THE Second World War it was a conflict of global proportions that took place between 1939 and 1945. Characterized as a conflict in a state of total war (in which all resources are mobilized for war), World War II did allies and Axle face each other in Europe, Africa, Asia and Oceania. After six years of conflict, more than 60 million people have died.
Summary
World War II extended from 1939 to 1945, resulting in the death of 60 million to 70 million people, although there are statistics to suggest that the war caused more than 70 million deaths. The conflict was triggered by invasion of poland by the Germans on September 1, 1939.
The war began in Europe, but spread to Africa, Asia and Oceania and had the involvement of nations from all continents, including Brazil. It can be organized into three distinct phases: the phase of German supremacy, the phase in which the forces were balanced, and the phase that marked the defeat of the Axis.
The groups that faced each other in the war were the allies
(United Kingdom, France, Soviet Union and United States) and the Axle (Germany, Italy and Japan). This conflict was marked by a series of impacting events, such as the Katyn massacre, O Holocaust, O Babi Yar Massacre it's the atomic bomb drop about Hiroshima and Nagasaki.World War II officially ended on September 2, 1945, when the Japanese signed a document that it recognized their unconditional surrender to the Americans (the Nazis surrendered to the Allies in May, 1945).
See too:Atomic Bomb Effects
World War II video lesson
Causes
World War II had as a great cause the expansionism it's the militarism gives Nazi germany. This stance by Germany directly reflected the ideology of the Nazis, who had come to power in Germany in 1933. The action of the Nazis resulted, in large part, from the dissatisfaction of a radicalized part of German society with the outcome of the First World War.
At the end of the First World War, an idea that the defeat in the war had been unjust was strongly consolidated in German society. Added to this, there was also the great humiliation that Germany suffered with the Treaty of Versailles, agreement that ended the First War and that prohibited Germany from having ships and warplanes, limited to the number of 100 thousand infantry soldiers, forced the German nation to pay a very high indemnity and to hand over its colonies to those who defeated.
To make matters worse, in the 1920s, during the Weimar Republic, Germany faced a very harsh economic crisis, which led the country to bankruptcy. This crisis was aggravated by the 1929 crisis, which, in turn, reinforced the crisis of liberal democracy and fostered authoritarian and fascist movements across Europe. O italian fascism and German Nazism are the great examples.
The Nazis seized power in Germany in 1933, and adolf hitler, the leader of the Nazi party, launched a campaign to recover Germany, indoctrinate the population and persecute minorities. Germany, on recovering its economy, went into rearmament – a clear challenge to the provisions of the Treaty of Versailles. The French and English did nothing, as they feared that a challenge to the Germans might lead Europe into a new war, an experience they wanted to avoid as much as possible.
As Germany strengthened militarily, Hitler began his territorial expansionism. Hitler's idea was to build the lebensraum, O "living space” that the Nazis so longed for. This concept consisted basically of forming an empire for Germany in territories that had historically been occupied by Germans. This was the Third Reich, an empire dedicated exclusively to the Aryans (the Nazis' pure-bred ideal) and which would survive at the expense of the Slavs' exploitation.
German expansionism took place at three different times. Initially the invasion was carried out and annexation of austria, event known as Anschluss and which occurred in 1938. In 1939, the Germans expressed an interest in invading and annexing the Sudetenland, region of Czechoslovakia. After negotiations conducted by the British and French, the Germans were allowed to annex the Sudetenland (they ended up annexing almost all of Czechoslovakia). Finally, came to Poland. This Eastern European country had emerged at the end of World War I in territories that had previously belonged to the Germans and Russians. Hitler's rhetoric against the Poles hardened in mid-1939. The invasion of Poland, however, would not be accepted by the British and French. Both countries had demanded of Hitler during the Munich Conference, that their territorial ambitions ended in Czechoslovakia.
Hitler, however, did not expect the British and French to react to his moves. On September 1st he ordered the invasion of Poland using as justification an alleged Polish attack on the German border (the attack was faked by the Nazis). Two days later, British and French responded to German aggression against Poland with a declaration of war. This was the start of WWII.
Mind Map: World War II

*To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
combatants
World War II had the involvement of dozens of countries. WWII participants can be grouped into two groups.
allies: United Kingdom, France, Soviet Union and United States were the main members;
Axle: Germany, Italy and Japan were the main members.
