THE cancer pill is a drug product created and produced by the research group of professor Osvaldo Chierice, at the University of São Paulo (USP), São Carlos campus. In this product, the substance called synthetic phosphoethanolamine (produced in the laboratory) is the active ingredient.
In 2015, the cancer pill gained prominence in the media because many people are demanding its use in court. This was because the distribution of phosphoethanolamine by the USP research group was prohibited, as the product does not comply with technical standards from Anvisa (National Health Surveillance Agency).
What is the phosphoethanolamine?
THE phosphoethanolamine is an organic compound produced in the endoplasmic reticulum of animal cells from a substance called ethanolamine, which has the functional amino and alcohol. It is an organic molecule because it has carbon atoms in its structure, as we can see in its chain shown below:
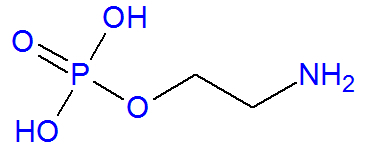
Structural formula of phosphoethanolamine
The phosphoethanolamine molecule has carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen atoms. Its molecular formula is: C
2H8AT THE4P. How the atoms of the elements that form the phosphoethanolamine molecule present atomic masses equal to, respectively, 12 g/mol, 1 g/mol, 14 g/mol, 16 g/mol and 31 g/mol, its molar mass is 141 g/mol.Main characteristics of Phosphoethanolamine
a) Biochemical characteristic
As phosphoethanolamine has a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms, it is biochemically considered as one the mine primary. For other authors, she it is a monoester (because it has an organic radical attached to an acid group), which can be proven by the fact that it participates in the synthesis of body lipids.
in addition to the amino group (NH2), the phosphoethanolamine molecule also has a phosphate group (composed of Phosphorus, Oxygen and Hydrogen and a group Hydrocarbon).
b) Physical characteristics
-
It is a white solid at room temperature.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Polarity
Phosphoethanolamine has atoms of high electronegativity, as is the case of Oxygen and Nitrogen. Therefore, it is a polar molecule.
Intermolecular Interactions
As the phosphoethanolamine molecule has several OH groups and an NH group, it performs several hydrogen bonds between its molecules. As hydrogen bonds are intense intermolecular forces, the melting and boiling points of this substance are greater than zero.
- Solubility
As the phosphoethanolamine molecule performs hydrogen bonds, therefore, it presents good solubility in water and oxygenated organic solvents (such as alcohols, ketones, ethers etc.).
Chemical functions in the body
Form phospholipids, such as phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine (examples of cell membrane-forming lipids);
Signaling function (indicates for the antibodies a place of action) for the action of macrophages (cell responsible for destroying solid particles or foreign cells to the organism);
Apoptosis (programmed cell death);
Cellular regulations (electrolyte balance of the cell membrane);
Fatty acid loading into mitochondria;
Regulation of mitochondrial metabolism (ATP production).
Example of Phosphoethanolamine Synthesis
A widely used method to produce phosphoethanolamine molecules is the one that uses ethanolamine and phosphoric acid as basic chemical reagents, represented below:

Ethanolamine and phosphoric acid are used to produce Phosphoethanolamine
When phosphoric acid interacts with ethanolamine, the hydrogen in one of the hydroxyl (OH) in the acid interacts with the hydroxyl (OH) in ethanolamine, forming a water molecule. Soon after, the carbon (where the OH was) of the ethanolamine binds to the oxygen (where the H was) of the acid.
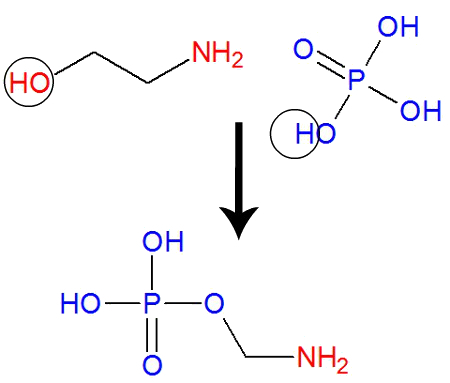
Equation representing the Phosphoethanolamine synthesis reaction
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "What is phosphoethanolamine?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-fosfoetanolamina.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Chemistry

Esters, Food Flavoring, Flavoring, Esterification Reaction, Methyl Anthranilate, Pentyl Acetate, Butyl Ethanoate, Ethyl Butanoate, Propanetriol, Glycerin, Stearin.
Physical characteristics of ethers, most common ethers, physical state of an ether, highly flammable liquid, manufacture artificial silk, celluloid, solvent for obtaining grease, anesthetic, paint thinner, prepare medicines.
Chemistry

Ketones, organic substances, carbonyl functional group, obtaining enamel solvent, propanone, ketone bodies in the bloodstream, extraction of oils and fats from plant seeds, solvents Organic.
Amines, classification of amines, amine properties, primary amine, nitrogenous organic compounds, alkyl radicals, dimethylamine, ethylamine, trimethylamine, compounds extracted from vegetables, putrescine, cadaverine, organic bases, syntheses organic
Chemistry

Hydroxyl functional group, Primary alcohols, Secondary alcohols, Tertiary alcohols, Methanol, Glycerol, Ethanol, preparation of nitroglycerin, manufacture of paints, production of alcoholic beverages, acetic acid, fuel automobiles.