THE Taigait is a biome that takes place in the Northern Hemisphere, in areas located above the temperate forest and below the tundra. It also receives the name of boreal forest or coniferous forest, which is due to its vegetation cover consisting of trees such as cypresses, pine trees and fir trees.
Both plant and animal species are adapted to the cold climate of the dry Continental type, marked by harsh winters and mild summers. Taiga is threatened by the increasing advance of animal and plant extractivism, as well as by the increase in temperatures in the Earth.
Read too: What are the main biomes in the world?
Taiga's main features
Taiga Location
Taiga is a characteristic biome of the cold lands of the Northern Hemisphere. between zones Tpie and Phello Áethics. This region is known as the subarctic, and lies between the 50º N and 60º N parallels.
Thus, the boreal forest, as it may be called, is bounded to the north by the Tundra and, to the south, through the temperate forest, marking the transition between permanently cold areas and regions with milder temperatures on the planet.
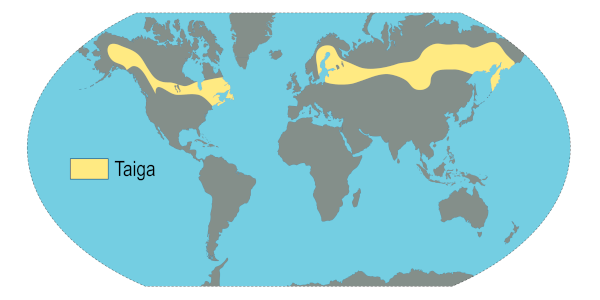
The Russian territory is home to the largest extension of this biome in the world, which is also distributed over large tracts of land in the northern portion gives Europe, as by:
Iceland
Finland
Norway
part of UK
At North America, the boreal forest covers a portion of Canada and of the U.S, which includes the northern and northeastern borders with Canadian territory and Alaska. In Asia, in addition to Russia, Taiga is a typical biome of the Japanese island of Hokkaido.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Taiga climate
The occurrence of Taiga occurs in areas with dry Subarctic and Continental climates. Its main aspect consists of the low temperatures throughout the year, notably in the Winter, when thermometers mark values below zero.
The minimums are usually registered in the month of January, and are around -10 ºC and -30 ºC, while the annual maximums are of 20 ºC. Some exceptions happen, as is the case of Siberia. This region of Russia east is home to the coldest cities on the planet, and parcels of land covered by coniferous vegetation can experience lows of up to -50 ºC in the coldest months of the year.
The main form of precipitation is snow, which can fall from three to six months and keep part of the Taiga, especially in the northern areas, covered for most of the year. Rains are not uncommon, although not very voluminous. Its incidence is associated with convection currents that form in the short hot season.

Taiga solo
You soils of Taiga are, for the most part, shallow and nutrient-poor, a factor that is due to the long periods they spend covered by snow, which delays the decomposition process of organic material. Because of this, they are also characterized by the high acidity indexes. During the hottest period, the melting of the surface ice layer gives rise to swampy land as well as lakes and swamps. Another aspect of the soils of this biome is its light color, often grayish.
In some regions, the presence of permafrost, which are soils that have a permanently frozen layer. However, this type of soil is typical of the Tundra domain.
Read too: What are the forms of soil degradation?
Taiga Vegetation
Taiga's vegetation cover is very homogeneous and composed predominantly of trees belonging to coniferous species.. For this reason, it is common that we find this biome being referred to as coniferous forest. Shrubs are also part of Taiga's natural framework, which has a greater diversity of species as it approaches the temperate forest to the south.
Due to the snow and low incidence of sunlight through the dense canopy of the boreal forest, especially in winter, the presence of undergrowth is less frequent, like mosses and lichens, although existing.
Taiga's plants are adapted to weather conditions area of occurrence, that is, long exposure to cold and snow. The leaves of the trees, in the shape of needles (acicular), have a thin coating of wax that serves as protection mechanism against low temperatures, in addition to containing little sap, thus preventing their freezing. The conical shape of the trees means that there is no accumulation of snow, and, in addition, there is no loss of leaves during the year. They are, therefore, evergreen trees.
Flora of Taiga
As we have seen, the characteristic vegetation of Taiga is the coniferous forest. Thus, its flora is formed by trees such as:
pines (Scottish, Siberian, wild, bush)
firs (black, balsamic, Siberian)
cedars
larch pine
spruces
birch trees
Among the shrubs, fruit species are found, such as wild strawberry, blueberry, boldo, cranberry or cranberry (cranberry), is wide variety of berries, more popularly known as wild berries. Added to this list, still, the boldo, the ferns, the mushrooms. Where the formation of peat bogs due to the accumulation of water, species such as tea, blackberries and cotton can be observed.
several species of grass cover certain areas of this plant domain, as well as mosses and lichen, like reindeer moss, and small plants, like fireweed. Of rare occurrence, are the shrub willows, oaks, maples, elms, poplars and brambles.

