When we study the motion of an electric charge immersed in a uniform magnetic field, we will notice that the trajectory described by it will depend on the angle formed between the particle's velocity and the magnetic field where it is immersed. In order to make the best use of the study of particle behavior in the uniform field, let us divide our analysis into three distinct cases.
first case: θ = 0º or θ = 180º
The case θ = 0º occurs when the velocity has the same direction as 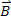 . The case θ = 180º, on the other hand, occurs when the velocity has the opposite direction to that of
. The case θ = 180º, on the other hand, occurs when the velocity has the opposite direction to that of 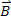 . We know that the magnitude of the magnetic force is given by:
. We know that the magnitude of the magnetic force is given by:
F= |q|.v .B .senθ
Since sin 0º = sin 180º = 0, we have that:
- in both cases the magnetic force is null. In such a way, if there are no other forces acting on the particle, the acceleration will be zero, and then we will have a straight and uniform motion.
second case: θ = 90º
When θ = 90º, the vectors are perpendicular to each other. In this case, the modulus of the magnetic force is given by:
are perpendicular to each other. In this case, the modulus of the magnetic force is given by:
F= |q|.v .B .senθ,
as sin 90°=1, we have:
F= |q|.v .B
In this case, we know that the force is always perpendicular to the velocity vector. It does not change the velocity modulus, only the velocity direction. In this way, a uniform circular movement occurs. How the particle describes a uniform circular motion, we have the possibility to determine the value of the radius of the trajectory traveled by the particle through the following equation:
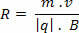
From the radius of the trajectory described by the particle, we can calculate the period T of the movement in the time interval of 1 revolution. The equation that allows us to make the calculation is as follows:
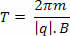
third case: θ ≠0°, θ ≠90°, θ ≠180°,
I.e, what is thrown obliquely to the direction of the field. In this case, it decomposes the speed 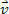 in two components:
in two components:
- component vx, towards 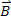 : causes an MRU
: causes an MRU
- component vy, perpendicular to  : causes an MCU
: causes an MCU
Therefore, the simultaneity of these two movements produces a uniform helical movement.
By Domitiano Marques
Graduated in Physics
Brazil School Team
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/carga-no-campo-uniforme.htm
