You metals they are chemical elements that have as their main physical characteristic the ability to lose electrons and, consequently, form metallic cations. For this reason, they can make two types of chemical bonds: the ionic bond and the metallic bond.
THE ionic bond occurs when a metal interacts with an element of a metallic nature, which can be a ametal or hydrogen. In this type of bond, we have the loss of electrons by metals and the gain of electrons by non-metals or hydrogen.
already the metallic bond is established between the atoms of a single metallic element. This type of bond occurs only between the atoms of a single metal and exclusively because a metal cannot establish a chemical bond with another different metallic element.
General characteristics of metals
Solids at room temperature, with the exception of mercury;
They are brilliant;
They have high melting and boiling points;
They are generally silver in color, with the exception of gold, which is golden, and copper, which is reddish;
Pure metals are formed by clusters of atoms (of a single chemical element) called crystal lattices.
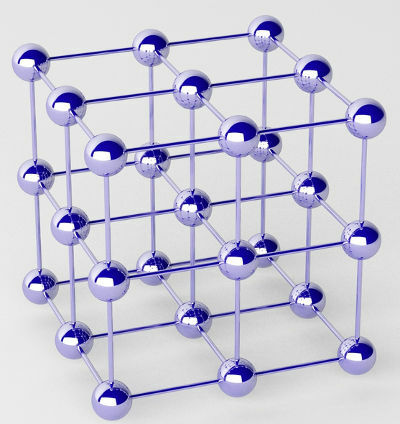
Representation of the crystalline lattice of a metal
Principles of metallic bonding
At metallic bond, the crystalline lattices that form the metals are actually an ionic cluster (composed only of cations and electrons). The electrons present in the valence layer of metal atoms are delocalized, that is, they leave the valence layer, causing the atom to become a cation (deficient in electrons).
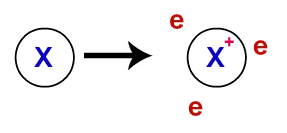
Representation of delocalized electrons from the valence shell
After being delocalized, the electrons from the metal atoms start to surround the cations, forming a true “electron sea”. Each of the electrons present in this sea has the ability to move freely through the crystalline lattice of the metal.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)

Representation of the electron sea model
NOTE: Electrons “from the sea” are not able to leave the crystal lattice and move through it.
Properties of metals justified by metallic bonding
a) Malleability
Through a metal, it is possible to produce sheets of different thicknesses and sheets. It is thanks to this property of metals that we can build various objects, such as knives, swords, etc.

The blade of a sword is made from a metal
b) Conductivity
Metals, in general, are good conductors of electrical current and heat. When any metal is in contact with a heat source or a source of electrical current, it is capable of conducting them.

An aluminum pan in the flame of a stove becomes entirely hot due to conductivity.
c) Ductibility
Through a metal, we can produce wires. The use of a metal in the form of wires facilitates its use, especially in relation to electrical conductivity.

A metal, such as copper, can be used to produce wires.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "What is metallic binding?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-ligacao-metalica.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
Chemistry
Ionic bond, arrangements between ionic compounds, ionic agglomerates, sodium chloride, table salt, ionic substance, electrostatic attraction forces, chloride anions, sodium cations, polar solvents, positive ions, cations, negative ions, anions.