O Congress of Vienna it took place between 11 November 1814 and 9 June 1815 and reorganized Europe after the Napoleonic Wars.
In addition, decisions were taken that affected Brazil, such as handing over Guyana to France and condemning the trafficking of enslaved persons.
The Congress of Vienna served to keep Europe safe from major confrontations until World War I in 1914.
Background to the Congress of Vienna

The governments of Austria, Prussia, Russia and Great Britain signed the Treaty of Chaumont in March 1814, shortly after Napoleon Bonaparte's defeat in Russia.
In April of the same year, Bonaparte abdicated the French throne and went into exile on the island of Elba, off the Italian coast.
Later, at the invitation of the victorious powers, other countries joined the treaty, such as France, Sweden, Portugal and Spain.
The Treaty of Chaumont established that all governments should send representatives to an international meeting to be held in Vienna.
However, in the meantime, Bonaparte escapes from the Isle of Elba and tries to defeat his enemies by fighting the Battle of Waterloo. The strategy fails and the former emperor abdicates and is arrested by the British.
holy alliance
Prior to the Congress of Vienna, Russian Emperor Alexander I proposed the creation of the Holy Alliance. This would be formed by Prussia, Austria and Russia. Later, Great Britain would be incorporated.
Therefore, it was decided that these four nations would be responsible for decisions on the future of the territories that had been conquered by Napoleon Bonaparte.
Faced with the reaction of other countries, the opening of the Congress of Vienna, scheduled for September 24, only took place on November 11th.
Objectives of the Congress of Vienna
The priorities of the Congress of Vienna were to end the vestiges of the French Revolution and the Napoleonic Era.
The intention was to redraw the borders of France, the Italian Peninsula and the German states, and to restore the Bourbon family in France, Spain and the Kingdom of Naples.
Likewise, issues such as the abolition of the slave trade and the use of slave labor in the American colonies were discussed.
Main decisions of the Congress of Vienna
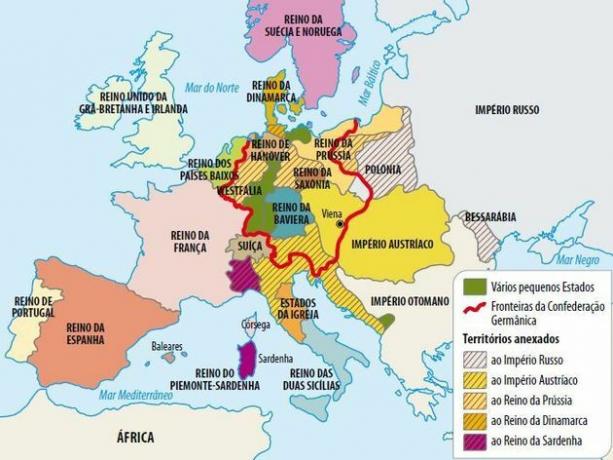
Among the main decisions of the Congress of Vienna are the European territorial reorganization and the isolation of France as a way to avoid new wars.
Great Britain
Great Britain received as compensation the territories occupied by France, such as Mauritius, Tobago and Saint Lucia. On the part of Holland, Ceylon was ceded; and from Spain, the island of Trinidad.
He also incorporated some islands such as Malta and the Ionian Islands into his kingdom.
Great Britain was the great victor with the defeat of Napoleon Bonaparte. Once the peace was concluded, the British boosted their industrial development and set out to conquer new territories.
France
Through the Treaty of Paris, the Bourbon dynasty returned to reign in France, in the person of Louis XVIII, brother of Louis XVI.
Part of French territory was occupied by the Holy Alliance for three years and France had to pay compensation to the winners.
As for territory, the country returned to the borders of 1791. Still, he received back to Guyana, from Portugal; Guadeloupe, from Sweden; Martinique and the Isle of Bourbon (present-day Reunion) in Great Britain.
Austria
Austria, together with Great Britain, will be the great European power after the conflict.
It occupies the northern territories of the Italian Peninsula, such as Venice, Lombardy and Milan, as well as three provinces in Illyria, Dalmatia and the port of Cattaro.
Also annexed to Austria were Galicia, from Poland; but Tyrol and Salzburg were transferred to the German territories.
German States
Bonaparte had extinguished one of the oldest empires in the world: the Holy Roman Empire.
During the Congress of Vienna, to satisfy the territorial demands of the Russian Empire and Austria, the German Confederation was created. Thus, the number of German states increased from 300 to 39.
Prussia
In turn, Prussia incorporated a number of German states and became the strongest country of German culture.
It received half of Saxony, the Grand Duchy of Berg, part of the Duchy of Westphalia, and some cities like Cologne, Trèves and Aachen.
It also brought together part of Swedish Pomerania and annexed Polish territories.
Russia
Russia occupied most of Poland as the Grand Duchy of Warsaw. In turn, Krakow became a free territory, under the protection of Russia, Austria and Prussia.
Finland and Bessarabia (now Moldova) were kept within Russian territory.
Poland
Poland loses its independence and is divided between Russia and Prussia.
Italian peninsula
Several regions of the Italian Peninsula had been divided up among Napoleon Bonaparte's brothers. So it was decided to restore the old dynasties to their thrones and create new states.
Thus, King Ferdinand IV, who reigned over Naples and Sicily, was once again recognized as sovereign with the union of his two kingdoms, now called the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies.
Austria, wanting to guarantee its exit to the sea, occupied several territories on the coast and in northern Italy.
The Kingdom of Sardinia incorporated the Republic of Genoa in order to form a strong state that could isolate France.
More curious was the case of Napoleon's ex-wife, Empress Maria Luísa. She became Duchess of Parma, Piacenza and Guastella and in return their son Napoleon II was taken to be educated at the Viennese court.
Portugal
To participate in the Congress of Vienna, the Portuguese court declares the elevation of Brazil to the United Kingdom of Portugal and Algarves. At this moment, Brazil formally ceases to be a colony.
Portugal had to vacate Guyana and this territory returned to France.
Spain
In Spain, the reign of Fernando VII, who had abdicated in favor of Napoleon Bonaparte, is reinstated. The country lost the island of Trinidad in the Caribbean to Great Britain.
Slave Trade
In February 1815, the Congress of Vienna condemned the slave trade as being incompatible with Christian and European civilization.
This decision will directly impact the Kingdom of Brazil, Portugal and the Algarves, as the workforce in Brazil was mainly slave.
Since then, the first laws restricting the slave trade in the Atlantic will be published.
Consequences of the Congress of Vienna
The participating nations created a new European political organization, replacing the Treaty of Utrecht, in 1713.
To solve the occupations that occurred during the Napoleonic Empire, between 1815 and 1822, an order based on the cooperation of states emerged, a model that appeared for the first time in history.
The new system sought to balance the power of European nations, carrying out a policy of allies and territorial compensation.
The Congress of Vienna, in this sense, was efficient, as Europe would only enter an all-out war a century later with the First World War in 1914.


