Chemistry laboratories have different equipment, glassware, devices and devices that allow the performance of numerous activities with greater precision and safety.
Know the names of the main materials used in the laboratory and their respective functions.
laboratory glassware
These materials are made of crystal or tempered glass and may vary in size, supported capacity, and function. Therefore, each glassware receives a specific application.
Flat bottom balloon

Used in the preparation of solutions, reactions with release of gases or heating of liquids.
As it withstands high temperatures, its main application is in heating systems under reflux in separations through distillation.
See too: chemical solutions
round bottom balloon

Used in distillation processes, separating components from a mixture or removing impurities.
The material inside the round-bottomed balloon is usually heated when the container is inserted into a heating mantle.
distillation flask
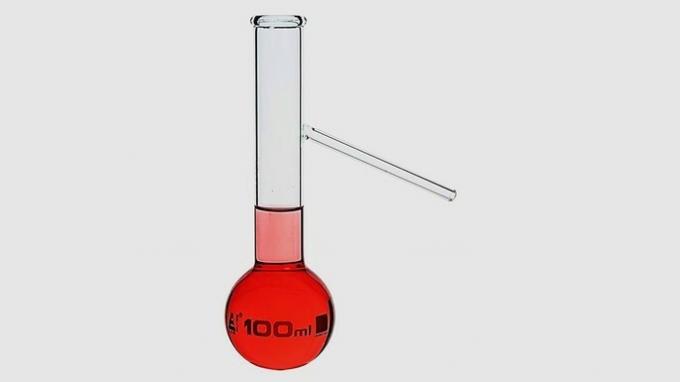
Used for heating a mixture and separating the more volatile compounds, which come out through the side tube.
After evaporation, the separated component is condensed in an equipment called a condenser.
volumetric flask

Used in the preparation of solutions or dilutions with greater precision because of the presence of a measuring trace in its neck.
As it is a volumetric glassware, heating can cause distortion in the glass and thus alter the calibration.
See too: solution dilution
Beaker or Becker

Used to measure volume of liquids or mixtures, with little precision, as it has a graduation on its body.
It can be heated and is therefore useful for dissolving substances or carrying out reactions in experiments.
Erlenmeyer

It is mainly used to prepare solutions and store them. Because of its shape, which prevents liquid spillage during handling, it is used in titrations to accommodate the titrated solution.
This laboratory vessel was named Erlenmeyer after its creator, German chemist Emil Erlenmeyer.
See too: titration
Test tubes

Used for reactions where reagents are in small amounts.
When an experiment involving a test tube requires heating, the Bunsen burner can be used and its flame placed in direct contact with the tube.
See too: chemical reactions
Burette

Used to perform titrations and measure the volume of liquid being drained.
For the dosage of liquid, this glassware is used vertically, positioned above a beaker or Erlenmeyer flask and fixed to the universal support using claws.
glass rod
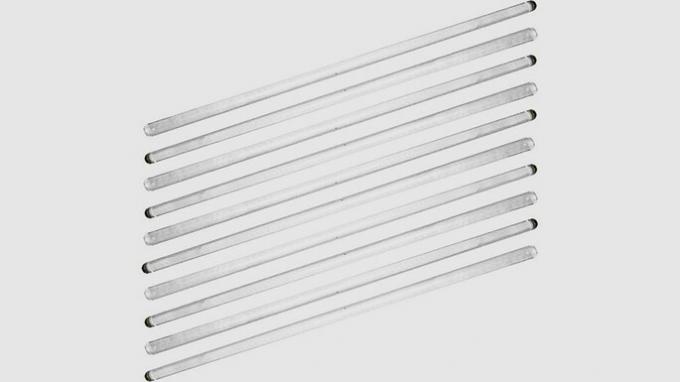
Used to homogenize or stir solutions in routine laboratory activities.
It is also used to assist in the transfer of liquids from one container to another, directing the liquid so that there is no spillage.
Condenser
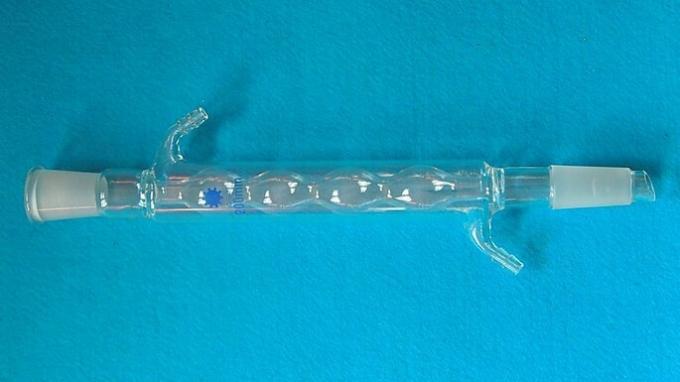
Used to cool gases separated in the distillation process and make them liquid.
When the steam passes through the condenser, heat is exchanged with the cold water that circulates through the walls of the glassware and thus the material is condensed.
Fraction Column

