Earthquake is a type of abrupt and intense tremor that occurs on the earth's surface thanks to geological phenomena that occur in the lithosphere. Its consequences for humans can be severe, leading to the destruction of cities and landscapes natural disasters, in addition to causing serious catastrophes, such as the disaster that occurred at the Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant, in Japan.
How do earthquakes arise?
The occurrence of earthquakes is directly related to the movement of tectonic plates and, more specifically, to fault or geological fault, which means the rupture of a rock inside the Earth. In some cases, this fault is not even visible on the surface, occurring many, many kilometers below, but its intensity is so great that the vibrations produced can be felt in the relief.
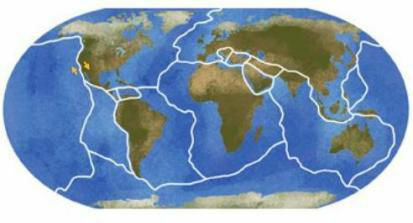
Earth's Tectonic Plates**
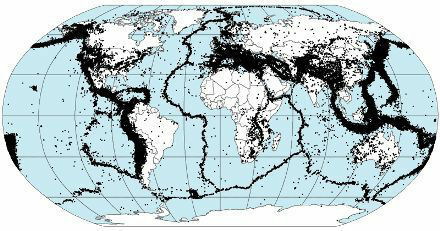
Earth's seismic zones. Note the similarity to the map above
The interaction of different tectonic plates causes what we call the tension zone, that is, zones in which the interaction between two rock bodies is intense, generating a continuous effort. Thus, when this tension exceeds the resistance limits of the rocks, some ruptures occur, which release large amounts of energy that manifest in the form of tremors and vibrations.

Schematic of a geological fault that can give rise to an earthquake
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Richter scale
Through an instrument called seismograph, it is possible to measure the Earth's internal vibrations. Thanks to this instrument, we were able to find important information, such as terrestrial layers and endogenous movements. In addition, another important function of the seismograph is to measure the force with which earthquakes occur.
This force is measured on a scale, which we call the Richter scale, which varies between 1 (very weak) and 10 (very strong). Tremors below 3.5º do not usually have great effects on the surface, being only registered by the seismograph; between 3.5º and 5.4º, they can already be felt, but without much damage; between 5.5º and 6º cause minor surface damage; between 6th and 8th, the damage can be severe and, above that, major catastrophes in a surface greater than 100 km in length will occur.
Studies on earthquakes, their causes and consequences were extremely important for the planning of cities, with buildings and houses adapted for these occasions. However, some tragedies resulting from seismic activity can still be recorded eventually.
_______________________
Image credits:
* Sadik Gulec / Shutterstock
** School Geographic Atlas. Rio de Janeiro: IBGE, 2012. p.13.
By Me. Rodolfo Alves Pena
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
PENA, Rodolfo F. Alves. "What is Earthquake?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/geografia/o-que-e-terremoto.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.