O Minas Gerais state it is located in the Southeast region, the richest and most populous in the country. In this way, mines is among the richest states in Brazil, with important cities throughout the national territory, such as:
the capital, Belo Horizonte
Uberaba
Uberlandia
Black gold
Read too: What are megacities?
General data for Minas Gerais
All of the following data were taken from the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE) and according to the last census (2010) and most updated surveys, with their respective years in parentheses.
Region: Southeast
capital: Belo Horizonte
![Aerial view of the capital of Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte. [1]](/f/82bb092c0909ffee864d98adf8d7db82.jpg)
Government: democratically elected, through direct elections, occupying the position for four years, and may be re-elected for an equal period.
Territorial area:586,521,123 km² (IBGE, 2019)
Population: 21,292,666 inhabitants (IBGE, 2020)
Monthly household income per capita: BRL 1,358 (IBGE, 2019)
Demographic density: 33.41 inhab/km² (IBGE, 2010)
spindle: Brasília time zone, 45º GMT West (-3 h)
Human development Index: 0.731 (IBGE, 2010)
Total vehicles: 11,191,341 (IBGE, 2018)
Gentile: miner
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Geography of Minas Gerais
In Minas Gerais we can find three brazilian biomesAttractions: Caatinga, Cerrado and Atlantic Forest, in addition to some areas with the occurrence of rupestrian fields, very common in high altitude areas.
THE Caatinga marks its presence in the north of the state, on the border with the Bahia, especially in the Jequitinhonha Valley. this region suffers from the aridity of the sertão, having the poorest cities in the state and a lot of similarity with the northeastern landscapes, both in terms of climate and relief.
THE Atlantic forestis the second largest biome in the state, being found in the eastern part, on the borders with Holy Spirit and Rio de Janeiro. Bromeliads, vines, ferns and orchids are common in this biome.
already the thick, largest biome present in the state, appears in 50% of the territory of Minas Gerais, being the cradle of important hydrographic basins that originate in Minas Gerais, such as the São Francisco and the Jequitinhonha river basins.
In relation to climate, presents variations of ttropical, with average annual temperatures around 18 ºC. In higher altitude areas, there are lower annual temperatures. In general, the state has two well-defined seasons: a hot and rainy one, between October and March, and a drier and milder one, between April and September.
In hydrography, the state is known as the water tank of Brazil, due to the large water storage in the territory and the biomes. The prominent rivers are:
big River
sweet River
São Francisco river
Jequitinhonha river
Paranaíba river
Paraíba do Sul river
brown river
already the relief miner understands areas with altitudes that can reach almost 2900 m, such as the Serra do Caparaó, the highest in the state, with a peak of 2890 m in altitude. Much of Minas Gerais is located on the Atlantic plateau, a region known for the seas of hills in Southeastern Brazil. plateaus and plateaus are very common in the state.
In the southwest of Minas, we find the most famous geological formation, the Serra da Canastra, home to the sources of the São Francisco River and the Serra da Canastra National Park, an important tourist and environmental preservation point in the country.
See too: Tietê River – one of the best known rivers in Brazil
Location of Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais is located in the Southeast region of Brazil. Its boundaries are:
Sao Paulo, South
Espírito Santo and Rio de Janeiro to the east
Bahia, to the north
Goiás, to the west
Mato Grosso do Sul, southwest
Look at the map:
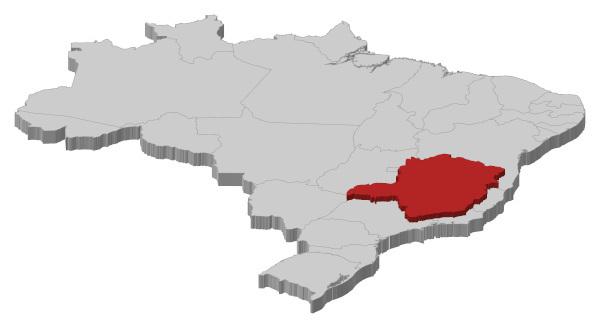
Geographical division of Minas Gerais
According to the government of Minas Gerais, the state is divided into 853 municipalities (the Brazilian state with the largest amount), which are subdivided into 10 Planning Regions, as shown in the map below.
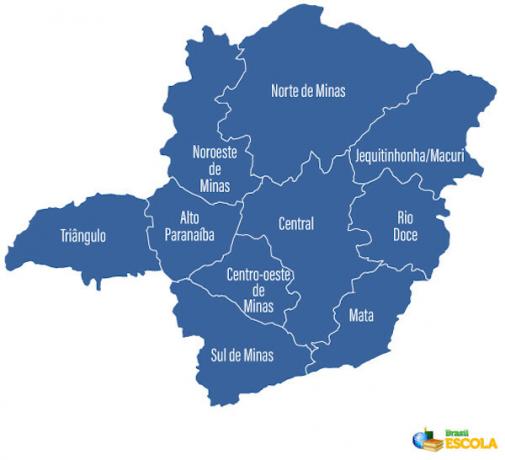
Also according to the government of Minas Gerais, the number of municipalities in each region is distributed as follows:
Alto Paranaíba (31)
Central (158)
Midwest of Minas (56)
Jequitinhonha/Mucuri (66)
Kill (142)
Northwest of Minas (19)
North of Minas (89)
Rio Doce (102)
South of Minas (155)
Triangle (35)
Minas Gerais Demographics
The population of Minas Gerais is the second largest in Brazil, behind the state of São Paulo, the most populous. This entire population has a strong tradition, which is passed from generation to generation, like the figure of the healers and healers, who use natural remedies as a source of healing and alternative medicine for those who search.