Used in small scale distillation to separate components from a mixture of miscible liquids, but with different boiling points.
The most volatile compound, that is, the one with the lowest boiling point, is separated first in the column and when it reaches the condenser, it returns to a liquid state.
Desiccator

Used to remove moisture from materials by the presence of drying agents, such as silica gel.
Its lid allows an airtight seal and thus a controlled atmosphere is created that prevents contamination of the material.
Bromine funnel

Also known as a decanting funnel, it is used to separate immiscible liquids by gravity.
In a heterogeneous mixture, the densest component is located at the bottom of the funnel and can be separated by turning on the tap and draining it into another container.
See too: decant
glass funnel
It is used in conjunction with filter paper to retain solids that are not dissolved in a liquid.
The mixture passes through the funnel and the liquid is recovered in another container. The solid components are in the filter medium supported by the funnel.
Kitassate

It is used together with the Büchner funnel and filter paper to carry out vacuum filtrations.
The side outlet in the glassware is useful for attaching a machine that sucks air from the container, making separation faster.
Petri dish
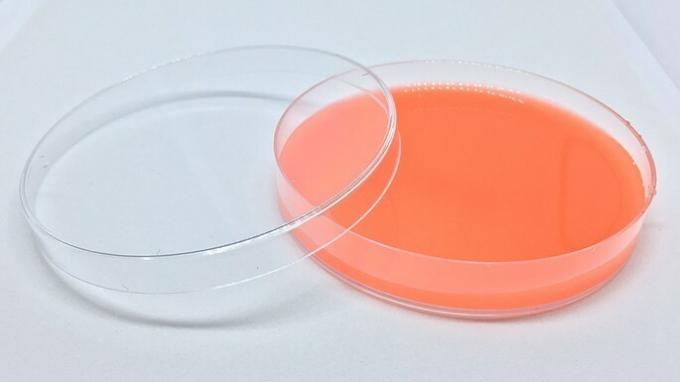
As it is a container with a lid, it is used to cultivate micro-organisms, such as bacteria. In this process, nutrients, salts and amino acids are gathered to promote growth.
This material was named after its creator, the German Julius Richard Petri.
graduated pipette

Used to measure variable volumes of liquids or solutions with greater accuracy and aid in transfer to other containers.
The material is aspirated into the pipette using a pipettor or suction cup and this instrument is also used to release the liquid. The volume that has been transferred is known from the starting and ending volume reading on the pipette.
volumetric pipette

Used to measure and transfer a fixed volume of liquid or solution. Therefore, it is more accurate than the graduated pipette.
Volumetric pipettes are calibrated to contain a specific volume of material and perform accurate transfer.
Beaker

Used to measure and transfer volumes of liquids and solutions since the cylindrical body of the glassware has markings that identify the volume of material inside.
However, this is not a very accurate instrument, being used for activities that do not require rigorous measurements.
Wristwatch glass

Used to hold small amounts of sample for weighing, cover containers and small scale evaporations.
Learn more about laboratory glassware.
laboratory equipment
The equipment used, in addition to being made of different materials, have specific applications and can work alone or together with other materials.
Hot plate/Stirrer

Used to heat substances evenly in a container placed on the metal platform. It also has the function of a stirrer to mix solutions while heating.
In this equipment, the temperature and agitation control of the material can be done manually.
Magnetic bar or goldfish

This equipment is inserted in solutions that are in the magnetic stirrer to be homogenized.
The magnetic field created by a magnet causes the goldfish to rotate within the solution.
See too: magnetic field
Mortar and pestle

Used for crushing small solid samples and also for mixing components, kneading or spraying. Usually, the material for manufacturing these utensils is porcelain.
The sample is placed in a mortar, a kind of bowl, and with the pistil, also called a pestle or mortar hand, the grinding takes place.
ring or ring

This metallic equipment is used to hold glassware that needs to be used vertically.
One of its ends is fixed to the universal support and the other end, with a ring shape, is used to support the bromine funnel during the decantation process.
precision scale

Used to accurately measure the mass of materials in the laboratory for chemical analysis.
Glasses that surround the region where the sample is placed are useful so that air currents do not interfere with the weighing value.
Bunsen burner

Used to heat substances, sterilize objects and perform tests that require a flame.
It is a gas burner and at the bottom of the equipment there is a valve to regulate the fuel output and thus adjust the flame.
water deionizer

Used to remove ions in water such as calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+), through ion exchange.
This equipment consists of an ion exchange column filled with cationic and anionic resins. These resins release H ions+ and oh- while the ions present in the water are fixed in the column.
See too: ion, cation and anion
water still

Used to purify water, remove ions, impurities and contaminants that can hinder chemical analysis.
Inside the equipment, the water evaporates and the steam generated is directed to another compartment where it will be condensed and will become a liquid again.
See too: evaporation
Laminar flow cabin

Used to promote air recirculation and the UV lamps inside create a sterile and biologically safe environment.
This equipment is useful for safely handling biological samples avoiding contamination.
exhaust chapel

