anglescollateralinternal and external are found in two parallel lines that were cut by a transversal straight and have important properties for the development of the geometry and for the study of Mathematics.
the expressions internal or external side angles are linked to position that these angles occupy with respect to the straightparallel and also to straightcross.
Remember that two lines are called parallel when they do not have any common ground along their entire length. A set of two or more straightparallel it's called beam of parallel lines.
Inner region of two parallel lines
Note in the image below the region that is limited by the straightparallel r and s:

This region, limited by two straightparallel, and the regioninternal from them. Angles that fall within this region are also called anglesinternal, just like any other element, geometric figure or object.
External region of two parallel lines
In the image below, the region which is not limited by the two straightparallel, r and s, is external, that is, it is the region that is not internal.

This highlighted region, the regionexternal, is formed by all the points that do not belong to the regioninternal of two parallel lines. Also, any angle present in this region is called external angle.
cross straight
given two straightparallel, r and s, any line t that cuts them is called straightcross. Furthermore, there is the particularity that defines the following: if a line t cuts a line r, which is parallel to a line s, then the line t also cuts the line s.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
See, in the image below, an example of straightcross.
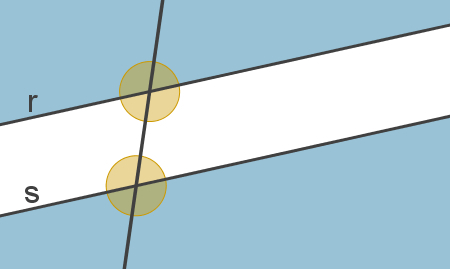
That straightcross shape with both straightparallel exactly eight angles. Four of them are in the inner region of the parallel lines and another four are in the outer region.
Two angles that are on the same side of the straightcross are called collaterals. In the case of the figure above, angles to the right of the transverse line are collateral each other, and the angles to its left are collateral to each other.
Inner and Outer Side Angles
With the studies done above, there is not much left to explain: given two straightparallel cut by a transverse, two angles that are in the regioninternal of these parallels and, at the same time, are collateral, are those that are known as internal side angles. If the angles occupy the outer region of the parallel lines and are on the same side of the straightcross, so they are called external side angles.
The following figure shows examples of anglescollateral external (in blue) and internal collateral (in yellow).

Property
You anglescollateralinternal and the outside side angles share the same property:
Internal side angles are supplementary and
external collateral angles are supplementary.
This means that the sum between two anglescollateralinternal will always be equal to 180°, just as the sum between two angles that are collateralexternal.
By Luiz Paulo Moreira
Graduated in Mathematics
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SILVA, Luiz Paulo Moreira. "What are internal and external side angles?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/matematica/o-que-sao-angulos-colaterais-internos-externos.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.


