Fusion is the change from the solid state to the liquid state. It occurs when a body, subjected to a given pressure, receives heat and its temperature reaches a certain value.
The amount of heat that the body must receive to become fully liquid depends on the substance that constitutes it.
Generally speaking, when a substance is in a solid state, it has a well-defined shape. Its atoms are neatly arranged in a structure called a crystalline network.
When it receives heat, the atoms that form the solid increase their vibration, increasing their temperature.
If the incoming energy increases, the vibration of the atoms will break the crystalline lattice and the body will go into a liquid state.

Merger Laws
- Keeping the pressure constant, the temperature throughout the melting process remains constant.
- The amount of heat per unit of mass is called the latent heat of fusion and is a characteristic of the substance.
- The temperature at which each substance melts is well determined, and is called the fusion point.
When subjected to a pressure of 1 atmosphere, water melts at 0 °C, while the melting point of iron is 1.535 °C and chlorine is 101.5 °C.
Amount of Latent Heat
The amount of heat needed for a body to change state depends on the value of the latent heat of fusion and the mass of the body.
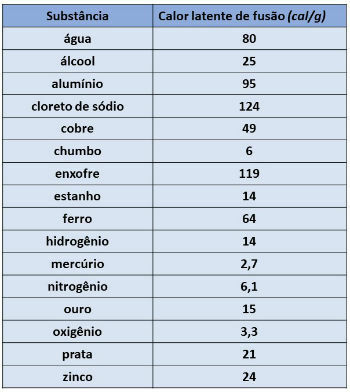
The value of latent heat varies according to the substance that makes up the body. In the table below, we present the values of some substances.
Formula
The amount of heat needed for a body to change phase is given by the formula:
Being,
Q: amount of latent heat (lime)
m: mass (g)
Lf: latent heat of fusion (cal/g)
Note that the formula for the amount of heat in the phase change does not take into account the temperature variation.
This is because the entire amount of heat received is used to break the crystal lattice, keeping the temperature constant throughout the process.
Example
How much heat is needed to fully fuse a block of gold with a mass of 200 g?
The latent heat of fusion of gold is equal to 15 cal/g (table above), so we will have:
Q = 200. 15 = 3000 cal or 3 kcal
To learn more, read also:
- Physical State Changes
- Physical States of Matter
- Physical States of Water
- Matter Properties
- Phases diagram
- Liquefaction or Condensation
- Boiling
- Evaporation
- Sublimation
- Solidification
- Electrolysis
- Vaporization