The fact that it is geographically in the middle of the Southeast region made Minas Gerais attract a population eager for conquest and glory in the discovery of precious stones, in the 17th century. This greed still lives on in Minas Gerais, who are always in solidarity with their greengrocer dishes, with cakes, bread and the famous cheese bread.
In cooking, the mineiro mixes ingredients from the three peoples that formed the population of Minas and, also, from a large part of Brazil. Dishes with indigenous, African and European ingredients permeate the cuisine of this state, such as tropeiro beans, crackling, green corn angu, dried meat paçoca, among others.
In baroque art, country fashions and/or indigenous and African traditions, the Minas Gerais population shapes its character over time, with the characteristic of being a caring and charismatic people.
Also access: What is the difference between relative population and absolute population?
Minas Gerais Economy
In the economic field, Minas Gerais has several highlights, such as mineral extractive industry, tourism and agribusiness, being the first the most important in the state. It is estimated that more than 50% of Brazilian iron ore production is located in Minas, in addition to 29% of the other ores being extracted from the soil of Minas Gerais.
There is strong industrial presence, especially the automobile industry. In agribusiness, the highlight is the creation/production of beef, corn, milk and coffee.
Due to the rugged terrain, the state has several waterfalls and parks, being the tourism an important sector for its economy. Among the cities visited, Ouro Preto, São João del Rei and Poços de Caldas stand out.
![Canyon in the city of Capitólio is a tourist attraction in the state of Minas Gerais.[2]](/f/eef213617fa3d9ffa48913aa7bc5cbb0.jpg)
Minas Gerais Infrastructure
Minas Gerais has the largest road network in the country, with 16% of the existing municipal, state and federal highways in Brazil. According to the state government, they are 272,062.90 km of highways. Of this total, the majority (240,571.90 km) consists of municipal roads, and a large part is unpaved.
As for state highways, 22,286 km are paved and 4,925.75 km are still dirt roads. As for the federal (9,205 km), only 576.60 km are unpaved.
by state cross the main federal highways in the Center-South of Brazil, being important means of communication between the states of this region, in addition to serving as an outpost for going to northeastern and northern states.
Highways such as BR 381, known as Fernão Dias, and BR 040 reveal the state's geostrategic position in the connection between interior areas and Brazilian coastal areas.
Minas Gerais Culture
The Minas Gerais culture knew how to take advantage of its historical roots, incorporating indigenous, African and European traditions and various segments of art, from culture, gastronomy and other similar items.
At literature, two Brazilian icons are from Minas Gerais:
Carlos Drummond de Andrade
Guimaraes Rosa
In baroque art, cripple He still enchants us today with his works made more than two centuries ago.
for lovers of Brazilian colonial history, historic cities abound: Ouro Preto, Congonhas, Diamantina, São João del Rei, Mariana, Tiradentes, being the first three Patrimony World Cup.
![Ouro Preto, a World Heritage Site. [1]](/f/aeda51a3254072bc7a98e3907359ee2d.jpg)
In Brumadinho, a city in the metropolitan region of the capital Belo Horizonte, is the Inhotim Museum, considered the largest open-air museum in the world.
Brief history of Minas Gerais
The region in what is now the state of Minas Gerais began to be occupied in the 17th century, through the work of the Girl Guides. In the next century, in 1720, the captaincy of Minas Gerais emerged, as the discovery of precious stones attracted the eyes of the Portuguese Crown to the locality.
Also in the 18th century, Minas Gerais observed rapid settlement and the emergence of urban agglomerations due to the exploitation of mineral resources, becoming a great economic center of colonial period.
The high tax collection by the Portuguese government in relation to the resources extracted from Minas Gerais generated a great popular revolt at the end of the 18th century, giving rise to the movement that became known like Mining Inconfidence. In this movement, its creators preached the rupture of relations between colony and metropolis. Even today, the state flag celebrates this feat, with the phrase Freed that will be the same, which means “Freedom, however late”.

In the nineteenth century, the introduction of coffee plantation made investments in infrastructure, such as railroads, and fostered the industrial development of the state. However, it was with food production, highlighting the dairy production, that Minas Gerais gained strength on the national scene in the early 20th century, with Minas Gerais politicians being protagonists of the so-called “latte policy”, alluding to São Paulo coffee and Minas Gerais milk.
Image credits
[1] Luis War/ Shutterstock
[2] Marco AM Oliveira/ Shutterstock
By Attila Matthias
Geography teacher
Minas Gerais is a Brazilian state. As such, it is part of one of the five regional complexes in the country. Therefore, mark the alternative that correctly indicates the Region that houses the state of Minas Gerais.

