Acids are substances that ionize in aqueous medium and are good conductors power. The acidity of a substance can be measured through techniques for measuring the hydrogen ionic potential (pH) of a solution. Some pH analytical methods use indicators such as litmus or phenolphthalein, which reflect the pH value of the solution in color.
Acids can be characterized:
by the presence or not of oxygen in its molecule;
by force;
by ionizable hydrogens;
by its volatility.
Read too:Comparison between acids and bases - differences and properties
Characteristics of acids
They ionize in an aqueous medium, releasing the H cation+.
They are conductors of electricity due to the release of ions in an aqueous medium.
In contact with basic environment, they suffer neutralization reaction, forming salt and water as products of this reaction.
They change the color of the solution in the presence of an indicator substance such as litmus or phenolphthalein.
The sour flavor of lemon, orange, among other citrus fruits, is due to the acid present in these foods.
Hydrogen potential (pH)
The hydrogen ion potential (pH) is a calculation that expresses the ion concentration of hydrogen in a certain solution. To determine the pH and analyze the medium, the following are taken into account:
Ostwald's law of dilution (the more diluted, the more ions will form in the solution);
water autoionization (Kw), which is the natural breakdown of the H molecule2O in H ions+ and oh-;
distilled water at 25°C has autoionization Kw = 10-14 and same concentration of H ions+ and oh-, that is, it is a neutral medium.
For pH calculation involving H concentration+, use: pH = -log[H+].
Know that:
pH > 7 → basic solution
pH < 7 → acidic solution
pH = 7 or pH = pOH → neutral solution
See too: What are acid formulas like?

Classification of acids
THE acid classification can be done taking into account four different criteria.
Degree of ionization (α) or acid strength
α = number of ionized molecules
number of dissolved molecules
Strong acids: α ≥ 50%.
Example: áacid sulfuric (H2ONLY4) → α = 61%.Semi-strong or moderate acids: 5% < α < 50%.
Example: phosphoric acid (H3DUST4) → α = 27%.Weak acids: α ≤ 5%.
Example: boric acid (H3BO3) → α = 0,075%.
→ Number of ionizable hydrogen
monoacid: releases an H cation+.
Example: áacid hydrochloric (HCL);
diacid: releases two H cations+.
Example: hydrogen sulphide (H2S).Triacid: releases three H cations+.
Example: boric acid (H3BO3).tetracid: releases four H cations+.
Example: pyrophosphoric acid (H4P2O7).
Attention! In the case of hydracids, all the hydrogens in the molecule are ionizable; but in the case of oxyacids, only hydrogens that are bonded to an oxygen atom are ionizable. An example is hypophosphorous acid (H3DUST2), which is a monoacid because, despite having three hydrogens in its composition, it only releases the hydrogen that is bound to the oxygen.
→ Presence of oxygen
oxyacids: have oxygen in their structure.
Example: hypochlorous acid (HO Cl).
Hidracids: do not have oxygen in their structure.
Example: hydrofluoric acid (HF).
→ Volatility
Fixed: boiling point(FOOT) > 100°C, slowly changing to a gaseous state.
Example: sulfuric acid (H2ONLY4) → PE = 340 °C.volatiles: boiling point < 100°C, changing quickly and easily to a gaseous state.
Example: hydrogen sulphide (H2S) → PE = -59.6°C.
Acid nomenclature
→ Hidracids
Acid + anion name + hydric
For all acids, the term “acid” is used before the nomenclature that characterizes the molecule. In hydracids, the suffix “eto” of the element's name is replaced by “hydric”.
Examples:
HCl → acid chlorinehydric
HBr → acid bromhydric
HF → acid fluorinehydric
→ oxyacids
The nomenclature of oxyacids varies according to the oxidation number (NOX) of the central element. See the table below:
NOX of central element |
Acid nomenclature |
||
prefix- |
-infix- |
-suffix |
|
+1 and +2 |
Hippo- |
-anion name- |
-oso |
+3 and +4 |
-- |
Anion name- |
-oso |
+5 and +6 |
-- |
Anion name- |
-ic |
+7 |
Per |
-anion name- |
-ic |
Examples:
HClO → Knowing that hydrogen (H) normally has NOX +1 and oxygen (O) has NOX -2, for us to have a 0 charge molecule, chlorine (Cl) must have NOX +1, so the nomenclature of this acid is hypochlorous acid.
HNO2 → nitrous acid
HClO4 →áacidperchloric
→ Exceptions to the rule
H2CO3 → carbonic acid, and not carbonaceous, as it would be under the NOX rule.
H3BO3 → áacid boric, and not borous.
Acids in everyday life
Fertilizers and Medicines: Phosphoric acid (H3DUST4) is widely used in the manufacture of fertilizers and also as a medicine. It is one of several acids that are used in the pharmaceutical field.
Citrus Fruits: have ascorbic acid (C6H8O6), also known as Vitamin C.
Vinegar: has in its composition Acetic Acid (CH3COOH).
- Sparkling water and soft drinks: composed of carbonic acid (H2CO3), which gives the product a refreshing sensation.
Also access:Role of acids in soft drinks

solved exercises
Question 1 - (Enem) The juice extracted from red cabbage can be used as an indicator of the acid character (pH between 0 and 7) or basic (pH between 7 and 14) of different solutions. By mixing a little cabbage juice and the solution, the mixture starts to show different colors, according to its acidic or basic nature, according to the scale below.
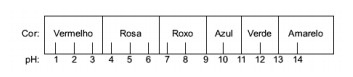
Some solutions were tested with this indicator, producing the following results:
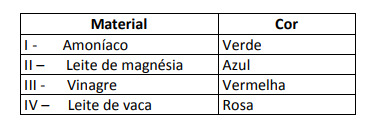
According to these results, solutions I, II, III and IV have, respectively, the following character:
A) acidic / basic / basic / acidic.
B) acid / basic / acid / basic.
C) basic / acidic / basic / acidic.
D) acid / acid / basic / basic.
E) Basic / Basic / Acid / Acid.
Resolution
Alternative E. To determine whether the substance has an acidic, basic or even neutral character, an analysis of the colors obtained in the test in relation to the data of the given scale is carried out. Knowing that solutions with pH = 7 are neutral, pH > 7 are basic and with pH < 7 are acidic, we arrive at conclusion that ammonia and milk of magnesia are basic substances, and vinegar and cow's milk are acids.
Question 2 - (PUC-Camp) Regarding the substances called acids, a student noted the following characteristics:
I - have corrosive power;
II - are capable of neutralizing bases;
III - are composed of two chemical elements;
IV - form aqueous solutions that conduct electrical current.
He made mistakes ONLY in
A) I and II
B) I and III
C) I and IV
D) II and III
E) III and IV
Resolution
Alternative B. Not all acids are corrosive, only the strongest ones, and acids can be composed of two or more atoms.
by Laysa Bernardes
Chemistry teacher
