wheels. Cars, motorcycles and trucks use combustion engines, which differentiate between the modes according to the amount of displacement (cc). There are motorcycles of 150, 250, 400, 500, 600, 750, 1000 displacement among others. The cars have acronyms in their models, see some examples: 1.0 (1000 cc), 1.4 (1,400 cc), 1.6 (1,600 cc), 2.0 (2,000 cc), 3.0 (3,000), 4.1 (4,100 cc).
The term “displacement” comes from cylinder and is originally known as the displacement volume of the engine, that is, the volume capacity of a piston's chamber. Combustion engines have cylinders (chambers), where the explosion occurs (air + fuel + spark) that moves the pistons, which are connected by the connecting rod to the crankshaft, which receives all the force of the movement of the pistons, transmitting the mechanical energy to the engine flywheel that is connected to the gearbox (gears), whose motive force will be transmitted or do not. At the other end of the crankshaft there is a pulley, responsible for setting it in motion through a belt other equipment such as water pump, air conditioning motor, power steering pump and etc. See representative diagram of a combustion engine:
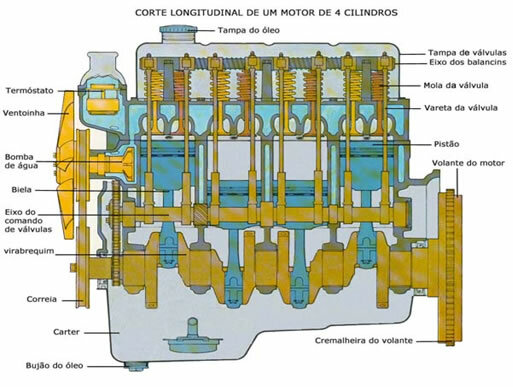
To better understand what the volume of a cylinder is, let's work with the example of a car 1.0. In the 1.0 car, that is, 1000 displacements, we have four cylinders (four pistons and four connecting rods). One displacement corresponds to 1000 cm³, which is equivalent to 1 liter. As the car has 1000 displacements and four cylinders, each cylinder holds 250 ml of gas, and it inhales and exhales one liter of gas for each complete revolution of the crankshaft.
The displacements of an engine are calculated according to the diameter and stroke of a piston, always given in millimeters (mm). We use the following mathematical expression to determine the displacement of an explosion engine:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)

Where:
N = Number of engine cylinders
π = 3,14
d = cylinder diameter
C = piston stroke inside cylinder
The diameter and stroke of the piston are usually informed in millimeters, so we must transform it to centimeters, just divide by 10.
Example 1
Determine the displacement of an engine with the following technical specifications:
Number of cylinders: 04
Cylinder diameter: 82.07 mm → 82.07/10 = 8.207 cm
Piston stroke: 75.50 mm → 75.50/10 = 7.550
π = 3,14
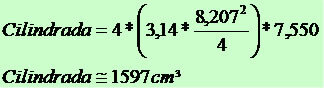
We say that the engine has 1597 displacements, which corresponds to a 1.6 engine.
Example 2
The engine of a motorcycle is considered a single cylinder (one cylinder). Determine the engine displacement of a motorcycle with the following specifications:
Cylinder diameter: 56.5 mm → 56.5/10 = 5.65 cm
Piston stroke: 49.5 mm → 49.5/10 = 4.95 cm
π = 3,14
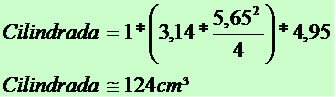
The motorcycle's engine has 124 cc, but on sale the industry usually informs 125 cc.
by Mark Noah
Graduated in Mathematics
Brazil School Team
Equations - Math - Brazil School