Trigonometry aims to calculate length measurements of everyday situations related to geometric models similar to right triangles. Based on the highlighted slope angle, we can use the sine, cosine, and tangent trigonometric ratios. Let's go through examples to demonstrate some everyday situations.
Example 1
When taking off, a plane ascends forming an angle of 30º with the runway. Assuming that the angle formed is continuous, determine the height reached by the plane when traveling 2 km (2000 meters).
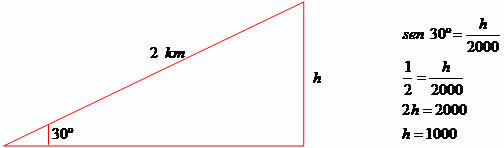
The plane will be at an altitude of 1 km or 1000 meters.
Example 2
In order to measure the height of a tower, a topographer using a theodolite outlined the following situation:

Determine the height of the tower according to the diagram.
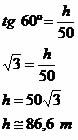
The tower is approximately 86.6 meters high.
Example 3
You want to stretch a rope from the top of a mast to a point P 40 meters away from the base of the mast. Knowing that the angle formed between the surface and the string is 60 degrees, determine the length of the string.
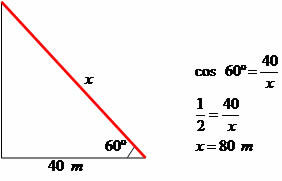
The rope will be 80 meters long.
by Mark Noah
Graduated in Mathematics
Brazil School Team
Trigonometry - Math - Brazil School
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/utilizando-as-relacoes-trigonometricas.htm

