When we talk about pH, we refer to the hydrogenionic potential of a solution, that is, the amount of hydronium cations (H+ or H3O+) which are dispersed in the solvent of a solution.
Hydronium cations are well known because of the definition proposed by the scientist Arhenius for an acid. This scientist claims that acid is every substance capable of ionize and produce hydronium ions in an aqueous medium.
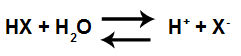
Acid Ionization Equation
the acronym pH serves as a reference for determining the acidity level of a medium. However, for a long time, chemists have also used the pH as a reference to determine, in addition to acidity, whether a medium is basic or neutral.
This is possible because chemists are now aware that water undergoes self-ionization, that is, it produces hydroniums (H+) and hydroxides (OH-). Thus, an aqueous solution never has only hydronium or hydroxide, but both, as we can see from the following equation:

Water autoionization equation
Values used as a reference for pH
The values used for the
pH refer to the ionization constant (Kw) of water at a temperature of 25OC, which is equal to 10-14. At this temperature, the concentrations of hydronium and hydroxide ions produced by water are absolutely equal, that is, 10-7 mol/L.[H+]=[OH-]= 10-7
From this reference, the values used for pH range from 0 to 14.
Formulas for calculating pH
a) Calculation from the concentration in mol/L of hydronium cations
The calculation of the pH value can be done directly, as long as we know the concentration of hydroniums ([H+]). Look:
pH = -log[H+]
or
10-pH = [H+]
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
b) Calculation from the concentration of hydroxide anions (OH-)
pOH = -log[OH-]
or
10-pOH = [OH-]
After calculating the pOH value, you need to use it in the following expression to determine the pH value.
pH + pOH = 14
Interpretation of pH values
Knowing the pH value, we can determine whether the solution in question has an acidic, basic or neutral character. For this, just use the following schematic relationship:
For pH values below 7 = acidic medium;
For pH with a value equal to 7 = neutral medium;
For pH values above 7 = basic medium.
Examples
1st Example: Knowing that the concentration of hydronium cations in a solution is 2.10-4 mol/L, what should be the pH value of this solution?
To determine the pH value of the solution from the concentration of hydroniums (H+), 2.10-4 mol/L, we must use the following expression:
pH = -log[H+]
pH = -log[2.10-4 ]
pH = –(log 2 + log 10-4)
pH = -log2 - log10-4
pH = –log 2 – 4.log 10
pH = –0.3 + 4.(1)
pH = -0.3 + 4
pH = 3.7
2nd Example: A solution formed by a certain solute has a hydroxide ion concentration equal to 10-11 mol/L. From this concentration, we can say that the pH of this solution is worth how much?
To determine the pH value of the solution from the hydroxide concentration, 10-11 mol/L, we must do the following:
1O Step: calculate the pOH value.
10-pOH = [OH-]
10-pOH = 10-11
We must multiply the expression by -1 because pOH is always a positive unknown.
-pOH = -11.(-1)
pOH = 11
2O Step: calculate the pH value.
pH + pOH = 14
pH + 11 = 14
pH = 14 - 11
pH = 3
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "What is pH?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-ph.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
Chemistry
Hydroxyapatite mineral, mouth pH, tooth decay, dental corrosion, periodic application of fluoride, oral health, smoking and teeth, tooth stains, lip cancer, hydrochloric acid, bulimia, lactic acid, pumice, Sil