Muscles are involved in each and every type of movement the body can perform. Half of the body weight comes from them. There are three types of organs: smooth, cardiac striatum and skeletal striatum.
Smooth muscle is found in the wall of hollow organs and has involuntary contraction. It is the only type of muscle present in invertebrate animals.
The striated cardiac muscle constitutes the myocardium (heart muscle) and presents involuntary contraction.
Skeletal striated muscle makes up the largest part of our body. The muscles in this category are responsible for the voluntary contractions and movements of the body. They can have their volume and size increased with physical exercise. These muscles attach to bones through tendons. When one muscle moves, it contracts and pulls on the bone it's attached to, but for movement to occur, the other muscle must also contract to the opposite side.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
SKELETAL SYSTEM
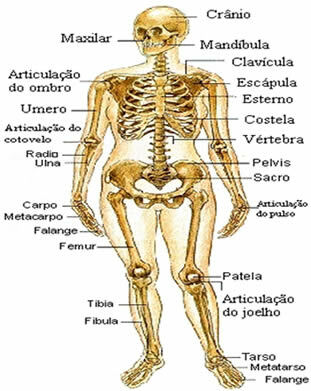
The skeletal system is formed by a set of bones that can be of various types (long, flat, short and irregular). In addition to supporting the body, bones also produce blood cells and serve as a store of calcium. Connected to muscles through tendons, they perform movements responsible for locomotion.
In the union of bones there are cartilages, which are responsible for preventing friction and eventual bone wear.
The skeleton also includes ligaments. They are found in joints and are firmly attached to bone tissue. Sometimes these ligaments may rupture, in more severe cases surgical intervention may be necessary.
By Paula Louredo
Graduated in Biology
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
MORAES, Paula Louredo. "Locomotor System"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/sistema-locomotor.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