Used as a physical barrier to handle hazardous materials and eliminate released gases.
It is an indispensable collective protection equipment in a chemical laboratory, as it absorbs the vapors released, for example, in a chemical reaction and keep hazardous reagents isolated from the environment.
Crucible

It is a porcelain equipment used for heating and melting solids, as it has refractory characteristics and supports high temperatures.
Due to its resistance to heat, it can be exposed directly to the flame of the Bunsen burner with the use of a suitable support.
See too: Fusion
porcelain capsule

Also called an evaporation capsule, it is used to concentrate solutions, calcine materials and evaporate compounds.
As it is made of refractory porcelain, the substance can be heated with the flame of a Bunsen burner, heated sand and, in some cases, in a muffle.
See too: concentration of solutions
Chromatograph

It performs separations and identifies the components of a mixture through chemical affinity using the chromatography technique.
The chromatograph works coupled to a detector, which presents data referring to the compounds separated in the chromatographic column.
See too: chromatography
Spectrophotometer

Used to identify and determine the concentration of components in a sample through light absorption.
The type of signal generated by the sample is picked up by a detector and the result is spectra that provide a relative measure of the absorbed light intensity.
See too: light - refraction, reflection and propagation means
Test tube shelf

Used to store test tubes and as a support to keep them in a fixed place during use.
Because of the U-shaped test tubes, the rounded end means that a support is always needed to keep it upright.
Spatula

This equipment made of stainless steel is useful for handling and transferring small amounts of solid materials from one container to another.
Due to its chemical resistance, wear and corrosion resistance, the spatula is widely used in the laboratory for handling chemical products.
Stove

Used to dry and eliminate microorganisms, through heat, allowing laboratory materials to be sterilized.
A common greenhouse works in a temperature range of 15 ºC above the local temperature and can reach up to 200 ºC.
Büchner's Funnel

It is a piece of equipment produced in porcelain and the various perforations in its interior allow the passage of a liquid.
Its use is done in conjunction with the kitassate to separate solids during vacuum filtration.
Pissette or Pissette

Used to store liquids, such as distilled or demineralized water, and facilitate handling when performing work.
With a washtub, it is possible to wash materials and transfer liquids with ease.
Metal clamp

Used to handle small objects without direct contact. This is extremely useful for picking up heated equipment and preventing burns.
The end that will have contact with the material to be handled has cleavages to increase friction and prevent slipping.
Pasteur pipette

Used to transfer small amounts of liquid through the drip. It is different from graduated and volumetric pipettes in that it does not have a specific volume.
This equipment was created by the French chemist Louis Pasteur and, therefore, was named after him.
suction pear

Used to suck liquids into the pipettes and release them into a container, so that the user does not have contact with the substance.
Also called a three-way pipettor, this equipment is made of rubber and facilitates the entry of liquid into the pipette by creating a pressure different from the atmosphere.
heating blanket

Used for uniform and controlled heating of materials during a chemical analysis.
Its use is indicated for handling flammable substances, as it does not generate sparks that would be an ignition source for an explosion.
Muffle

Used to calcine samples and remove volatile compounds as it works at high temperatures.
It is a chamber lined internally with refractory material and can reach temperatures above 1000°C.
filter paper

Used to retain solid materials that have not been dissolved in the liquid that passes through it.
The type of filter paper is chosen according to its porosity and consequently affects the filtration speed.
pH meter

Used to measure pH (hydrogen potential) in samples through conductivity. The millivolts detected in the device are transformed to a pH scale, which varies from 0 to 14.
Standard solutions are used to calibrate the instrument and minimize reading errors.
See too:what is pH?
Universal support

It is equipment used to support materials that are used vertically.
Grippers or tweezers are attached to the metal rod to carry out experiments that require glassware, such as test tubes and burettes.
asbestos screen

Used to support the sample container during heating and promote even heat distribution.
It is usually placed on an iron tripod and heated with a Bunsen burner or electric heater.
Thermometer
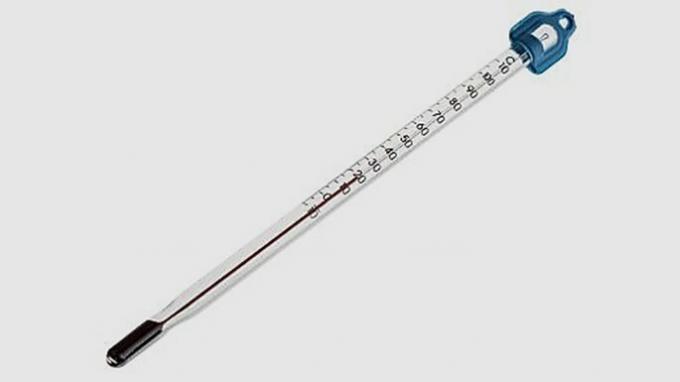
Used to measure or monitor the temperature of liquids or solutions during an experiment.
The thermometer is made of glass and the liquid that fills it is mercury. To be used it must be dipped in the substance.
iron tripod

This equipment is made of metal and the three support rods connected by a ring allow the asbestos screen to be used when heating samples.
To gain more knowledge, learn more about Chemistryit's thescientific method.


