For classify a sigma link, it is essential to know how to recognize it in the structure of a molecule. The sigma bond is actually a covalent bond that occurs when two incomplete atomic orbitals (with only one electron) interpenetrate on the same axis. An example is when a p-type (helix) orbital interpenetrates with another p-orbital.

p orbitals interpenetrating in a p-p sigma bond
In practice (in exercises), the recognition and classification of a sigma link is made from the structural formula of a substance, as in the structural representation below:

Structural formula of hydrocyanic acid
Before classifying a sigma link, it is necessary to know how to recognize it in a structural formula. For this, just remember the ways like a covalent bond is represented: the call simple is represented by a single dash (-), the pair is represented by two (=) and the link triple is represented by three (≡). The sigma bond is present in any of the three representations of covalent bonds as follows:
Simple: has a sigma bond;
Pair: Of the two links, only one is sigma;
Triple: One of the three links is sigma.
Knowing how to recognize a sigma link, the next step is to learn how to rank it. For this, we must know what is the incomplete orbital of each atom involved in the bond:
H - presents the incomplete s orbital, thus, in the classification, it is represented by s.
Ametals- have an incomplete p orbital, thus, in the classification, they are represented by p, with the exception of the following elements:
Carbon: Your incomplete orbital depends on the type of hybridization that he suffers. The possibilities are: sp hybridization3 (how much does it make four simple calls), sp2 (how much does it make two single and one double bonds) or sp (how much it carries out two double bonds or one single and one triple). Thus, in the classification of a sigma bond, Carbon can be represented by sp3, sp2 or sp depending on the call you are making.
Beryllium:suffer sp type hybridization, thus, in the classification, is represented by sp.
Boron:suffer sp type hybridization2, thus, in the classification, it is represented by sp.2.
With all this information, the easiest part is to classify the sigma links present in a structure. Let's see some examples:
Example 1: sigma connections in water

Structural formula of water
The structural formula above shows that water has two sigma bonds (two simple), being they between the oxygen (represented by p) it's the Hydrogen (represented by s). Thus, we have two sigma links classified into:
s-p
Example 2: Sigma bonds in phosphorus trichloride

Structural formula of phosphorus trichloride
The structural formula above shows that phosphorus trichloride has three callssigmas (three simple), being they enter the Phosphorus (represented by p) it's the chlorine (represented by p). Thus, we have three sigma links classified into:
p-p
Example 3: sigma bonds in boron trifluoride
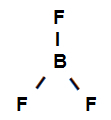
Structural formula of boron trifluoride
The structural formula above shows that boron trifluoride has three sigma links (three simple), being they enter the boron (represented by sp2) it's the Fluorine (represented by p). Thus, we have three sigma links classified into:
p-sp2
Example 4: sigma bonds in ethanol
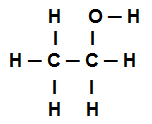
Ethanol structural formula
The structural formula for ethanol above shows that we have the presence of eight calls sigmas (eight simple links). Are they:
One among the Oxygen (represented by p) and the hydrogen (represented by s). Thus, the link is classified into sigma s-p.
One of two carbons that perform only sigma connections (and then represented by sp3). Thus, the link is classified into sp3-P3.
One among the Carbon (represented by sp3) and the oxygen (represented by p). Thus, the sigma link is classified into p-sp3.
five between carbon (represented by sp3) and the hydrogen (represented by s). Thus, all five are classified into s-sp3.
Example 5: Sigma bonds in Dichloroethene

Dichloroethene structural formula
The structural formula of Dichloroethene above shows that we have the presence of five sigma links (the four single bonds and one of the double bonds). Are they:
One of two carbons that perform two single and one double bonds (and then represented by sp2). Thus, the sigma link is classified into sp2-P2.
Four are between carbon(represented by sp2)and the hydrogen (represented by s). Thus, all four are classified into s-sp2.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/classificacao-uma-ligacao-sigma.htm
