Various substances enter and leave the cell through the processes of diffusion and active transport. Some particles, however, are very large and need other processes for the transport from extra environment to intracellular and vice versa.
Cellular ingestion of particles is a process known as endocytosis. This process is intended to ensure nutrition, defense and maintenance of cell activities. The endocytosis process is divided into two types: phagocytosis and pinocytosis. THE phagocytosis relates to the enclosing of solid and large particles, while the pinocytosis relates to liquid and small particles.
THE phagocytosis it is performed only by cells that are capable of moving, such as amoebas, macrophages and neutrophils. This process consists of the cytoplasmic prolongation with the formation of pseudopods that enclose the particle to be ingested. After capture, a vesicle delimited by the plasma membrane of the cell and with the free particle inside. This scholarship is named after Phagosome.
Once formed, the phagosome merges with lysosomes, and digestive enzymes are released inside. At that moment a digestive vacuole is formed and the digestion of the particle begins. What has not been digested is called residual bodies and is later excreted by the cell. The accumulation of waste in the cell can trigger the cell to age.
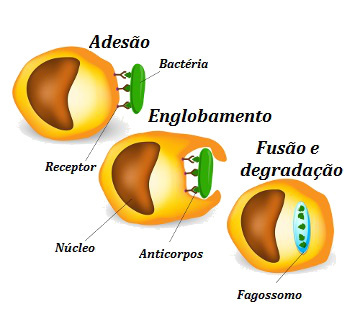
Carefully analyze the stages of phagocytosis.
Briefly, we can divide phagocytosis into four steps:
→ Accession = Particles that will be ingested are labeled by antibodies.
→ agglomeration = Pseudopods form.
→ Fusion with enzyme-rich vesicles = Fusion with lysosomes.
→ Degradation = Carrying out the intracellular digestion process.
By Ma. Vanessa dos Santos

