Refractive index is dimensionless physical magnitude which measures the reduction of speed of light when it is transmitted through some transparent optical medium. The ability to reduce the speed of light is called refringence.
They exist two types of refractive index: the absolute and the relative. O absolute refractive index, whose smallest possible value is 1, is calculated by the ratio between the speed of light in a vacuum and the speed of light in any other medium. O relative refractive index, in turn, is determined by the ratio between the speed of light in two mediums other than vacuum, which may be less than 1.
A refractive index equal to 1 indicates that, in the medium in which it propagates, light travels at the same speed as it would travel traveling through a vacuum. An index of refraction equal to 2, for example, indicates that, in a vacuum, light would propagate twice as fast as in a medium whose index of refraction is equal to 2.
See too: After all, what is light?
Absolute and relative refractive index
O index ofrefractionabsolute is calculated by the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum, whose symbol is ç and which has a value approximately equal to 3,0.108 m/s (299,792,458 m/s), and the speed of light in a quitetransparent and homogeneous any, symbolized by the letter v:
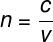
no - refractive index
ç – speed of light in vacuum (3.0.108 m/s)
v – speed of light in the middle
The formula above indicates that there is no way to refraction value less than 1, since the medium in which light is able to move with greater speed is the vacuum itself.
O relative refractive index is calculated by the ratio between the absolute refractive indices of two optical media, 1 and 2, when crossed by a light beam. Such index can be calculated according to what is shown in the following figure. Look:
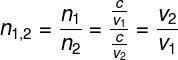
no1,2 – refractive index of medium 1 in relation to medium 2
v1 and you2– speed of light on media 1 and 2
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
refractive index and wavelength
O refractive index of an optical medium depends on the lengthinwave of the light that passes through it. This phenomenon is known as chromatic dispersion. It is for this reason that, when passing through a prism or a drop of water, the white light, which is formed by the combination of all visible colors (that's why it can be called polychromatic), it undergoes dispersion, thus allowing us to observe the separation of the colors of the visible spectrum.
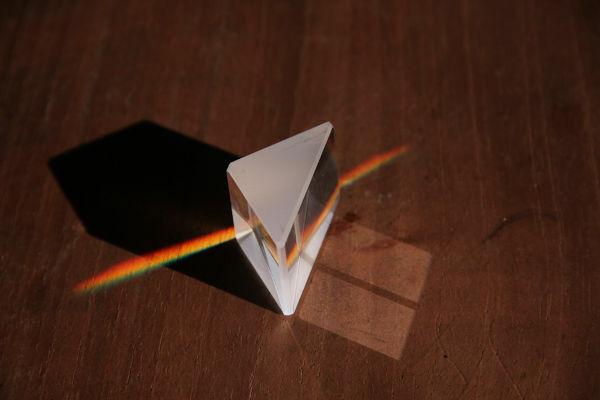
The refractive index is inversely proportional the wavelength of light, so the shorter the wavelength of light, the higher the refractive index of light for a given medium. Therefore, the refractive index of the same medium will be higher for violet light than for red light, for example.
refractive index and temperature
The refractive index has a relationship with the temperature in the middle, but this does not mean that it changes because of changes in temperature, but because of changes in density. This relationship between refractive index and temperature is what causes the formation of distortions and mirages above heated surfaces, such as asphalt or the hood of a vehicle on a very hot day, as the heating of the air causes its dilation. In this way, its density decreases, as well as its refractive index.
Read too:Main topics of the study of Optics
Refractive Index Table
The following table presents some refractive indices of known materials.

Solved exercises on the refractive index
Question 1 - (UFPR) A given medium has an index of refraction n1. Another medium has a refractive index n2. Check the alternative that correctly expresses the relationship between the modules of the speeds of light in the two media, when n2 = 2n1.
a) v2 = 4v1
b) v2 = 2v1
c) v2 = v1
d) v2 = v1/2
e) v2 = v1/4
Template: letter D.
Resolution:
Since the refractive index of the medium 2 is twice the refractive index of the medium, it must be understood that the speed of propagation of light in medium 2 is twice less than this same speed in medium 1.
Question 2 - (Eear) Considering the propagation speeds of light in two homogeneous and distinct media, respectively equal at 200,000 km/s and 120,000 km/s, determine the relative refractive index of the first medium to the second. Consider the speed of light in a vacuum equal to 300,000 km/s.
a) 0.6
b) 1.0
c) 1.6
d) 1.7
Template: letter a.
Resolution:
To solve the question, it is enough to divide the speeds at which light propagates in the two media. Since we want to know the relative index of refraction of the first medium in relation to the second, we must do the following calculation:
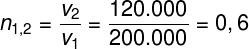
Question 3 - (Enem) The figure represents an optical prism made of a transparent material and whose refractive index increases with the frequency of light that falls on it. A light beam, composed of red, blue and green lights, falls on face A and emerges on face B and, after being reflected by a mirror, it hits a film for color photography, revealing three points.
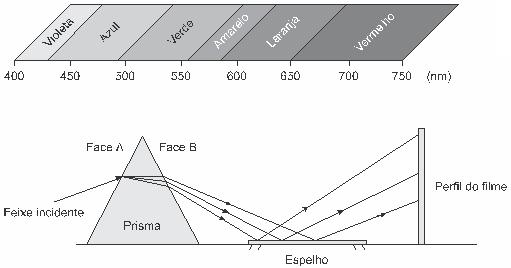
Observing the bright spots revealed in the film, from the bottom to the top, the following colors can be seen:
a) red, green, blue.
b) green, red, blue.
c) blue, green, red.
d) green, blue, red.
e) blue, red, green.
Template: letter a.Resolution:
It is known that the refractive index is directly related to the wavelength of light – the shorter the wavelength, the higher the refractive index of the medium. In this way, the ray of light that undergoes the greatest deviation is the blue one, which, after being reflected, becomes the first point of light, from the bottom to the top.
By Rafael Hellerbrock
Physics teacher