THE Gulf War it was a conflict that lasted between 1990 and 1991 and was caused by invasion of Kuwait by Iraqi troops. This invasion took place in the second half of 1990 and prompted an international coalition to be formed with the aim of expelling Iraqi troops from the territory of Kuwait. Through aerial bombing and ground attacks, the international coalition managed to expel Iraqi troops from Kuwait.
Some historians understand that this military action led by the United States against the forces of Saddam Hussein, the ruler of Iraq, was the first stage of a conflict that extended until 2003. That's why some understand this confrontation as "first gulf war”, since further US actions were taken in 2003.
read more: How were the September 11 attacks?
What were the reasons for the Gulf War?
![The invasion of Kuwait was ordered by Iraq's ruler, Saddam Hussein, on August 2, 1990.[1]](/f/567fbd968c4a95f41f400a0f6595be43.jpg)
The Gulf War is inserted in the context of diplomatic relations between the nations of the Middle East and it was motivated, above all, by Iraq's interest in reaffirming itself, through a military operation, to Kuwait, a neighboring nation. THE
invasionIraqi it began on August 2, 1990, but the motivations go back to the succession of events that involved Iraq in the 1980s.In the 1980s, Iraq was widely used as a tool to contain Iran's influence after the 1979 Islamic Revolution, which handed the country into the hands of Islamic radicals and caused the United States to lose an important ally in that region. THE rivalry between iran and iraq, in this context, resulted in a conflict: the Iran-Iraq War.
This conflict began in 1980, thanks to a surprise attack carried out by Iraq, and lasted for eight years, resulting in the death of around one million people. Iraqi forces were aided by a series of nations, among which are the United States, France and the United Kingdom, which provided weapons and military training to Iraqi soldiers.
Financially, Iraq received loans from neighboring nations – Kuwait and arabiaArabia – both interested in weakening the Shiites who ruled Iran. The conflict lasted until 1988 and ended with an impasse, as neither of the two nations managed to impose itself militarily.
Thus, the conflict ended without significant achievements, but with the Iraq weakened economically, diplomatically and militarily. It was therefore necessary to recover the country's economy quickly, mainly because Saddam Hussein still wanted to put Iraq in a position of supremacy in the Middle East, and for that, it needed to rebuild its army. parents.
Iraq's economic recovery would be accomplished through the sale of barrels of oil, the country's most valuable commodity. It was, therefore, in Iraq's interest for the price of oil to be high, but the reality was different. Influenced by Kuwait and the United Arab Emirates, the oil price in 1990 had plummeted from $21.00 to $11.00.
Iraq was outraged by Kuwait's attitude of selling oil in large quantities, which made the barrel cheaper on the international market. To make matters worse, Kuwait started tocharge Iraq for the loans granted during the Iran-Iraq War. Saddam Hussein did not want to pay them, as he understood that he had fought in that war to defend the common interests of Iraq and Kuwait.
The relationship between Iraq and Kuwait had other sources of strain, such as when Saddam Hussein accused Kuwait of stealing Iraqi oil he when exploring wells in a border region and started to demand compensation, and when Kuwait refused to give up two islands so that Iraq could expand its access to the Persian Gulf. While negotiations to resolve all the impasses were taking place, Saddam Hussein ordered the deployment of troops to the border with Kuwait.
Accessalso: Bosnian War - one of the first major conflicts after the Cold War
Kuwait invasion
The negotiations between Kuwait and Iraq were mediated by the United States, but failed. With that, Saddam Hussein ordered the invasion of Kuwait and it started on August 2, 1990. Kuwait was quickly dominated for being a very small country and having very simple military defenses. Furthermore, Iraq was one of the largest troops in the world at that time, having around a million soldiers.
Iraq managed to conquer Kuwait in about 12 hours and forced the Kuwaiti royal family to take refuge in Saudi Arabia. The Iraqi military action alarmed the great Western powers, especially the United States, because through it Iraq now controls about 20% of the world's oil reserves|1| and started to represent a real threat to Saudi Arabia, the great ally of the United States in the Middle East.
Thus, the US and the UK became favorable to a interventionforeign to force Iraqi troops to withdraw from Kuwait. The first action, however, occurred by meansdiplomatic from the performance of the security advice of the United Nations, the UN.
