THE angular geometry is one of several types of molecular geometry, which can still be linear, pyramidal, flat trigonal, tetrahedral, etc. Angular geometry can only be found in molecules that have the following characteristics:
Triatomics, that is, they have only three atoms;
Have at least three electron clouds in the central atom.
Note: electronic cloud is all covalent bond (single, double, triple or coordinate) between atoms and electron pairs of the valence layer who are not participating in a call.
See some examples of molecules that have angular geometry:
1st Example: water (H2O)

conventional water structure
In the structure of water, we have:
Three atoms: two hydrogens and one oxygen;
Oxygen is the central atom because it makes a greater number of bonds (two, as it belongs to the VIA family);
Two single bonds between oxygen and hydrogens. This is because each hydrogen can only make one bond and oxygen two bonds;
Four non-bonding electrons in oxygen, as it has six electrons in the valence shell and uses only two in the bonds.
Therefore, as in the water molecule there are three atoms and four electronic clouds (two single bonds and two non-bonding electron pairs) in the central atom, the geometry is angular.
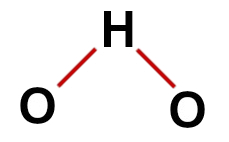
Correct structural formula of water
Note: Whenever the molecule presents these patterns, the angle formed between the atoms is approximately 109º 28'.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
2nd Example: Sulfur dioxide (SO2)

Conventional structure of sulfur dioxide
In the structure of sulfur dioxide, we have:
Three atoms: two oxygens and one sulfur atom;
Sulfur is the central atom as it is the smallest element in the molecule, since all elements need to make the same number of bonds (two);
A double bond between sulfur and one of the oxygens. That's because both need two connections;
One coordinate or dative covalent bond, because the sulfur was stable after doing the pairing with the other oxygen, but there is still an oxygen atom needing two electrons;
Four non-binding electrons in oxygen. That's because oxygen has six electrons in the valence shell and uses only two in the bonds.
Thus, as in the sulfur dioxide molecule there are three atoms and four electronic clouds (two single bonds and two non-bonding electron pairs) in the central atom, the geometry is angular.
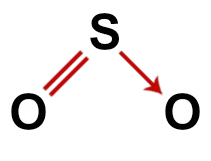
Correct structural formula of sulfur dioxide
Note: Whenever the molecule has these patterns, the angle formed between the atoms is approximately 120O.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "What is angular geometry?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-geometria-angular.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.