Communism consists of a political and economic doctrine whose ideology defended the “natural state”, that is, it defended a egalitarian society that would extinguish private property so that everyone had the same rights.
Since antiquity, more specifically since prehistory, communist principles were already put into practice.
During this period, the so-called primitive communism aimed to supply the needs of the entire group, without concern for the accumulation of goods.
Everything belonged to everyone and the concern to keep society as a whole with conditions to live in a dignified way was more important than the interest in material goods.

In the flag of communism, the red represents the blood of the martyrdom suffered by the workers, the sickle represents the agricultural working class and the hammer the industrial working class. The five-pointed star represents both the five continents and the five groups of communist society: peasants, workers, army, intellectuals and youth.
Check out a summary of the main characteristics of communism:
1. The communist regime was against private property
One of the main ideas of the communist regime was directly linked to the means of production: factories, mines, etc. they should be publicly available so that the products would be the common property of all citizens.
According to the communist philosophy, if everyone started to have access to the goods produced, the inequalities would be eliminated and this would cause opposition and rivalry between classes and social groups disappeared.
The communist regime promoted a classless society and was in favor of common ownership of the means of production.
2. Communism did not support the existence of different social classes
Communism considered that society should not be divided into social classes.
The communist theory defended that everyone should work and share everything that was achieved with their own effort, so that the coexistence between citizens was equal.
The result of what was produced was to be shared among all members of society. All people should have the same rights..
The main aim of communism was to achieve equal rights.
3. The communist doctrine aimed at the end of capitalism
The communists believed that capitalism fostered inequality and social injustice because labor was used as if it were something marketable.
While the capitalist system was developing, a large part of the population lived in extreme poverty and misery.
The bourgeoisie owned the means of production and consequently most of the wealth generated.
Thus, the proletariat was left with only its own labor, which was sold as a commodity to those in possession of capital.
In factories, workers were poorly paid and often treated like servants.
Communism advocated that capitalism be overcome through a revolution that gave power to the workers so that, in this way, the conflict between citizens could come to an end.
Learn more about the meaning of bourgeoisie and proletariat.
4. Communism was subordinate to socialism
According to Karl Marx's theory, communism was seen as the final step in the evolutionary process of society.
The philosophy of egalitarian society had communism as the outcome of an evolutionary sequence through which the history of mankind must pass.
The first phase of this sequence contemplated the capitalist system, which sought an ever-increasing increase in productivity, always taking into account factors such as competition.
Capitalism had as its objective profit and the accumulation of wealth through private properties, that is, the profit of production was centralized in the hands of the business owners.
In a second moment, society should implement socialism, thus giving up the logic of private property and, consequently, the division of society into social classes.
Unlike capitalism, socialism advocated the balanced distribution of wealth and property, closing the gap between rich and poor.
know more about Private propriety.
According to socialist principles, the goods produced would be distributed to each one according to his own work and effort.
Only after the end of private property and the implementation of socialism, power would be handed over to the people, thus ending the abuses imposed by capitalism and emancipating society:
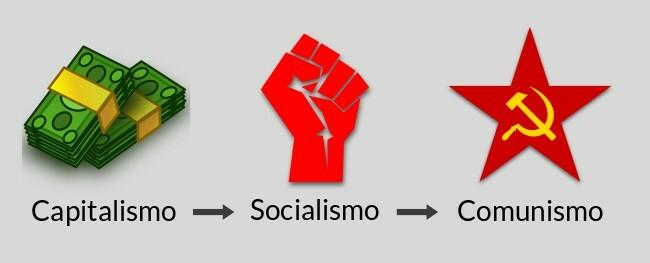
Finally, with the socialist system already in place, the communist regime would be applied, and the goods would then be distributed equally.
With this distribution system, the existence of a State with a controlling government would no longer be necessary.
While socialism was considered by Karl Marx as a transitory phase and advocated a move away from capitalism, communism was in favor of a retreat through armed conflict as a way of acting.
See more about communism and socialism.
5. The goods produced would be distributed according to the needs of each one.
The communist regime was apologist for the distribution of goods to each individual according to their respective need, that is, each one would receive what he needed, regardless of the amount there was produced.
Karl Marx's communist theory followed the following principle: “From each according to his capacity; to each according to their needs”. The message to be passed with this sentence is as follows:
of each according to his capacity: each person would work with the activity they loved, as it was understood that this way they would perform their function very well.
With the happiness of being able to use their skills to help the community, people would help the economy to prosper.
To each according to their needs: the community would be in charge of taking care of those who were not able to work. Goods and services would be distributed to everyone as needed.
According to communism, the people should have the power and therefore own their own labor and the goods produced by it.
Thus, the distribution of these goods would be done through self-management, thus abolishing the need for a government.
know more about Marxism.
6. Communism was in favor of the non-existence of a government
Unlike capitalism and socialism, which were in favor of the existence of a state responsible for controlling the In social life, communism defended absolute equality among citizens and considered that the state could be abolished.
The communists believed that in this way social oppression would be extinguished and that, in this way, society would be able to find a way to manage itself.
Workers would then become owners of their own work and the goods used for production.
Learn more about capitalism, communism and socialism.
Top names of communism
Now that you know the main characteristics of communism, see what the most important names of this political doctrine were:
Karl Marx
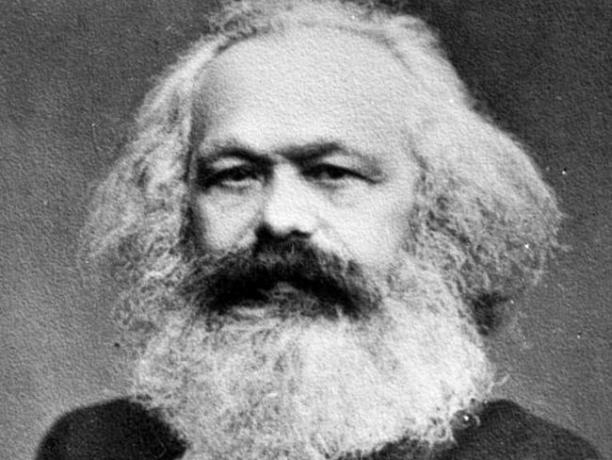

