Have you ever put a pencil or pen into a glass of water? If so, did you notice that the object appears to be broken up when looking out of the water? The set consists of two transparent means (in our case we are considering the air and Water) and the interface between them are called diopter. The shape of the separation surface between the media, dioptric surface, characterizes the type of diopter: plane, spherical, cylindrical, etc.
Based on the air-water means of a lake at rest, for example, we will study the formation of images consisting of a flat diopter. Initially, the object of our study is submerged in water (more refracting means) and the observer is outside it, in the air (less refracting means).
We know that from the submerged fish rays of light come out in all directions; we also know that these rays are refracted at the surface of the water and reach the observer's eyes. Among the infinite rays of light that come from the fish, let's consider the two rays highlighted in the figure below. The corresponding refracted rays define a virtual image of the object.
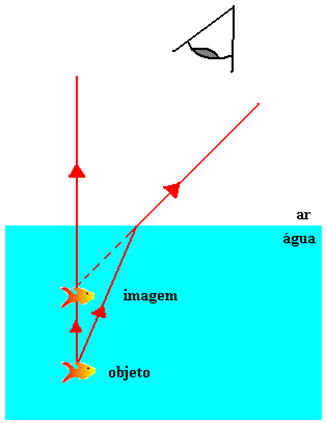
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
The fish image is defined as virtual because it is formed by the intersection of the refracted rays extensions. See that the image is formed in the same medium as the object is. We can also see that both the image and the object are on the same perpendicular straight line N with respect to the dioptric surface, so the image is formed closer to the surface of the water.
Gaussian Equation for Flat Dioptro
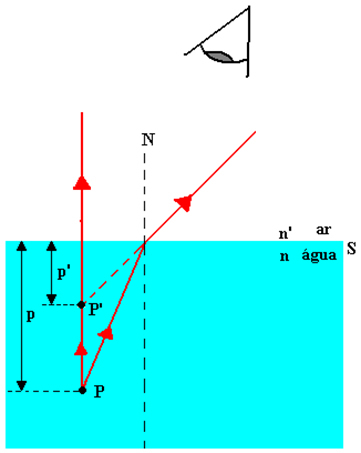
The figure above shows the apparent depth of a fish (point P’). Through the Gauss equation we are able to determine the apparent depth of the fish. The equation that gives this possibility is the following:
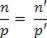
In the figure above we have:
- p is the distance from point P to surface S
- p’ is the distance from point P’ to the surface S
- n is the absolute refractive index of the light incident medium
- n’ is the absolute refractive index of the light's emergence medium, where the observer is.
By Domitiano Marques
Graduated in Physics
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SILVA, Domitiano Correa Marques da. "Dioptro Flat"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/dioptro-plano.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.