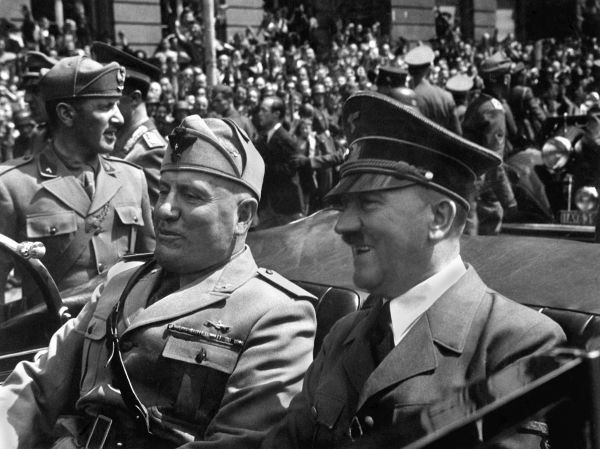

Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini were the leaders of Germany and Italy, respectively. Both nations belonged to the Axis.
Naturally, throughout the war, several other countries were taking sides and joining one of the two sides that were in the fight. On the side of the Allies, for example, fought the Canada, O Brazil, a Australia, a China, a Netherlands etc. In the Axis, nations such as Hungary, Romania, Croatia etc. It is important to mention that in several places where the Nazis stepped there were collaborationism, but there was also resistance.
A symbol of collaboration with the Nazis was Vidkun Quisling, a Nazi from Norway who organized the invasion plan of his own country with the Germans. Symbols of resistance against the Nazis were, for example, the guerrillas (partisans) of Belarus (now known as Belarus) who organized forces in their country's forests and acted for years in sabotaging the Nazis.
World War II Phases
World War II can be divided into three phases for a better understanding of the events of the conflict, namely:
Axis Supremacy (1939-1941): at this stage, the use of blitzkrieg and the conquest of several locations by German troops. In addition, in Asia, the Japanese conquered a series of territories dominated by the British, French and Dutch.
balance of forces (1942-1943): In this phase, the Allies managed to recover in the war, both in Asia and in Europe, and balanced forces with the Germans. This phase was marked by the indefiniteness who would win the conflict.
Axis defeat (1944-1945): at this stage, the Axis was in decadence. Italy was invaded; Mussolini, deposed; the Germans and Japanese were successively defeated and both countries collapsed.
The war, as mentioned, was started when the Germans invaded poland on September 1, 1939. From that moment on, the Germans started using a tactic that stood out in the conflict: the blitzkrieg. That word in German means “lightning war” and basically consisted of a tactic in which artillery and infantry made coordinated attacks against opposing lines in order to open them up. From the opening of the lines, infantry and armor made rapid movements in the territory to penetrate the breach that was opened.
Between 1939 and 1941, the Germans conquered Poland, Denmark, Norway, Netherlands, Belgium, France, Yugoslavia and Greece. During this period, the conquests happened at an amazing speed, with the German forces coming to dominate much of the European continent.
In 1941, Germany seemed invincible, and the Germans organized their most daring plan of the entire war: the Operation Barbarossa. This operation consisted in coordinating the invasion of the great adversary of the Germans in Europe: the soviet bolshevism. Until that time, both nations were at peace, as in 1939 they had signed a non-aggression pact, in which they agreed not to fight each other for a period of 10 years.
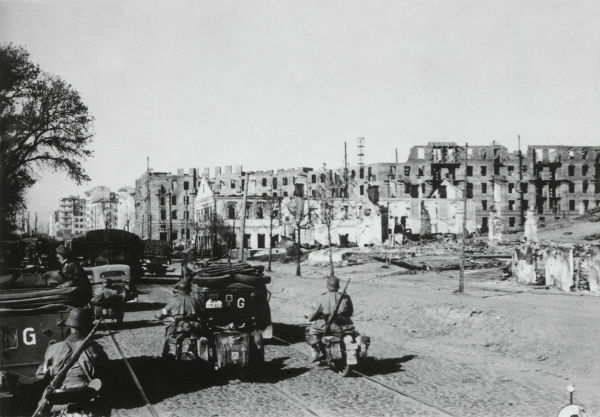

German troops in Minsk, Belarus, during Operation Barbarossa.
THE invasion of the Soviet Union happened on June 22, 1941, and the plan of the Germans was to conquer the country in eight weeks. The failure of the Germans in this regard destroyed any and all possibility of doing so in a long time. term, as Germany had neither the resources nor the money for a long-term war against the Soviets.
The Germans had three goals: Moscow, Leningrad and Stalingrad. The Soviet capital was almost conquered (Moscow) because the Germans arrived within a few kilometers of it, but failed. Leningrad it was surrounded by the Germans for 900 days and left to starve – reports of famine in the city show the population's despair at the lack of food.