Karl Marx (1818 - 1883)
Karl Heinrich Marx was a German philosopher, economist, sociologist, historian and journalist. Marx wrote a series of publications and among them, two had great prominence:
- The Communist Manifesto: created to guide the action of workers during the emergence of labor movements. The work, written in partnership with Friedrich Engels, defined and made known the purposes of the League of Communists and called for the union of all workers in the world.
Learn more about Communist Manifesto.
- The capital: set of books that consisted of a critical analysis of capitalism, an economic system whose principles were totally opposed to those of communism.
Only the first book of the work was published by Karl Marx while still alive. The others were posthumous publications.
Capitalism defended, for example, the existence of private property and the control of production goods by private owners and the State. In the work, Karl Marx drew attention to the fact that the motivating force of capitalism is labor exploitation.
For him, the end of the division of society into different social classes, one of the main ideals of communism, would only happen when capitalism was extinguished.
Friedrich Engels
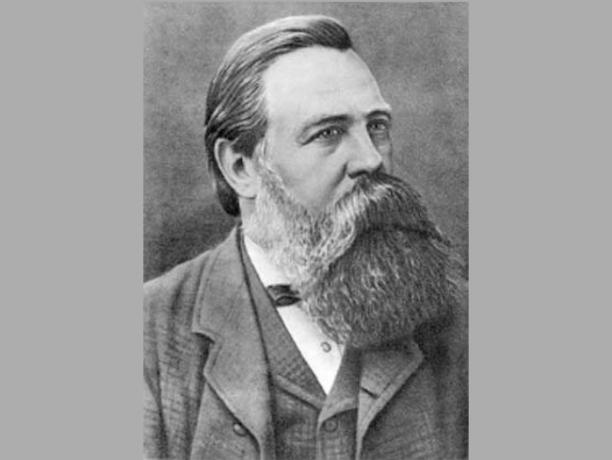

