At proteins are macromolecules formed by the condensation polymerization of α-amino acids, which, in turn, are substances formed by a peptide bond between an amino group and a carboxylic group, forming an amide group.
the proteins are not like the carbohydrates that can be stored in cells, they are part of the biological structure. So the construction and maintenance of the human organism depends on the supply of these proteins.
1- Functions of proteins
They have countless functions in our body, among them, we have:
a) Structural
the proteins they are the basic constituents of muscle fibers, hair, bones, teeth and skin;
Example: Phenylalanine is a precursor of tyrosine, which produces melanin, the molecule responsible for hair and skin color.
b) Catalysts
Enzymes catalyze biochemical reactions (important intra- or extracellular reactions that occur in animals and plants). Without the enzymes, these reactions would not take place in a timely manner and life would end;
Example: Carbonic anhydrase is an enzyme that catalyzes the carbonic acid formation reaction that maintains the
pH of constant blood. Through this enzyme, this reaction occurs about 10 million times faster.c) Regulators of the metabolism (Hormones)
Example: Insulin is a protein synthesized in our body and its main function is to control blood glucose levels. Its deficiency is one of the factors that result in the development of type 1 and 2 diabetes.
d) Immune system (Antibodies)
Example: A class of proteins found in blood plasma are gamma globulins and among them are immunoglobulins that help prevent and fight major infections and diseases. In specific cases, some doctors prescribe injections of gamma globulin extracted from the plasma of people who have already acquired immunity to the disease the patient is exposed to.
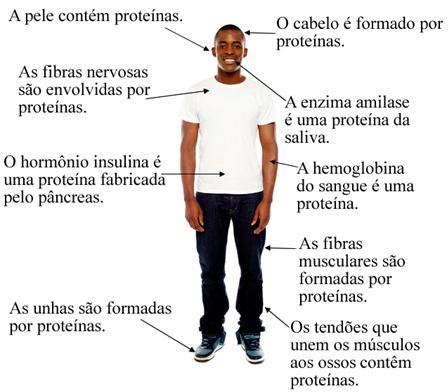
Examples of protein functions throughout the body
2- Protein digestion
When we eat foods that contain proteins, they are broken down during digestion and the organism absorbs the monomers that constitute them, which, as already said, are the amino acids.
There are numerous amino acids in nature, but only 20 are present in proteins. Our body synthesizes some of them, but 9 of these amino acids we don't produce, so they are called essential amino acids, which are: phenylalanine, histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, threonine, tryptophan and valine.
3- Protein sources
Since the body cannot synthesize these essential amino acids, we need to ingest them through our diet. The main sources of amino acids are:
Incomplete fonts (which do not contain all the essential amino acids): Legumes such as beans, corn, lentils, rice, fruits and vegetables;

Examples of legumes that can be used as a source of protein
Full sources: meat, fish, eggs, dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt), whole wheat, nuts, soy, wheat germ, Brazil nuts and peanuts.

Examples of foods that can be used as a source of protein
Since each food provides a type of amino acid, we need to have a very balanced diet. For example, when we eat beans and rice, beans provide lysine and rice provide methionine, which are important amino acids in protein synthesis.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/funcao-das-proteinas-suas-fontes-na-alimentacao.htm

