An electric motor is a machine designed to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. It is the most used of all electric motors, as it combines ease of transport, economy, low cost, cleanliness and simplicity of command. They are machines that are easy to build and easy to adapt to any type of load.
The machines we currently know do not produce energy, they convert other types of energy into mechanical energy so that they can function. As Lavoisier said: “In nature nothing is lost, nothing is created, everything is transformed”. That is, nothing can be created from nothing, only transformed from something that already exists. An example of this is our dear old blender. It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy so it can process food. Today, in view of the great need to save the ozone layer from the emission of polluting gases, engines electric vehicles are being widely used in automotive vehicles in order to save energy and save the environment environment. Polluting gases, such as carbon dioxide that is released from motor vehicle exhausts and factory chimneys, have great destructive power in the ozone layer.
The operation of electric motors is based on the principles of electromagnetism, through which conductors situated in a magnetic field and traversed by an electric current, they suffer the action of a mechanical force, a force called torque.
There are several types of electric motors, the main ones being direct current and alternating current. Direct current motors are more expensive because a device that converts alternating current into direct current is needed. On the other hand, alternating current motors are cheaper and the most used, as electricity is distributed in the form of alternating current, thus reducing its cost.
Direct current: current in which it has a continuous and ordered flow of electrons always in the same direction.
Alternating current: is a current whose magnitude and direction varies cyclically. In other words, there is variation in electrical current, as opposed to direct current.
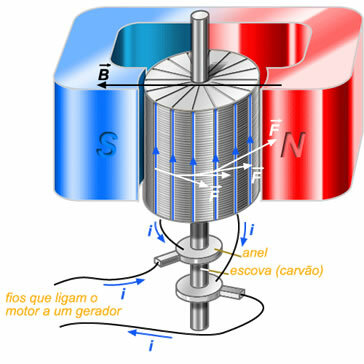
Above is a picture of a simplified schematic of an electric motor. It has a magnet that produces a magnetic induction field, a cylinder where conductors and wires are connected to a generator.
By Marco Aurélio da Silva
Brazil School Team
Electricity - Physics - Brazil School
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/eletricidade-acionamento-motores-eletricos.htm