Friedrich Engels (1820 - 1895)
Friedrich Engels was a German social scientist, philosopher, author and political theorist. Together with Karl Marx, he co-authored the Communist Manifesto.
Engels was also of fundamental importance in the preparation of the work The capital, as he was the one who gave financial support to Karl Marx so that he could carry out research and write the books.
Later, he was also responsible for the posthumous publication of some of the books in the work through notes left by Karl Marx.
Other famous communist leaders and activists
The list of known communists also includes:
- Vladimir Lenin;
- Fidel Castro;
- Raul Castro;
- Leon Trotsky;
- Pol Pot;
- Nikita Khrushchev;
- Kim Il-Sung;
- Imre Nagy;
- Jiang Zemin;
- Ho Chi-Minh;
- Joseph Stalin.
Important events of communism
Check out some of the main facts related to communism:
- Vladimir Lenin takes power in 1917: he was the first communist leader to take power after the Russian Revolution of 1917;
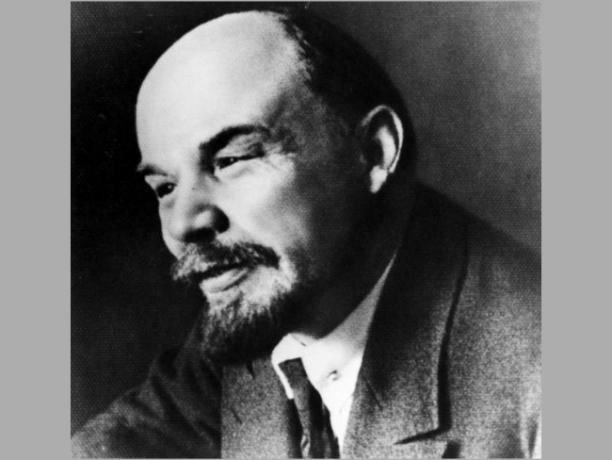

Vladimir Lenin (1870 - 1924)
- China became a communist country in 1949;
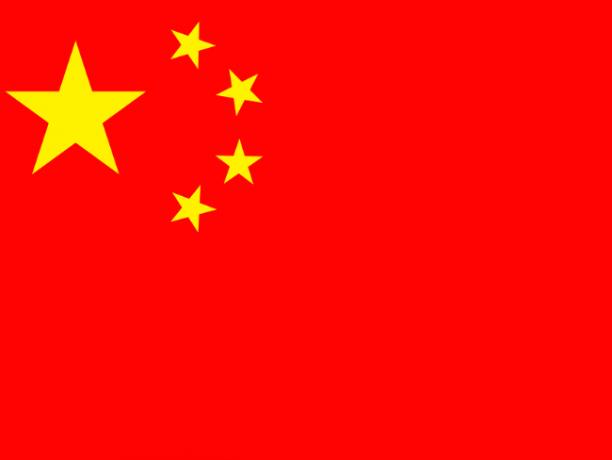

The flag of China is inspired by the flag of communism: the red symbolizes the revolution and the CCP (Communist Party of China) that took power after the civil war of 1949; the big star symbolizes the CCP and the smaller ones, the Chinese people. The position of the stars represents the union between the party and the people.
- Cuba became a communist in 1959;
- Vietnam became communist in 1975;

The red background of the Vietnam flag was inspired by the communist flag. The Vietnam flag was used by an organization founded in 1941 and led by communists to oppose the Japanese occupation.
- In 1945, the Cold War: the conflict began when the United States and NATO allies, and the Soviet Union and its allies of the Warsaw Pact were involved in a large indirect conflict that gave rise to several crises, such as the Cuban Missile Crisis, in 1962. This conflict was seen as a struggle by the Western Allies against communism.
- The construction of the Berlin Wall in 1961 it was seen as a great symbol of the Cold War as in West Germany there were liberal capitalist democracies and in East Germany several communist states. The fall of the wall in 1989 heralded the imminent end of the conflict, which ended in 1991.

Berlin Wall: built in 1961 and demolished in 1989.
Learn more about Cold War and about the Berlin Wall.
