Maps are cartographic representations of the world around us. They are used to portray the planet as a whole (world maps) or just a part of it, such as maps of continents, countries, regions, cities or even neighborhoods.
They can only represent the borders and limits of an area, called political maps. They can also have a specific theme, such as vegetation, climate, relief, minerals, etc.
Whatever his role, the author must always include the necessary elements for building a map, which are: title, scale, orientation, legend and projection.
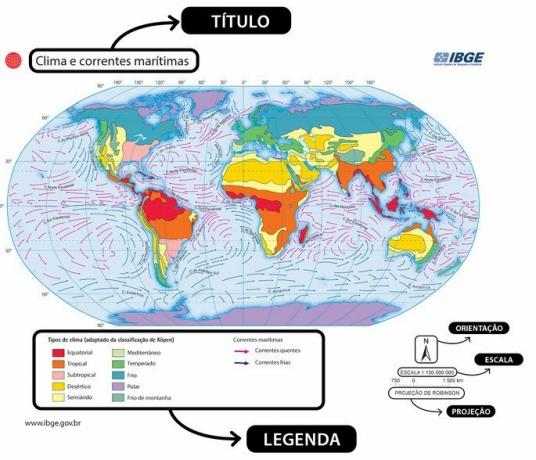 Title
Title
Indicates the subject or theme of the map in question. It may carry other information necessary for your understanding, such as a subtitle or historical period portrayed. It is the first element that must be observed by the reader, as only then will it be possible to understand what the observed map is about.
Scale
To portray the real world on a map, we must reduce the size of reality so that it fits on this map. Therefore, scale is the relationship between the size of the map and the actual size of the area represented.
To calculate the scale (E), we divide the distance on the map (d) by the actual size (D), in centimeters:
The larger the result, the smaller the scale, as it will present less detail. The smaller the result, the larger the scale and the more detail this map will have. For example:
- A 1:10,000 scale map has a large scale, as reality has been reduced 10,000 times, therefore it has many details;
- A 1:2,000,000 scale map has a small scale, as it has been reduced 2 million times, so it has few details.
Guidance
This is the representation of the cardinal points or just the North. Normally, it is located in the corner of the map, represented by an arrow or the complete compass rose. It helps the reader to orient themselves and properly locate what they are looking for on the map.
Subtitle
Its purpose is to help you read the map. The legend translates the symbols and colors used on the map so that the reader can identify what is represented even if they have no prior knowledge of the subject.
To achieve this, the legend follows a series of conventions, such as the use of anchors to locate ports, planes for airports, red areas for the highest temperature in a location, among other examples.
Projection
It is usually indicated next to the scale, this is the shape chosen to represent the planet on a plane. There are several techniques for doing this and none of them are perfect. Due to the spherical shape of the planet, there will always be some type of irregularity on the map (which is flat). Therefore, there are several projections that seek to better portray distances, sizes, polar and equatorial areas, etc.
To know more:
- Thematic Maps
- Cartographic Scale
- What is Cartography?
- Cartographic Projections
- Exercises on compass rose (with template)
MARQUES, Vinícius. Elements of a map: what they are and how to interpret them.All Matter, [n.d.]. Available in: https://www.todamateria.com.br/elementos-de-um-mapa/. Access at:
See too
- All types of maps and their characteristics
- What is Cartography: concept, importance and history
- Cartographic Projections: definition, properties and exercise
- Cartographic scale
- Geographic coordinates: how to read and locate
- Cartographic Scale Exercises
- Latitude and longitude
- wind rose