Through Resolution 660, on August 2, the UN disapproved of the invasion of Iraq and demanded immediate withdrawal of the Iraqi troops. Four days later, Resolution 661 was issued, imposing embargoes to Iraq and, thus, the country was prohibited from receiving imports by air and sea. As UN resolutions did not have the desired effect, US President George Bush ordered the deployment of troops to Saudi Arabia.
Accessalso: Fall of the Berlin Wall - the prelude to major transformations
North American intervention
![The invasion of Kuwait motivated then US President George Bush to order a military intervention against the Iraqi army.[2]](/f/c4e20e3f324339048a7796ec567f8b24.jpg)
The sending of US troops to Iraq began on August 7, 1990 and was intended to safeguard Saudi sovereignty and prevent an eventual Iraqi attack. The Iraqi response came with the announcement of the annexation of Kuwait, transforming it into Iraq's 19th province.
Troops from other countries began to be sent to Saudi Arabia, and a coalitionInternational began to be formed with soldiers from 34 countries and which had approximately 750,000 soldiers|2|, most of them soldiers sent by the United States. The leadership of the troops stationed in Saudi Arabia was handed over to General Norman Schwarzkopf.
Negotiations with Iraq extended over the following months, but as there was no agreement, the UN Security Council, on November 29, 1990, issued Resolution 678, which authorized international military intervention if Iraqi troops did not leave Kuwait by January 15, 1991.
As Iraqi troops were not withdrawn from Kuwait by the deadline, the United States began intervention in the Gulf War through the Operation Desert Storm. As of January 17, 1991, the United States began a succession of attacksair that extended during 42 days and were responsible for severely damaging the power of the Iraqis.
During this period, American-led attacks succeeded in destroy the Iraqi air force, as destroyed the air defenses of that country. The last step in the air strikes was to weaken the Iraqis' ground firepower through frequent attacks. These events took place in three stages that stretched from January 17th to February 23rd, 1991.
ground attack
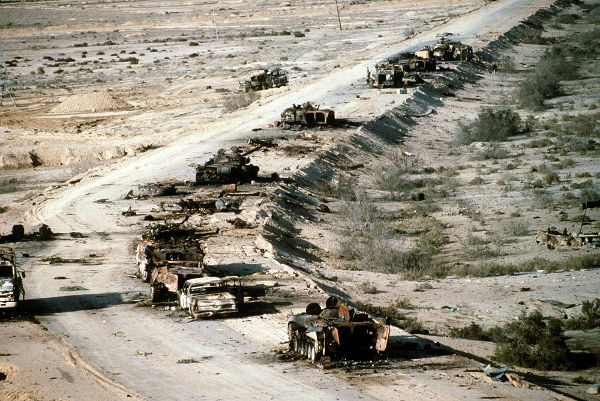

The last stage of Operation Desert Storm began on February 24 and took place through the ground attack of the international coalition troops who had the fundamental support of the air strike. At that time, a considerable part of the Iraqi army's infrastructure had been severely damaged by air strikes and this facilitated the success of the land campaign.
The international coalition's ground campaign spanned minus 100 hours. This was the period necessary for the troops led by Schwarzkopf to be able to force the Iraqi troops to withdraw from Kuwait. Troops that survived the attacks started a escapedisorganized back to your country.
This forced Iraq to accept UN resolutions and thus US President George Bush announced the end of military campaign against Iraq on February 28, 1991.
Iraqi troops while withdrawing from Kuwaiti territory are over burning about 700 oil wells. The fires spread throughout 1991, and the last fire was not put out until November 6th. At the end of the fires, Kuwait lost about 1 billion barrels of oil, which corresponded to up to 2% of the country's reserves|3|.
Image credits
[1]Georgios Kollides/Shutterstock
[2] Mark Reinstein/Shutterstock
Grades
|1| FARO, Miguel Coldron de Tovar. The 1991 Gulf War. To access, click on here.
|2| IRAQ: U.S. Deployments at the War's Height. To access, click on here [in English].
|3| Hi Well Fires. To access, click on here [in English].
By Daniel Neves
History teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/historiag/guerra-golfo.htm