volcanoes they are geological structures constituted of molten rock mass, due to the high temperatures in its interior. Basically represent a opening in the earth's surface able to expel magmatic material and gases from the interior of the planet.
volcanic eruptions can cause a lot of destruction, especially when your area is inhabited. Not every region of the planet has volcanoes, and their formation and distribution are related to the existence of tectonic plates.
Visually the volcanoes resemble mountains, they can even be confused, especially when they are inactive. However, they are different structures from their formation to their composition. Volcanoes can be located both in the continents how much in oceans, and the study of these structures is very relevant for understand the events taking place inside the Earth.
Read too:Difference between hurricane, tornado and cyclone

how are formed
The formation of volcanoes is associated with the existence of
tectonic plates. It is known that the lithosphere terrestrial is not formed by a single and immobile rock block. THE Earth is formed by large semi-rigid blocks that move over the mantle, either slowly or continuously. This movement can cause these plates to move closer or further away from each other.This movement happens due to the high temperatures inside the planet. The heat triggers a circular drive of cloak (convective movement), causing the heat in the earth core be transferred to the other layers of the Earth. Thus, it causes the movement of the plates located under the mantle.

When the tectonic plates collide, occurring the so-called convergent movement, the denser plate sinks returning to the mantle and melting, while the other plate, when under pressure in the opposite direction, then originates folds in the earth's crust. These folds give rise to small volcanic islands in the so-called subduction zone. Thus, it is possible to say that The occurrence of volcanoes is associated with boundary regions between the tectonic plates.
The Pacific Plate that moves to the north collides with the North American Plate, and in this region are located, according to the Mineral Resources Research Company (CPRM), approximately, 60% of active volcanoes on the planet (Ring of Fire of the Pacific). The Nazca Plate, on the other hand, collides with the South American plate, and in this region volcanoes and mountain ranges were formed. The African Plate collides with the Eurasian Plate.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
It is worth saying that it is not just the approaching movement that causes the formation of volcanoes. O separation of tectonic plates causes the formation of underwater volcanism as the ocean floor expands, according to the CPRM.
Another important point to be addressed is that there is no occurrence of volcanoes only on the boundaries between the plates. They can be found in hot spots, in the regions inside the plate. These points are called and known, in English, as hot spot, having the possibility of magma rise. An example of this is the volcanoes located in Hawaii.
parts of the volcano
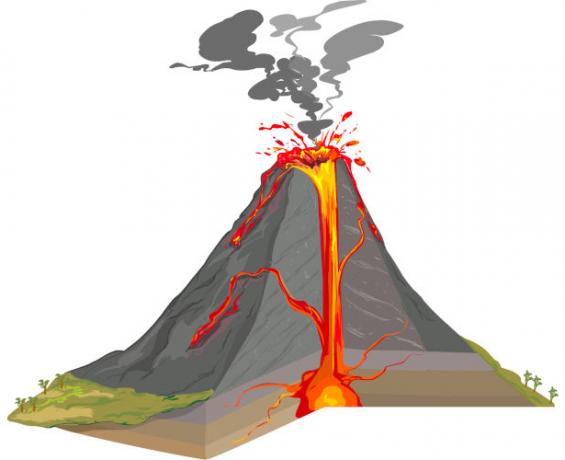
The volcanoes, formed mainly by silicates that mix with water vapor and gas, have a structure that connects to a deep underground chamber. Basically, volcanoes are made up of:
- magma chamber
- Chimney
- volcanic cone
- Crater
Read too: Yellowstone Super Volcano
Types of volcanoes
Volcanoes differ in their form and also about the eruption type (which can be explosive, effusive, mixed or catastrophic) and what about the expelled material (such as Hawaiian, Strombolian, Vulcanian, Plinian eruptions, among others).

The main types are:
- volcano-shield: is capable of expelling huge amounts of magmatic material that travel long distances, forming a large mountain sending a shield.
- slag cone: it is the most common, has smaller dimensions, and the expelled magma is of low viscosity.
- Stratovolcanoes: has the shape of a cone and is therefore steep. It remains active for a long time, its expelled lava is highly viscous and sometimes violently ascends to the outside of the volcano.
- Boiler: had a large diameter, between 15 km2 and 100 km2, which can be formed in hours or days. It is characterized by the violent outflow of gases from the planet's interior.
- underwater volcano: lies on the ocean floor and is responsible for the formation of a new floor.
Classification regarding your activity:
→ Active: shows activity, that is, shows signs of instability.
→ Dormant: it is not active, however, it may be that, at a given moment, it shows signs of instability again.
→ Extinct: possibly will not show signs of activity.
How an Eruption Occurs
At Earth's internal forces trigger volcanic eruption. The movement of the plates is stimulated by the agitation of magmatic material, caused by the high temperatures inside the Earth. The movement causes the magmatic material to rise, reaching the surface. This material is sometimes called lava, being composed of metals like iron and magnesium.
Read too: Tectonic plates: main plates, types, mind map
Volcanoes and earthquakes
Did you know there is a relationship between earthquakes and the distribution of volcanoes? And do you know what earthquakes are? Let's understand. Earthquake is, in general, a earthquake, that is, tremors caused on the earth's surface of high or low intensity. These shakes can occur due to the movement of tectonic plates and also by volcanic activity that releases accumulated forces.
The regions where the tectonic plates converge cause pressure buildup and energy discharge, thus triggering the volcano. The intensity of the volcanic eruption can then trigger surface tremors, hence the earthquake.
Read too:worst earthquakes in history
Volcanoes in Brazil
To the relief of many, no! There are no active volcanoes in Brazilian territory. However, volcanism already existed in Brazil at the end of the Mesozoic era, according to the CPRM, specifically in the South and Southeast regions of the country. In these are found basalt rocks.
The country currently has its continental area on the South American tectonic plate, therefore, it is not among a meeting of plates, so there is no formation of volcanoes.
Curiosities
- According to CPRM, there are about 20 active volcanoes worldwide.
- On Mars there is a volcano, Mount Olympus, about 26 km high, in addition to three other volcanoes.
- According to the CPRM, in the last 250 years, there were about 90 tsunamis caused by volcanic eruptions.
- There is about a volcano, every 100 km, in the Andes Mountains.
- The science that studies volcanoes is Geology, specifically Volcanology.
- The most dangerous volcanoes in the world are: Vesuvius (Italy); Eyjafjallajökull (Iceland); Sakurajima (Japan); Kilauea (Hawaii); and Merapi (Indonesia).