The key point of the Second World War took place in a city in the south of the Soviet Union (southern of present-day Russia) that lies at the gates of the Caucasus and on the banks of the Volga River: Stalingrad. The conquest of this city was crucial for the Germans to guarantee control over the wells of Caucasus oil, in addition to being symbolic of conquering the city named after the Union leader Soviet, Joseph Stalin.
THE fight in Stalingrad it was very hard and lasted from July 1942 to 1943. Before Stalingrad the Germans had conquered vast territories of the Soviet Union (the Germans had conquered the Baltic countries, Ukraine, Belarus etc). At Stalingrad, the Germans suffered the defeat that started the Allied turn.
The battle for Stalingrad resulted in the death of 1 to 2 million people, and the description of that battle defines it as hell. The city was razed to the ground, and the Germans came very close to conquering it, but Soviet resistance guaranteed the defeat of the Germans. During this battle, thousands of soldiers and ammunition were sent daily to the Soviet troops. The defeat of the Germans came shortly after the Operation Uranus.

Destruction in Stalingrad caused by the battle that took place in the city between 1942 and 1943.
German troops were pushed out of the city and, without permission to retreat, were surrounded by the Soviets. At that moment, the German army, industry and economy began their collapse. The recovery of the Allies in the fight against the Germans began. Another important battle that sealed the fate of Germans in the Soviet Union was the battle fought in Kursk, in 1943.
After the end of First World War, European countries sought ways to prevent the disputes that engendered this disastrous conflict from recurring. However, the severe punishments imposed by the Treaty of Versailles and the inefficiency of the League of Nations – in its role of maintaining world peace – failed to contain the revenge of the defeated nations. In a short time, imperialist and expansionist actions gave the signal that the wounds were far from being healed.
Approaching Italy, Japan and Germany
In the East, the japanese they promoted the invasion of Manchuria and continued their imperialist project, dominating parts of Asia and the islands of the Pacific. O italian government, controlled by Mussolini, took over Abyssinia (present-day Ethiopia) and promoted the invasion of Albania. On the other hand, the Nazi germany reintegrated the Saarland territories and established the military occupation of the Rhineland. In a short time, the similar actions of these three nations resulted in a threatening political approximation.
During the Spanish Civil War, Germans and Italians signed their union with their participation in that conflict. The sending of troops served as an efficient test for the new technologies of war produced by these countries. The Berlin-Rome axis. Shortly thereafter, Japan, which had come into comfort with the Soviet Union during the Asian occupation, incorporated the Italo-German alliance with the signing of the Antikomintern pact, which advocated the fight against the communists.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Nations that believed they could circumvent the possibility of another war still sought to diplomatically negotiate the advance of those nations. At Munich Conference, the Germans, who had incorporated Austria, pledged to respect the domains of Czechoslovakia and Poland. However, contrary to what had been defined, the Germans dominated the entire Czech territory and exerted strong political pressure under Polish territorial autonomy.
Mind Map - World War II

*To download the mind map, Click here!
Alliance of Germany with the USSR
Through this situation, the British and French signed an agreement to defend Poland in case of any kind of invasion of their territories. The Anglo-French political decision was viewed with suspicion by the Soviets, who decided to sign a military pact with the Germans. According to the German-Soviet Pact, the troops of the Soviet Union would remain neutral if the French and British declared war against the Germans after a possible invasion of Poland.

Hitler and Stalin signed a non-aggression pact in 1939 *
With this definition, the Germans felt that this would be the best time to establish the invasion of poland and, consequently, the control of Eastern Europe. On September 1, 1939, adolph hitler went public to announce the first phases of the operation that would conquer Polish territory. In this way, the Germans showed total failure to comply with the Munich Conference and, therefore, required more incisive action from the British and French.
In a last attempt, England and France sent a warning to the Germans, demanding the cancellation of military action against the Poles. However, taking advantage of its alliances with the Japanese, Italians and Soviets, the government of Adolf Hitler did not hesitate to continue its project. With no alternatives, France and Great Britain declared war on the Germans, starting the conflicts of Second World War.
Until 1940, the war did not have major confrontations, even being called a “fake war”. However, from the following year, the powerful and unexpected attacks of the Germans - better known as blitzkrieg – established the advance of the conflict. At this point, the French-British authorities asked the United States for help in defeating their enemies.
In this way, taking into account the largest nations involved in the confrontation, we can divide the WWII alliances as follows:
-
England, France and the United Statesformed the group of “allies”;
- Germany, Italy and Japan formed the leading countries of the “Axle”.
Later, after the break with the Germans, the Soviet Union also decided to collaborate militarily with the allied countries.
