the definition of matter is given by a simple and comprehensive phrase: it is everything that occupies a place (the same as volume) in space and has weight (a product of mass and gravity). Some examples of matter: tree, bacteria, virus, human being, air, water, table, vehicle, etc.
We could cite thousands of examples, as the matter it's pretty comprehensive. But is there anything that is not matter? Of course, yes, however, in this case, it is called energy, as in the following examples:
Light: called light energy;
Pressure: called pressure energy;
Sound: called sound energy;
Fire: association of thermal and light energy;
Electricity: called electrical energy;
Heat: termed thermal energy;
X-ray: a form of electromagnetic energy;
THE energy can be defined as a strength capable of producing action and movement. Thus, it is very simple to differentiate matter from energy, since one occupies space and has mass, and the other does not.
An important curiosity about the matter is that it can be called in two different ways: body and object.
Body: it is a part of the matter. Examples: wool yarn, broken glass, wind, tree trunk;
Object: it is a part of the matter which has a specific use. Examples: shirt, compressed air, pen, chair.
Mind Map: Matter
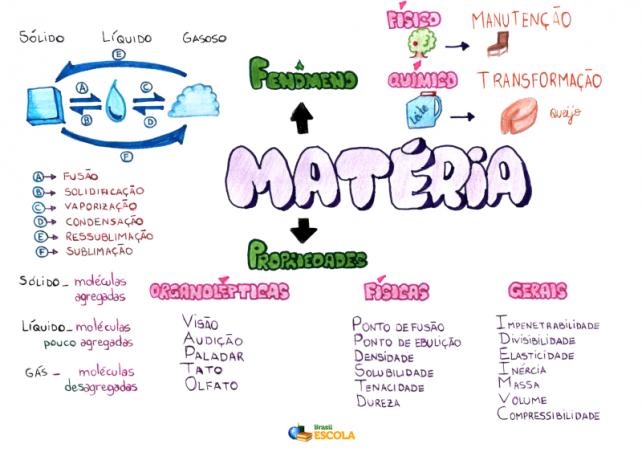
*To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
Composition of matter
Generally speaking, all matter is formed by a basic structural unit, called atom, which has the following composition:
Core: composed of protons and neutrons;
protons: positively charged particles;
neutrons: uncharged particles;
Energy Levels: regions where the sublevels are located;
Energy sublevels: regions where the orbitals are;
Orbitals: regions where electrons are most likely to find;
-
electrons: negatively charged particles.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
When two or more atoms combine, they form molecules, which can form substances as well as single atoms.
physical states of matter
You physical states most common in which we can find the matter are:
Solid: state in which the particles (atoms or molecules), which form matter, present the highest level of organization;
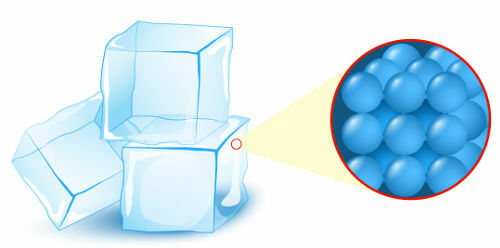
Representation of the organization of particles in the solid state
Liquid: state in which the particles (atoms or molecules), which form matter, present a lower level of organization;
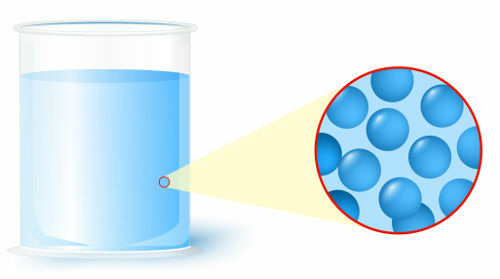
Representation of the organization of particles in the liquid state
Gaseous: a state in which the particles (atoms or molecules), which form matter, have no organization.
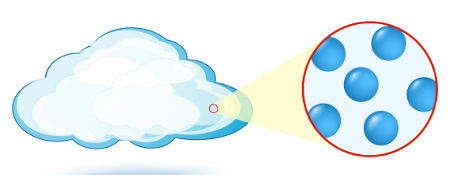
Representation of the organization of particles in the gaseous state
General properties of matter
any and all matter, regardless of the chemical elements that form it, must have the properties specified below:
Elasticity: property that matter presents in the solid state when it is subjected to an extreme elastic force, without its structures being broken. When this force ceases, matter returns to its original form;
Compressibility: when a portion of matter in the gaseous state is subjected to compression, it occupies a smaller volume;

Material being compressed into a cylinder
Inertia: when matter is in motion, it tends to remain in motion. If it is at rest, the tendency is for it to remain at rest;
Divisibility: matter can be broken down into smaller portions;
Impenetrability: two subjects cannot occupy the same space at the same time.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "What is matter?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-materia.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.