Taiga fauna
The fauna of Taiga is composed of mammals like:
bears
bobcats
moose (the largest animals that live in the biome)
tigers (like the Siberian tiger)
deer
deer
reindeer
wolves
martens
minks
muskrats
northern flying squirrels
hares
The latter belong to the group of rodents, present in areas where there is an abundance of small and medium-sized vegetation.
At Birds of prey are also common in this domain, such as owls and eagles, falcons and migratory birds moving to high latitudes during their reproductive period. A great diversity of insects that live both in the forests and in the wetter areas also make up the fauna of the boreal forest.

Degradation and conservation of Taiga
Taiga represents, approximately, a third of the planet's forest cover. Despite the very low demographic density in the areas covered by this biome, it faces serious problems arising, direct and indirectmind, of human activities, whether by plant extraction and hunting, or by the effects of the intensification of the global warming. The increase in the temperature of this environment can partially or completely change the distribution of animal and plant life, as well as the already reduced number of species.
The coniferous forest has become a source of raw material for the wood industry, which aims at pine, cedar and spruce for a diverse use that goes beyond civil construction and furniture production. Cutting is predatory in itself, but the most common tactic used is called clear cut, which consists of removal of all trees from a given area, with consequences for the soil (increased risk in erosion, for example) and for animal life, as there is habitat destruction of a wide variety of species.
The degradation process of Taiga also happens by the underground exploration, as the presence of features such as Petroleum, coal, natural gas and other ores of great economic value. The conservation of these environments is necessary to maintain the ecosystem balance not only locally but also globally.
See too: Burning in the Pantanal - a process whose consequence is the destruction of this important biome
What are the differences between Taiga and Tundra?
Taiga and Tundra are both characteristic biomes of cold climates and share a few elements, but are quite distinct when analyzed a little more carefully. The main difference is found in the landscape. THE Taiga can be called coniferous or boreal forest by the large presence of trees, vegetation that does not occur in the Tundra.
As it is located in a region with a Subarctic climate, temperatures in Taiga are milder, that is, less severe than in Tundra, especially in areas closer to the temperate forest. To learn more about this other biome, read the text: Tundra.
Taiga Summary
Taiga is a subarctic climate biome that is located in the Northern Hemisphere, between the temperate forest and the tundra.
Its climate is characterized by very cold winters, with temperatures below zero, and mild summers.
It has light colored, shallow and nutrient-poor soils. In cooler areas, it is possible to observe the presence of permafrost.
It is called boreal or coniferous forest because it has dense vegetation formed mainly by pine, cedar and fir trees.
The fauna of Taiga is formed by large mammals (wolves, bears, tigers), birds and insects.
The biome is at serious risk due to mineral and plant extraction, hunting and also the increase in global temperatures.
solved exercises
Question 1 - (Unicamp) The map below shows the global distribution of carbon flux. The regions indicated by numbers I, II and III are, respectively, regions of high, medium and low carbon absorption.

Considering these regions, it can be said that the respective types of predominant vegetation are:
A) I- Tropical Forest; II- Savannah; III- Tundra and Taiga.
B) I- Amazon Forest; II- Plantations; III- Temperate Forest.
C) I- Tropical Forest; II- Desert; III- Temperate Forest.
D) I- Temperate Forest; II- Savannah; III- Tundra and Taiga.
Resolution
Alternative A. The numbers correspond to the rainforest, sadvances and Tundra and Taiga, the latter represented by the number III in the northern areas of the map.
Question 2 - Taiga is a biome typical of the Earth's subarctic areas, marked by intense cold. It is currently threatened by the advance of exploratory activities and by global warming. Check the incorrect alternative about this domain:
A) Its main plant formation is the coniferous forest.
B) It has acidic soils that are not conducive to agricultural development.
C) Frozen soil layers prevent mineral extraction from the subsoil.
D) The melting of accumulated snow can form swamps and lakes in the lower and flat areas.
E) It differs from the Tundra mainly by the presence of trees.
Resolution
Alternative C. Differently from what has been stated, in many places in Taiga, the extraction of mineral resources from the subsoil takes place without any physical impediments.
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography teacher