____________________
*Image credits:Shutterstock / vicspacewaller
By Me. Rainer Sousa
*Mental Map by Daniel Neves Silva
Graduated in History
In that year too (1943), British and Americans expanded their efforts in the fight against the Germans. From the efforts of the United States and England, the German troops were expelled from the North of the African continent. Afterwards, the Allies debated the possibilities of an attack against the Germans in Normandy. That plan, however, was postponed, and the Americans and British chose to invade the Sicilia.
With the landing of Allied troops in Sicily, the reconquest of Italy, and the Germans were forced to reinforce defenses in northern Italy. It was on the front of the battle fought in Italy, in fact, that the Brazilian troops fought between 1944 and 1945. From 1944, Germany's situation in the war was chaotic, and more defeats occurred.
In June 1944, the British and Americans led on the 6th the landing of troops known as Day D. This operation was part of the plans to reconquer France (occupied by the Germans since 1940). On D-Day, around 150,000 soldiers were mobilized and landed on five beaches in Normandy: the beach's codenames were Utah, Juno, Sword, gold and Omaha.
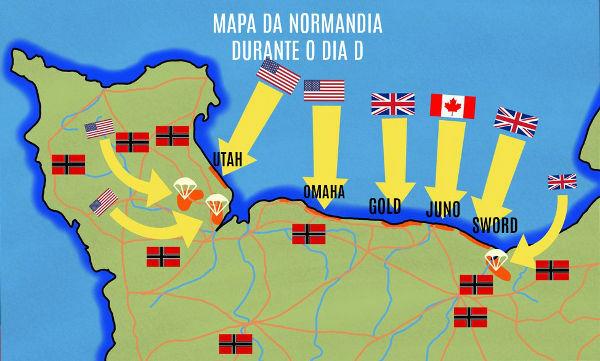
On the map, we can identify the five beaches designated for the landing of Allied troops.
At the turn of 1944 to 1945, the situation in Germany was desperate. In the early months of 1945, the Germans accumulated most of their losses throughout World War II. At the turn of the year, the last German offensive in the Battle of the Ardennes, which aimed to recover territories in France and Belgium. The campaign was a failure and served to weaken the German troops who still resisted in the front Eastern.
A direct consequence of the defeat in the Ardennes was the loss of territories in Poland, when the Soviets succeeded. to advance from the Vistula river to the Oder river and stay on the edge of the German border. In addition, the Soviets advanced through Eastern Europe conquering places like Budapest (Hungary) and Yugoslavia.
WWII in Asia
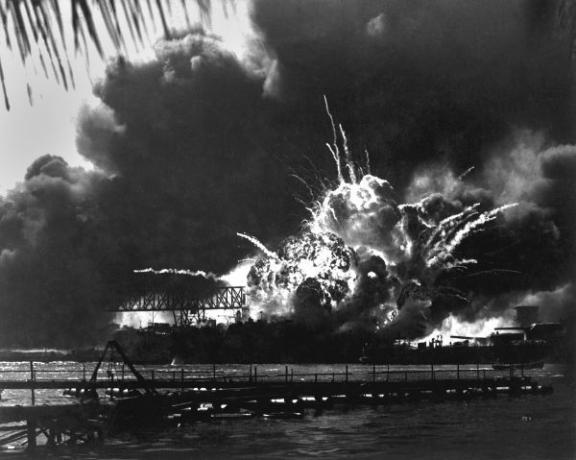

In December 1941, the Japanese attacked the Americans by surprise at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii.
The conflict in Asia was marked by the struggle between Japanese and Americans in what was also known as Pacific War. Throughout the 1930s, Japan also expressed expansionist intentions based on strong militarism. The direct result of this was the Second Sino-Japanese War, a conflict that began in 1937 that merged with World War II and therefore only ended in 1945.
See too: First Sino-Japanese War
Even before the start of World War II, the japanese they had taken part in a battle against the Soviets between June and August 1939. THE Battle of Khalkhin Gol, as it became known, was basically fought by territorial disputes between Japanese and Mongols (supported by the Soviets).
The Japanese were defeated in this battle, which was fundamental to the path the Japanese took next. With the defeat in that battle, the Japanese began to prioritize taking the war to South Asia, that is, to the European colonies that were in Southeast Asia, and against the United States.
In 1937, Japan's war against China began. In 1940, the Japanese invaded the IndochinaFrench and, in 1941, in addition to attacking the Americans in pearl harbor, invaded a number of British colonies and the Dutch colony.
The attack on Pearl Harbor is understood to mark the War in the Pacific and took place in December 1941. Because of this attack, the Americans declared war on Japan and began their fight against the Japanese army and navy. Some important moments of the struggle in the Pacific were the battles of midway (seen as the turn of Americans in the fight against the Japanese), Guadalcanal and Tarawa, that took place between 1942 and 1943.
From 1944 onwards, the situation in Japan was similar to that in Germany: the country was in ruins, but it continued to resist. In the final year of the war, crucial battles were fought in IwoJima, Okinawa and in the Philippines, being the first two islands belonging to the Japanese territory. In these battles it was evident that the resistance promoted by the Japanese would be carried out to the death.
Japanese soldiers, in fact, fought to the death – very few surrendered to the Americans. In addition to the indoctrination imposed on soldiers, surrender in Japanese culture was viewed shamefully, so soldiers fought until they were killed or, in extreme cases, committed the seppuku – a suicide ritual in which a dagger is thrust into the bowels.
After the surrender of the Nazis, the Allies demanded in the Potsdam Declaration, in July 1945, the unconditional surrender of the Japanese; otherwise, they would face their own destruction. The Japanese refused to surrender and, in retaliation for this, the Americans organized attacks on Hiroshima and Nagasaki with atomic bombs.
Atomic bombs
There is an intense debate among historians regarding the ethical question behind the dropping of these bombs over Japan. There are those who defend the hypothesis that the launch was just a show of strength by the Americans and totally unnecessary, in view of the situation in which Japan was in that time.
On the other hand, there are those who claim that the release was justified within that scenario because the Japan refused to surrender, and the invasion of Japan's main island would cost the lives of thousands of soldiers Americans. Furthermore, within the framework of Japanese resistance to the death, the Americans did not know how long the conflict would extend. Thus, the launch would be justified as a tool to force an end to the war.
Arguments aside, the dropping of the atomic bombs was one of the saddest chapters in world history. The accounts chronicle all the destruction and horror that unfolded on August 6 and 9, 1945. After the second bomb was dropped, the Japanese surrendered unconditionally to the Americans.
See too:Japanese victories in WWII and Japanese Defeat in World War II
End of World War II
The final battle on the European war scene was fought in Berlin, the German capital, where the Nazis' final resistance in a situation so desperate that there were troops made up of old men and kids. The attack on Berlin was carried out only by the Soviets and shortly after the Red Army troops entered the Reichstag (German parliament), Hitler and his wife (Eva Braun) committed suicide. Command of Germany was transferred to Karl Dönitz, and the Germans officially surrendered on May 8, 1945.
On the Asian scene, the war officially ended on September 2, 1945, when the Japanese signed their unconditional surrender to the Americans. The Japanese surrender was a direct result of the dropping of atomic bombs on Hiroshima on 6 August and Nagasaki on 9 August.
See too: Japan after World War II
Consequences
After World War II, the world underwent intense and radical transformations. Right after the war, the scenario that would characterize the world for the following decades was already predefined: that of the bipolarization of the period of Cold War. Eastern Europe was occupied by Red Army troops, and the entire region came under the influence of the soviet communism.
The Allied powers met in 1945 and debated the territorial changes that would take place on the European map. Thus, Germany, for example, lost territories to the Soviets (so-called East Prussia passed to the Soviet Union and is currently known as Kaliningrad Oblast and is in the current Russia). It is also worth mentioning that Germany was occupied by British, American, French and Soviet troops.
After World War II, courts who judged the war crimes committed by Germans and Japanese. People who were directly involved with the Holocaust and with the massacres committed by Japan in Asia were tried in the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg and in the International Tribunal for the Far East.
See too: Einsatzgruppen, the Nazi death squads
After the end of World War II, the United Nations Organization, known as UN and responsible for maintaining peace among nations. The intention of an organization like the UN is to prevent another conflict like World War II from happening.
Finally, a direct consequence of the bipolarization of the world, with the Soviets representing a model and the Americans representing another, was the creation of a plan for the reconstruction of Western Europe financed by the United States: the Marshall Plan.
See too: World War II Peace Accords
World War II movies
World War II is one of the most explored historical events in cinema. There are countless options for movies that narrate events of this war or that have the conflict as a backdrop. Here are some tips for you:
The Pianist, a 2002 film directed by Roman Polanski;
Amen, 2002 film directed by Costa Gavras;
Saving Private Ryan, 1999 film directed by Steven Spielberg;
Circle of Fire, 2001 film directed by Jean-Jacques Annaud;
Schindler's List, 1993 film, directed by Steven Spielberg;
Son of Saul, 2015 film directed by László Nemes;
Admiral Yamamoto, 2011 film directed by Izuru Narushima;
White Light, Black Rain: The Destruction of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, 2007 documentary directed by Steven Okazaki.
By Daniel Neves
Graduated in History

